Types of everyday work and the sequence of their execution. Types of construction and installation work What kind of robots should be placed before the construction work
Before category:
Pipe laying cranes
-
The main types of construction and installation work and their design methods
Behind-the-scenes reports. The main types of construction and installation robots for the construction of linear parts of main pipelines and preparation, excavation and transport, welding and installation, excavation, insulation, laying and ballasting robots , as well as the routine of transitions through natural and artificial passages, emptying and testing of pipelines. This type of work is done by mechanized methods.
The main mechanisms for the installation of line pipe-laying robots, in addition to preparatory robots, are pipe-laying machines.
Preparation of work on the pipeline route, which will follow the significant advances of other types of construction and installation work.
The preparation warehouse includes the following tasks: updating and securing geodetic signs; clearing the smog from the forest and tea leaves; Smuha planning; there will be time-consuming roads and drives to the highway; quenching of aqueous spores to dry out smog.
During the construction of pipelines from the city's minds to the warehouse, the preparatory work also includes the removal of overhanging stones and rocks, carrying out dry anti-landslide and anti-drainage operations, excavation of crooked robots, washing of "polishkas", cutting of steep slopes, in establishing the features of anchoring machines, cleaning the entrances to the pipeline route in in places, the removal of “police”, tunnels, installation maidans, inspection of culverts and other robots.
In winter, in addition, visits should be made to ensure minimum (in the trench area) or maximum (in the area of machinery passage) freezing of the ground, winter roads and ice crossings across rivers and watercourses.
Preparatory work begins with the updating and securing of geodetic signs, which indicate the position of the axis of the pipeline and timely spores. This is necessary for transferring to the site from the technical project the dimensions of the width of the building block, the site of moving shut-off valves, etc., as well as for the beater robots. Geodesic signs are secured with wine posts or pins, which suggests a posture of alertness with the method of preserving them for the entire period of wakefulness.
After updating and securing the geodetic marks on the shaved plots, the clearing of the soil begins, which includes the following operations: felling trees and cutting off branches, forming a cart and hauling logs to stacks , clearing, picking up branches, uprooting stumps, filling holes, etc. The clearing of the smudging begins after the withdrawal of the lumber ticket (order). The work of forest clearing is carried out by complex teams. Trees are felled with gasoline-powered saws and logging machines, stumps are uprooted with grubbers, and they fall asleep and plan to destroy them with bulldozers. The smog is cleared from the chagarbush and wood is cut using bulldozers, brush cutters and feller bunchers.
Timing roads are designed for the passage of everyday vehicles and vehicles during the construction of main pipelines in swamps, waterlogged plots, on granular, highly soluble soils and on plots with permafrost and subsidence soils.
The main structures of time-hour roads are roadways and winter roads. Flat roads are laid with decks with a diameter of 14...20 cm, which are laid on late logs (flat) with a diameter of 18...25 cm and a depth of 6...8 m, placed on a platform of 1...1.5 m one kind of one. Along the edges of the other part, pressing logs are placed, which are creased with the old tensile twists. Sprinkle a ball of peat with a thickness of 5 ... 10 cm and draining soil with a thickness of at least 20 cm on top of the flooring. The ball of scattered peat and soil protects from chipping from the deck decks due to rubbish by tractor caterpillars.
Winter roads must be sealed during the first winter months when frost sets in. The winter road is cleared of forest vegetation and dark brown with a thickened snow cover and frozen frosty surfaces. When roads cross rivers and watercourses in winter, ice crossings must be blocked.
During this time, the roads will be staffed by specialized teams equipped with bulldozers, truck-mounted cranes, single-bucket excavators, flatbed vehicles, self-skidding vehicles, motor graders, rollers and watering machines.
To drain surface water from the smog on the flooded sections of the route and reduce the level of groundwater, drill later ditches to which the level of water supply of the area and the influx of groundwater are laid. transverse water drainage ditches for discharging water from water reservoirs (rivers, lakes). With a folding topography of locality on plots with significant slopes, drain the upper ditches. The water drainage and drainage ditches are designed to be drained with a trapezoidal profile with a depth of 0.8...1.2 m (after settling the soil) in depth according to the intensity of the influx of water and with a bottom width of up to 0.5 m.
On the crossbars of pipelines that are being laid, with roads, streams, small rivers, grinding channels, culverts should be installed near the appearance of reinforced concrete trays or pipes.
