Sex system of cilia worms. Food of flat worms. What fastened flat worms
Source level of knowledge:
Answer:
- External and internal structure of flat worms
- Reproduction of flat worms
- Classification of flat worms, species manifold
- Features of the structure and development of worms of the classified class on the example of a dairy plane
- Features of the structure and development of the wives of the class of the losers on the example of a hepatic sequence
- Features of the structure and development of worms of the ribbon class on the example of a bovine chain, etc.
General characteristics of flat worms
Number of species: About 25 thousand.
Habitat: Inhabit everywhere in wet environments, including fabrics and other animal organs.
Structure: Flat worms - These are the first multicellular animals, in which bilateral symmetry, three-layerness, real organs and tissues appeared during evolution.
Bilateral (bilateral) symmetry - this means that through the body of the animal you can spend an imaginary axis of symmetry, while the right side of the body will be mirrored to the left.
During the embryonic development of three-layer Animals are laid three layers of cells: outdoor - etoderma, middle - mesoderma, internal - entoderma. Each layer develops certain organs and fabrics:
skin (epithelium) and nervous system are generated from the ectoderm;
mesoderma - muscle and connective tissue, sexual, excretory system;
from Entoderma - digestive system.
In flat worms, the body is flattened in the spin-abdominal direction, the body cavity is absent, the space between the internal organs is filled with mesoderm cells (parenchyma).
Digestive system Includes mouth, throat and blind intestinal. Absorption of food and excretion of undue residues occurs through the mouth. In the ribbon worms, the digestive system is completely absent, the nutrients are absorbed by the entire surface of the body, being in the intestine of the owner.
Selective organs - protonefridia. They consist of thin branching tubules, at one end of which are located flame (flicker) cellsstar shape immersed in a parenchyma. Inside of these cells, a bug of cilia is departed ( flickering flame), the movement of which resembles flickering of the flame (hence the name of the cell). Flame cells are captured from parenchyma liquid decay products, and the cilia drive them into the canal. The tubules open on the surface of the body separating sometimes, through which decomposition products are removed from the body.
Nervous system staircase ( orthogon). It is formed by a large head paired nervous knot (ganglia) and six nervous barrels from him: two on the abdominal side, two on the dorsal and two sides. Nervous trunks are interconnected by jumpers. The nerves to organs and the skin depart from Ganglia and trunks.
Reproduction and development:
Flat worms - hermaphrodites. Sex cells ripen in germ glanes (gonads). Hermaphrodis has both men's glands - the seeds and women's - ovaries. Fertilization - internal, usually cross, i.e. Worms exchange seed fluid.
Class Classified Cherry
Dairy plane, a small water animal, an adult individual has a length of ~ 25 mm and a width of ~ 6 mm, the body is flat, milk-white. At the front end of the body there are two eyes, distinguishing light from darkness, as well as a pair of tental (chemical feeling) necessary to search for food. Planaria move, on the one hand, thanks to the work of cilia covering their skin, on the other hand, thanks to the reduction of the muscles of the skin-muscular bag. The space between the muscles and the internal organs is filled with Parenkhima, in which they meet intermediate cellsresponsible for regeneration and useless reproduction.
Planaria - predators feed on small animals. The mouth is located on the abdominal side, closer to the middle of the body, there is a muscular throat from it, from which three branches of the closed intestine are departed. Capturing the sacrifice, the planaries sucks its contents. In the intestine, digestion under the action of enzymes (intestinal), intestinal cells are able to capture and digest pieces of food (intracellular digestion). Unpained food remnants are removed through the mouth.
Reproduction and development. Rishichny - hermaphrodites. Fertilization cross. Fertilized eggs fall into the cocoon, which worm postpones on underwater items. Development direct.
Class of chowers

Class of tape worms
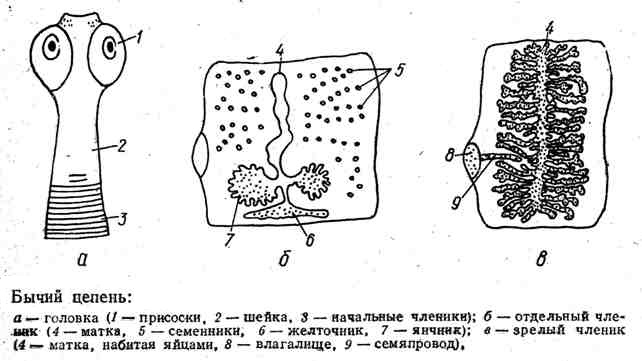
Bull chain - Ribbon worm, reaches a length from 4 to 12 meters. The body includes a head with suction cups, neck and gate - sealer tape. The youngest segments are at the neck, the oldest are the bags filled with eggs, are at the rear end, where they come off one by one.