To drain the bottom of trenches when there is a small influx of groundwater, stagnate the open water pipe, then pump the water out with self-propelled water pumping units directly before laying the pipeline in the trench and backfilling it.
We are planning to ensure a safe supply of emergency equipment and vehicles. When planning to level the microrelief, cut the later and transverse tendons, and nourish the low areas. Microrelief planning is carried out on a daily basis in the trench digging area using rotary trench excavators. This is necessary for leveling the bottom of the trench and reducing the additional stresses in the pipeline; the fragments of the bottom of the trench, wetted by a rotary trench excavator, copy the surface relief. The microrelief is planned with 2 bulldozers (div. Fig. 1) with later passes along the axis of the soil.
Planning for permanent relief in the areas of severely crossed muscle tissue includes cutting the later and transverse contusions, as well as feeding the lower muscles. When cutting the soil from local trays, move it to a lower place whenever needed. When there is a shortage of soil, deep depressions are fed with soil that is crushed from the lateral reserve.
On slopes with a transverse slope steeper than 8°, in order to facilitate the development of mining operations and the passage of mining equipment, a working slurry (“shelf”) should be used, the width of which should correspond to the transverse dimensions of the pipe-laying equipment. the largest sized machines and pipeline diameter, not less than 8 m, including and including part. When clearing the soil, the soil is broken up with bulldozers and single-bucket excavators. First fluff up the rocks using a blow-blow method.
Vantage-rozvantage and transport robots. After preparing the route before the work and the organization of time-hour roads, transportation of pipes and building materials from their points of origin to pipe-welding bases, work-sites, time-hour warehouses and production sites begins. it.
Pipes that arrive at the loading station, when dismantled, are stored in a transshipment warehouse, in a stack, or hauled directly onto pipe carriers.
The pipes are laid in a stack of curls no more than 8 m on a planned horizontal platform. The bottom row of pipes is laid on pads made of round wood with a diameter of at least 200 mm. Place stops at the ends of the linings so that the pipes do not come loose.
The pipes from the carriages are removed by truck cranes in stacks. Using cranes, lift pipes from stacks onto pipe carriers for transportation to pipe welding depots. To transport pipes, pipe carriers based on high-speed vehicles are used.
At pipe welding bases, pipes are separated from pipe-laying trucks by taking one or a handful of pipes at a time, depending on the weight of the pipes and the capacity of the pipe-laying.
In the lower regions of the river, pipes and other waste materials are delivered to the place of work by waterway - on anchorage motor ships, river barges, dry anchorage barges, as well as on deck barges from universal pontoons iv. There will be special docks for the removal of pipes and fittings. Renovate pipes and fittings using floating cranes, truck cranes or pipe layers.
Welding and installation robots. For the construction of main pipelines, establish a basic scheme of welding and installation robots. Based on the design of the pipes that are placed on the pipe welding bases, the lengths of 10.5 to 12 m are dismantled by a pipelayer and are subjected to large-scale selection on mechanized lines.
The pipe welding base is folded into a folding rack with central conductors and internal centralizers, a welding stand with a wrapper and a welding equipment. In these installations, pipes are welded in sections with a length of 24...36 m, which are then transported to the route by haulage trucks, and laid out by pipe laying machines in each of the existing trenches for welding of a continuous line of the pipeline.
On the route, pipe sections are welded together mainly by manual arc welding. The electric jet for welding on the highway vibrates the welding generator.
The welding on the route is carried out using two methods: elementary and flow.
In the first method, the team of welders is divided into two sections: one of them welds the first (root) ball, the other - the steps. The application method is most often used for industrial pipelines with a diameter of up to 530 mm.
The flow method is used for laying main pipelines with a diameter of 1020...1420 mm. This welding method can be divided into flow-group and flow-divided. In the case of the flow-group method, a team assembles the construction work and prepares the pipes before collecting the pipe section; perform heating and welding of the first and other seams, as well as sealing and facing balls. The flow-dismemberment method ensures that the process of welding pipe joints is not dissected at the borders of technological operations. The skin strip is welded with one (singing) section of the skin stick. With the flow-dismembered method, the team is equipped with the following tasks: stripping sections of pipes and laying them out along the route; preparing them before boiling and pre-heating; a folding that comes together at once from the boiled root ball; hot passage;, cooking of smelly and facial balls.
The team that installs welding and installation robots on the highway is equipped with pipe laying machines, bulldozers, welding installations, an internal centralizer, a propane pre-heater, clamps, and a gas cutter.
When welding a pipeline, great care is taken to control the quality of the welding and installation robots, which results from periodic inspection of the steel and the quality of welding materials; systematic operational control of the process of folding and welding of pipes in a section on the pipe welding base and welding of a section in a pipeline on the route; external inspection and modification of geometric parameters of welded joints and preparation of their surface before control by physical flaw detection methods; periodic verification of the qualifications of welders; monitoring the quality of welded joints using physical flaw detection methods
To control welded joints, non-invasive methods are widely used to control the way the welds are scanned using gamma-rays. A beam of gamma-rays, penetrating the control stick, makes it possible to detect defects (for example, cracks, lack of boiling, gas pores, slag inclusions). During the rest of the day, X-ray tests began to be used on the highway to control the flow. When turning the yak, the boiled stack of pipes can be seen through each stake. The internal body of the welded stick, when scanned, is photographed on a light-sensitive melt and, if there are defects in the stick, they appear on the melt. All welds rejected based on the results of control are inspected and repaired in accordance with applicable standards and regulations (SNiP Ш-42-80).
Welding and installation robots follow additional pipe-laying machines. Pipelayers at a pipe welding base transfer pipes from a pipe carrier to a storage and welding line or place them on a stack; welded sections of pipes are removed from a welding stand and transported to a welding truck or placed on a stack. In addition, they are present in all operations involving lifting, support and movement of pipes during straightening and cleaning of their ends.
After welding, install the two- and three-pipe sections onto the braiding truck using the pipe-laying method using the tension method. In this case, the pipe-layer goes around the pipe-carrier behind the contour of its raft.
Along the route, pipelayers take part in folded and welded fixed booms: lift (with one or two pipelayers) a section and thread of the pipeline and, supporting them, create sinks for sticking, centering and welding the next section of the previously welded pipeline. Moreover, during the execution of these operations, a particularly precise robot of the pipe-laying operator is required. After welding the base section, the pipelayer lays the trenches on the ground on a wooden bed.
When welding laps, welding shut-off valves or welding pipe-laying coils, the same operations are performed as when welding fixed rods on the route, only you need particularly precise pulley hooks and arrows.
Earthen robots - digging and filling trenches, reclamation of native lands, etc. Trenches under pipelines are dug mainly with rotary trench excavators (div. Fig. 1). Trenches on curved sections of the highway with a radius of 50...60 m when working in soft, unstable soils, as well as from inclusions of boulders and rock formations, trenches are crushed using single-bucket excavators with buckets. stu 0.5...1.6 m3. Frozen and rocky soils must first be fluffed using a blower or mechanically, with the help of pushing bulldozer fluffers. In wet and swampy soils, trenches are made using single-bucket swamp-modified excavators or basic excavators with portable decks, as well as special floating swamp excavators.
The trenches are filled with bulldozers or trench-sealers right after the pipeline is laid. After suction and hardening of the soil, the thickness of the ball above the pipeline is no less than 0.8 m.
When laying a pipeline through native lands, carry out their reclamation: remove the native ball before the beginning of the work, save it at the shafts and turn it in place after the end of the work. In deserted areas, after completion of the work, the smudge that adheres to the pipeline is secured by planting dry-resistant plants.
When laying pipelines on land, the complex of earthworks consists of improving the foundations of well-drained, low-volatile soils (pebble, gravel and rocky soils), diking the foundations and waterways and adjacent ditches.
If the pipeline is laid on finger supports (as a rule, on permafrost soils), drill holes behind it and install the finger supports. The technology of these robots and types of mechanisms depend on the structure and temperature regime of permafrost soils.
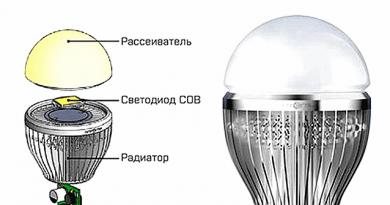
Insulation-laying robots (cleaning the outer surface of the pipeline from waste, rust, scale, applying a primer and insulation coating to it; monitoring the abrasion of the coating; laying the pipeline in a trench) vikola mechanized column , equipped with specialized machines: a group of pipelayers and one pipelayer; cars.
Insulation-laying robots are installed in three ways: stacking, separating, and laying insulated pipes behind.
A proven way to prevent stagnation when laying pipelines on plain terrain in rocky soils, on swampy sections of the highway without any pain or shaking, as well as at the intersection of terrain with a bump or a slope up to 3%. With this method, cleaning the outer surface of the pipeline, applying a primer and insulating coating, as well as laying a trench for the pipeline is completed simultaneously - directly on the route in a single technological flow.
Separate method of stagnation when laying pipelines near soils with weak load-bearing structures. In this case, the pipe-layers, which support the pipeline, due to the possibility of collapsing the walls of the trench, are moved to a certain distance from cutting the trench. A separate method also applies to vicorization when laying pipelines in areas with large slopes, swampy and waterlogged sections of the highway, etc. In this case, the stench is technologically reinforced and it works by laying the pipeline in a trench. In this case, after the pipelines have been cleaned and insulated, the pipelayers are lowered onto a wooden bench placed on the berms of the trenches, and then when the pipelayers pass again into the trench.
When pipelines are damaged from pipes without insulation applied to them, cleaning and insulation of pipes is carried out on permanent or stationary bases. In this case, before insulation, the pipes are welded at the 24...36 m section of the pipeline, then they are insulated and transported to the route. On the route, the sections are welded together with a continuous thread and laid on a piece of wood parallel to the axis of the trench. After this, the insulation-laying column team renews the damaged insulation, cleans the area of welded joints, applies a primer and insulation coating to them, and then lowers the pipeline with pipe layers in a trench Well, it’s the same as with the separate method of laying.
To protect the outer surface of pipelines from corrosion, use bitumen-hum mastics or polymer (polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride) coatings. When applied to a pipeline, bitumen-hum mastic is usually reinforced with a non-woven fiberglass cloth, applied with an overlap of 20...25 mm.
When laying pipelines near rocky and rocky soils, on “hot” plots where the product is transported at a temperature higher than 55° C, at crossings through automobile roads and slides, as well as through water areas, bitumen-hum mastic and polymer plastics The sheepskin coatings are stolen with scalding material for they are caused by mechanical damage.
The coating material is applied to the surface to be insulated, in one or two balls with an overlap of 3...4 cm, midway behind the application of the anti-corrosion coating.
Bitumen-hum mastic is poured onto the surface of the pipes using pipe insulation machines. Prepare the mastic in bitumen-smelting cauldrons installed on the building maidans near the base of the colony. The finished mastic from boilers to pipe insulation machines is delivered by bitumen trucks on vehicle chassis.
Polymer strips are applied using pipe insulation machines, as well as combined machines that immediately clean the pipeline and insulate with polymer strips.
The main machines used for the installation of insulation and laying robots are pipe-laying machines. The number of pipe layers in the column and their strength are installed depending on the diameter and thickness of the pipe walls, the terrain relief and the nature of the soil.
Pipelaying when installing insulation-laying robots follows the next step: raising the pipeline from the trench to a height of 0.8...1.8 m and supporting it from installation on it with pipe cleaning and pipe insulation machines. During these operations, pipelayers immediately collapse along the pipeline that will be, manipulate the booms with different inclinations, displace the insulation of the pipeline from the cut to the axis of the trench, and finally connect the entire pipeline to the trench axis. the entire trench and lower the pipeline into the trench.
When carrying out insulation-laying work, there is a step-by-step control of the cleaning, priming, insulation and installation of the pipeline in the trench. To control the purity of cleaning and insulation, vikorist devices are used to check the cleanliness of cleaning, the strength of insulation and adhesion to the surface of the pipeline. The placement of the pipeline is checked visually.
Ballasting robots. Pipelines of large diameters, laid in flooded areas, swamps or in swimming pools, impair buoyancy. To give the pipeline negative buoyancy, it should be anchored with reinforced concrete (Fig. 118, a) or steel linings with a mass of 4 tons or secured to the bottom of the trench with anchors (Fig. 118 b). Ballasting with anchors is difficult because the loose part of the anchor may be embedded in mineral soil.
The life of transitions. Pipelines move through various natural and artificial crossings (for example, slides and highways, springs, rivers). It is important to distinguish between underground and underwater pipeline crossings.
Pipeline crossings are connected to the underground ones, which are used by automobiles and skids. These crossings will be carried out, most importantly, in a trenchless manner, that is, without opening the roadbed or the top surface of the road, and therefore without breaking the road. When roads are blocked, pipelines are laid in dry casings. To lay out the casings, install a horizontal boring machine.
When crossing great rivers and lakes, it is important to cross and live under water (dukery). Work to manage water crossings follows individual design solutions. When crossings on ships, alloys, and water drains, the construction project works with the help of ship inspection, with the organization of timber rafting, and with pool management.

Small 118. Ballasting the pipeline:
a - tight fittings, b - anchors; 1 - pipeline, 2 - tie rod, 3 - power belt, 4 - lining mat, 5 - anchor rod, 6 - anchor
The life of underwater passages consists of the following operations: preparatory work; welding, hydraulic testing, insulation and lining of pipelines; excavation of onshore and underwater trenches; installation of a descent track under the hour of laying using the pulling method; Ballasting of pipelines; laying pipelines in trenches; secondary testing; bubbling trenches; Bank protection robots.
There will be underwater passages of specialized units.
The preparatory work includes: verification of hydrogeological and cryological data (which is carried out during the winter period), depth measurements to clarify the actual profile of the bottom at the crossing point and the type of its project.
Welding and insulating robots are carried out in the same ways as for the linear part of the pipeline. As an insulating coating, vikorist polymer strips are protected from mechanical damage by wrapping material and lining from wooden slats.
Underwater trenches are excavated using dredgers, dredgers, scraper units, excavators installed on floating units, special mechanisms used to bury underwater pipelines, either by laying or by the jack method.
It works most effectively during underwater crossings of main pipelines and is laid on the bottom of a water crossing. The following are the main methods of laying pipelines: pulling the bottom of a water crossing; it is more difficult due to the influx of water into the pipeline or its privatization; lowering of floating cranes or supports equipped with lifting structures; laying of pipe-laying barges with subsequent extensions of pipe sections; laying of towed sections (lashes) and welding of inter-sectional sticks afloat.
In case of emergency underwater passages, pipelayers are used in the process of removing welding, installation and insulation work, as well as in case of dismantling of surrounding pipes and sections. In certain situations, the pipe layers act as traction mechanisms when pulling the drainage pipes.
Cleaning the empty and testing the pipeline for integrity and tightness. The positions in the pipeline trench are tested for consistency and tightness. First of all, clean it of scale, tar and soil that was lost in it, water and other objects. The pipeline is cleaned by blowing through cleaning pistons or elastic spacers, as well as by flushing with water and passing elastic spacers. Blowing is carried out using compressed air, sometimes with natural gas. Aboveground gas pipelines must be cleaned according to special rules. After cleaning, stock plugs are installed at the open ends of the pipeline.
Before they are put into operation, main pipelines are tested under pressure for tightness and tightness of pipes, water or product, for any reason. The order of testing parameters is determined by BNiPs.
When emptying and testing pipelines are cleaned, remote control and monitoring equipment, as well as a specially equipped set of vacuum-testing units, should be installed. To carry out emptying and testing of the pipeline, prepare a technological map-schedule and instructions.
Cost of the object to be insured for the technological warehouse of the cap. insert:
Z zag = KV = Z side + Z mont. + Z rev. + Z pr.z., de
Z side– costly variety of everyday work;
Z mont.– the cost of installation work;
Zor.- Costly equipment, furniture, inventory;
Z pr.z.– cost of other capital works and costs.
Koshtorisna Vartіst BIS take out insurance: Z smr = PZ + NR + SP.
Directly with PZ - Basic The total amount spent on the budget of the BIS, the physical obligations of which are assigned to the project, and the value of the amount - according to the cost norms:
PZ = Z mat + Z ozp + Z emm, de
Z mat- quality of materials, parts and design;
Salary- Koshty to pay for the share of workmen-budivelniks (installers), then. workers employed in the BIS manufacturing industry (basic salary);
Z emm - versatility in the operation of machines and mechanisms (including payment for the work of robotic drivers – Salary mash.).
Payroll fund for workers: FOP slave = Zp + Zp. mash.
Invoices with HP - Indirect expenses related to the care of the minds of the BIS production and the activities of the SMO.
Insure these types of HP:
administrative-state expenditures;
spend on the services of doctors;
spend on organizing work;
Other invoices have been spent.
The amount of overhead costs is calculated for MDS 81-33.2004:
NR = N NR FOP slave /100, de
N nr- standards for overhead costs (in%) are adopted either for the types of BIS or for the types of housing. Since 2005 to the HP standards, the reduction coefficient is 0.94.
Koshtorisny profit of the joint venture - the contractor’s income (accumulation area), the amount of funds necessary for the development of the material and technical base and the stimulation of CMO practitioners, is assigned to MDS 81-25.2001:
SP = N sp FOP slave /100, de
N sp- SP standards (in %) are adopted either for the types of BMR, or behind the scenes (50% - repair robots, 65% - everything else).
For everyday life that is financed from extra-budgetary funds, it is allowed:
SP = N sp (PZ + NR) / 100, the Derzhbud of the Russian Federation recommended the standard of cost income from cost price N sp = 12%.
3. System of pricing and cost regulation Varosti everyday life
The totality of rules, regulations, norms, ratings, etc. materials, necessary assessment of the quality of future products (set No. 81 of regulatory documents for the State Duma of the Russian Federation - Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation).
System foundation – State elemental cost norms (GESN), Initial wastage of resources from natural workers (waste of labor workers, wastage of machines, wastage of materials) per unit of BIS, which is the basis for the transition to varity indicators (Federal single rates (FER), Territorial single rates (TER), Galuzev single rates (VER), larger indicators of varosti for types of work, etc.).
| System of pricing and cost regulation in Budivnytsia (System TsISSN) | ||||||||||||
| Methodology for assessing the value of household products of the Russian Federation (MDS 81-35.2004) | Koshtorisno-regulatory (koshtorisno-information) base | Additional cost documents (ASD) - methodological. that hand doc | ||||||||||
| Federal rhubarb | Galuzevy rhubarb | Territorial rhubarb | Firm rhubarb | |||||||||
| State cost standards (DSP) | Galuzev's Kostorisni Standards (OSN) | Territorial cost standards (TSN) | Firm cost standards (FSP) | |||||||||

GESN collections place the technical part (indications, rules for the assignment of duties, correction coefficients to the norms) and tables of elemental cost norms, for which the skin care is established:
number, name, name and warehouse;
spend 100% of the employee's salary on a permanent job;
average robot category;
expenditure of drivers per person-hour on operating robots;
the shift in the operating hours of machines and mechanisms from the machine year to the existing robots;
transfer and waste of materials, viruses, structures, energy sources from physical substances. in units of vimiru on vimiruvach robots.
Collectors FER (TER) take revenge quietly. part (filler inserts, rules for assigning obligations to work, correction coefficients to rates) and a table with single rates (EP), in which hundred percent skin work is indicated:
number, name and name of the work (selected from GESN);
one vartіst (direct expenditures on vimiryuvach robots) in rub. as of 01/01/2000 r. - all the parts of the PZ seen (the quality of materials, parts and structures, the cost of paying for labor workers (installers), the quality of operating machines and mechanisms, including the remaining stock in the warehouse payment for a portion of the robotic drivers is assigned);
wastage of materials not insured by the Russian Federation, from natural units to vimiruvach robots;
spend a lot of work workers and installers (at the end of the year there is a death of work).
Prices for FER (TER) collections may be closed or opened :
1) U closed prices The completeness of all elements of direct expenditures is insured.
2) U in the following prices The quality of the main materials is not guaranteed. The stinks are injected into the EP in rows and rows due to the appointment of their names and spending on vimiruvach prices. FERM (TERM) – all open: Unauthorized materials should be found at the entry points.
Construction and installation robots are busy with all the robots that end up at the hour of wakefulness or immediately at the place of wakefulness. Works are usually called laborious or assembly work depending on what process is important. Prior to the installation, work is carried out from the standstill of finished parts, for example, installation of reinforced concrete structures, lighting or power electrical wiring, ventilation, elevators, etc.
All work on duty is divided into custodial work, special work, transport work and vantage work.
Before cheerful These are the robots associated with the creation of everyday structures of life and disputes.
Construction work is divided into types of recycled materials on earthen, stone, concrete, etc., and structural elements that are being constructed - on roofing, plaster, etc.
Earthling robots: digging of pits, pits and trenches under the support frames, line foundations, trenches for underground communications, transportation (drilling, relocation, vivantage) and fluffing of soil, planning of maidans, excavation work, gate filling smoothing the soil, strengthening the soil.
Pale robots: hammering or tightening of fingers, lashing of finger foundations.
Kamiani robots: construction of stone structures (walls, piers, footings) from piece stones and blocks, rubble and rubble concrete masonry, masonry from prepared natural stone of regular shape, purpose, piece stone and large blocks.
Concrete and reinforced concrete robots - construction of concrete and reinforced concrete structures: preparation of concrete mix, transportation and laying of them in reinforced forms (formwork); creation of minds, necessary hardening of concrete (monitoring of concrete); monolithation of sections and sticks between prefabricated elements and so on. When erecting reinforced concrete monolithic structures, formworks (attachment of formwork) and reinforcement (installation of reinforcement cages in the formwork) are also laid.
Installation of the structure I like the delivery to the work site, installation, alignment and fastening of finished parts and elements (steel, concrete, reinforced concrete, wood, asbestos-cement, etc.).
Tesla and carpentry robots On the premises, as a rule, the processes of transportation to the place of installation and installation of finished parts (frames, windows, doors) or the construction of previously prepared and fabricated parts, elements or materials (boards, bars, etc.) n.). This also applies to the laying of plank and parquet floors.
Painting robots- these are the robots that are used for washing the coatings of hot and non-burning waters. In one type, the coating is made from steel and asbestos-cement sheets, in the other, rolled materials (tar paper, parchment, roofing felt) are glued onto the prepared base.
Healthy robots: plastering, tiling, fretting, taping with trellises and premises. Plastering robots, as a rule, work with mechanized feeding and cutting, and for small jobs they work manually. Facing robots are completed from the hardening of large-sized slabs and small-sized tiles, as well as facing sheet materials, and are rotated after the completion of stone work. The work on the fabricated structure and the taping of trellises is brought to the painter's shop. The consumer warehouse also includes robots covered with linoleum, plastic, etc.
Before special is the main focus of the work, associated with special types of materials and fabrication methods, which will form when the structure and materials are assembled. For example, the varnishing of mine shafts, the lining or lining of technological units and equipment with acid-extracting or fire-extinguishing masonry, the application of anti-corrosion coatings to structures, as well as the varnishing of power, lighting, telephone and etc. construction, installation of sanitary systems and fittings, elevators.
Transport and vantage items Works include delivery to everyday life and work places of materials, structures and parts, supplies, equipment and tools. For the transportation of various items that need to be carried out on a daily basis, we use a variety of transport means: self-skidding trucks, panel carriers, trailers, suspended and conveyor transport vehicles.
Control food
- What architectural and structural elements are based on functional significance?
- What elements will be brought to the carriers, what will be stolen?
- What kind of materials can be used to formulate the foundations?
- How many people are going to be satisfied with the design, what are they going to steal?
- What is the initial sign when dividing the livestock and vibrator?
- What difference will there be between the two?
- What are the main signs to classify the booths?
- What kind of constructive types of living quarters will there be?
- What are the warehouses of the everyday process?
- How is a work operation characterized?
- How are everyday processes classified based on complexity and significance?
- What is Lanka Robotnik?
- What is a plot, capture, front work, work place?
- What are the main types of construction and installation work?
→ Living robots
Organization of construction and installation work
Warehouse for construction and installation work. The organization of future construction and assembly production during the production process using industrial methods consists of the organization of work: preparatory work, zero cycle work, and assembly work.
Preparatory work will be completed by the future and installation organizations.
Before the preparatory work, which is completed by the future organization (general contractor), the following must be planned: planning the installation platform; controversies of local roads; budova of warehouses and folding maidans; setting up time alarms necessary for carrying out installation work; supply, for example, electricity, compressed wind to the place of living; geodetic robots; fencing of the assembly square; installation of building structures on the mounting platform; delivery and installation of mechanisms for zero-cycle work (if they are confirmed by the necessary organization).
Installation organizations carry out the following preparation work: delivery, installation, registration with State Technical Supervision authorities, testing of suitable installation mechanisms; preparation and delivery to the site of the work of the necessary equipment, tools, inventory devices, auxiliary materials and control of auxiliary devices necessary for carrying out the installation work.
All preparation work will be completed before the start of the assembly work schedule established by the schedule.
Installation robots perform the following zero-cycle tasks: excavation of foundation pits and trenches; Budovu foundations; laying internal underground communications; the gates of the sinuses of the pits and trenches; planning the Maidan; budova paths for mounting mechanisms; concrete preparation under pretext; Vlastuvannya pavement nakolo zvedeniya budіvlі or sporudi.
The work of the zero cycle is completed by the development organization, the general contractor.
Installation robots - installation of all structures from the construction site, including installation robots. These robots are completed by installation subcontractors.
The main aspects of the organization of construction and installation work. The organization of construction and installation work is based on the following principles:
industrial methods of life;
complex mechanization of robots;
More precise methods of waking up.
Industrial methods of production - production of materials from prefabricated structures and factory-produced parts, with complex mechanization and automation of manufacturing processes, using advanced technologies progressive methods of organizing construction and installation work. It is important to directly industrialize and widely establish a free-sector labor force. Therefore, the level of profitability in everyday life is steadily increasing.
Thus, during the previous five-year period (1971-1975) the tax rate for the new election in general increased approximately twice, more than twice (twice the increase in the stagnation of factory-made structures, significantly There has been an increase in the use of reinforced concrete precast structures from lightweight concrete, as well as aluminum structures).
The advancement of industrial methods of everyday life will quickly lead to the creation and implementation of the objects that will be created, changing the complexity and skill of their everyday life.
Integrated mechanization of robots. In construction and assembly production there are three types of mechanization: partial (partial), complex and automation.
In case of incomplete mechanization, only a part of the robot is bent using a mechanized method. For example, when digging trenches for laying utility lines, the soil should be excavated with an excavator, and after laying pipelines, the excavator should be excavated using shovels. Unnecessary mechanization may cause the machine to stomp during small operations, or during outbursts, if for some reason it is not possible to stomp the machines.
With complex mechanization, the main processes that go into the robot are completed in a mechanized manner. The use of manual work is allowed except for other ancillary operations of minor complexity. Mechanization of processes can be carried out using one or more machines (set). Most often, complex mechanization involves a set of machines and mechanisms. For example, the excavation of soil in a pit and its transportation into transport is carried out using excavators, transportation and recovery - with self-propelled trucks, demolition - with bulldozers (earthing mechanism) and compaction - with compactors. The butt of complex mechanization of earthworks uses one machine to crush the soil with a scraper (earth-transport mechanism).
The complex mechanization of the work results in great efficiency. Vaughn promotes the productivity of work, shortens the term of alertness, and reduces your productivity. Thus, when using excavator excavator excavator robots with a bucket capacity of 0.25-0.35 m, the productivity of the excavator will increase approximately 10-15 times compared to the manual method. On modern robots that follow additional machines, productivity increases by 20-30 times. The use of units for preparation, transportation and machining of the structure reduces the complexity by two to three times. The current period of development of industrial production is characterized by a broad transition to complex mechanization. Automation is called mechanization if all robots are completed automatically by a working system of machines controlled by the robot operator. Automation in everyday life is still stagnant, at the top level, in the production of everyday life. Created around automated and automated enterprises: factories for the production of concrete, asphalt concrete, precast concrete, at factories automated around technological processes (electrical supply, welding operations, thermal treatment room isoconcrete viruses).
Recently, automation has begun to be more widely used in the production of construction and assembly robots. Some earth-moving shells have an automatic control system; the installation cranes of the new system are equipped with automatic interconnectors; Trenchers are released to automatically dig trenches of a given profile.
Precise methods of organizing everyday life are the most progressive forms of organizing everyday production that will ensure the uninterrupted, even and rhythmic production of building and installation work. Exact methods are transferred: dismemberment of construction and assembly production at the edge of the warehouse process; divided the people among the Viconavians; understanding everyday processes in the hour; establishing the correct vibration rhythm. The most widespread in everyday life are the flow-spitting and flow-linear methods for the installation of drilling and installation work.
With the flow-grabbing method, robots break up the plots (grabs), which are approximately equal in labor intensity. In its own way, the grips are divided into the front of the work, and the rest into the plots. The capture is part of the object, where the installations of the brigade and the several brigades mark the beginning of the work, the front work is a whole part of the capture, and the teams of workers mark part of the daily process, which is no more than the capture. The site is part of the front line of work, the work of the brigade is one step closer to the operational process carried out by the brigade.
On the grips, in order of technological sequence, complexes of construction and installation robots are carried out step by step. At the same object, work and at the same time carry out a variety of work, such as specialized or complex teams of warehouse workers, successively move from one object to another, so that over the course of the day there will be one And the same cycle works on the skin tissue. A robot cycle is a set of technologically interconnected robots that can be processed on one gripper at the same time (in parallel).
The duration of one cycle on one gripper is called the rhythm of the flow, and the hourly interval between the start of work on the same gripper of two sequentially working teams is called the flow rate. An indicator of the most precise organization of flow generation is the perpetual flow, in which the rhythm of the flow represents a constant value to the hour and is similar to the time of the flow.
The flow-spitting method stagnates when the alarm is raised; flow-linear – with the introduction of spores or structures of a linear-extended nature (roads, main pipelines, canals, radiators). With this method, teams of robot workers successively, one by one, move along the track with steady speed.