Reproduction and development. Bull Chain - Hermaphrodge: There is one ovary in every segment and many seeds. It is observed both cross fertilization and self-exploitation. The rear segments filled with ripe eggs are opened, and, with the feces, are outward. Cattle (intermediate owner) can swallow eggs along with grass, microscopic larvae with six hooks come from eggs, which through the intestine wall fall into the blood and spread throughout the body of the animal and are recorded in the muscles. Here, the six-sided larva grows and turns into finn - A bubble, inside of which is a chain chain head. A person can become infected with docks, aief is not sufficiently roasted or woven meat of an infected animal. In the stomach of a man from the fins, the head comes out, which is attached to the intestinal wall. From the neck, new segments are buded - the worm grows. The bullish chain allocates poisonous substances that cause intestinal disorders and anemia in humans.
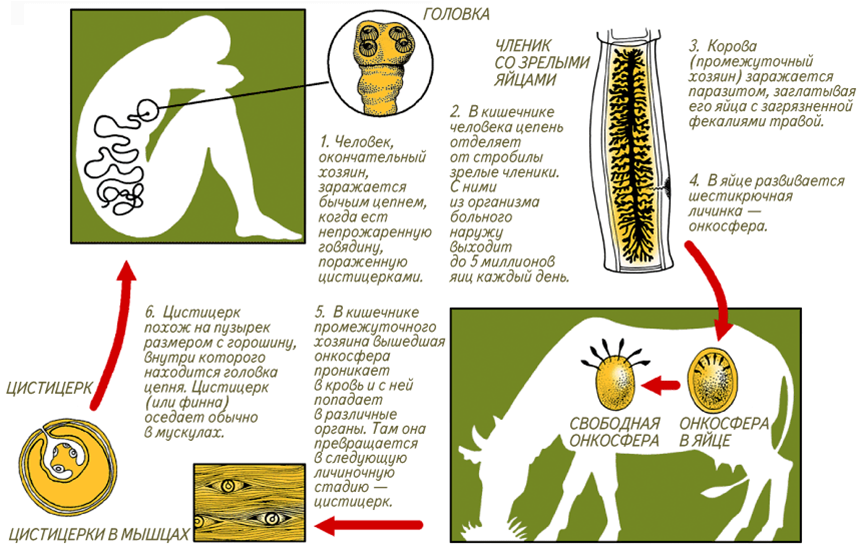
Development pork chain It has a similar character, his intermediate owner besides a pig and boar, there may be a person, then in his muscles are developing.
Development wide Lenteza accompanied by a change of two intermediate owners: the first - the wrapping (cyclops), the second is a fish, eating the lap. The final owner can be a person or a predator, eating infected fish.
New concepts and terms: Mesoderma, skin-muscular bag, tugement, hypoderma, reduction, protonphridey (fiery cells), orthogon, gates, gangliy, gonads, hermaphrodis, direct and indirect development, final and intermediate owner, Miracidium, churches, Finn, segment, armed and unarmed tapeworm.
Literature:
- Bilic G.L., Kryzhanovsky V.A. Biology. Full course. In 3 t. - M.: LLC Publishing House "Onyx 21st Century", 2002
- Pimenov A.V., Pimenova I.N. Invertebrate zoology. Theory. Tasks. Answers: Saratov, OJSC Publishing House "Lyceum", 2005.
- Chebyshev N.V., Kuznetsov S.V., Zaychikova S.G. Biology: allowance for applicants to universities. T.2. - M.: LLC "Publishing House New Wave", 1998.
Salar class (trematodes)
Class Belt Worms (Cestodies)
General characteristic type
- Three-layer animals: a third embryonic leaf appears between ecto- and edoderma - mesoderma.
- From the Mesoderm, the muscular, sexual and excretory system is developing for the first time.
- There is no body cavity.
- The space between the authorities is filled Parenkhima (Mesenchymy) - tissue of mesodermal origin. It is little differentiated, almost homogeneous and consists of crossed cells of the wrong shape. Neighboring cells are intertwined by these processes, and thus mesh structure is formed. The spaces between the cells are filled with liquid.
Parenhima functions:
- spare nutrients (glycogen, fats);
- the products of metabolism are received, then transmitted along the channels of protonfritis outward;
- regeneration;
- reference;
- Transport (transport substances between organs). - Bilateral (bilateral) symmetry.
- Body shape ribbon or sheet.
- The front end end of the body, with the main senses located on it: view, touch, smell, chemorescape, which allows these animals to better navigate in space and make directional movements;
- Skeletal function performs the skin-muscular bag - the body wall formed by the skin epithelium and several layers of muscles: ring, longitudinal, diagonal.
- The digestive system is closed, consists of a mouth hole, pharynx (front intestine) and a branched bowel (middle intestine). Unauthorized residues are removed through the oral hole.
- The nervous system consists of a paired head nerve node ( ganglia) and longitudinal nerve trunks connected by transverse ring jumpers ( connectivations). Such a "stairs" type of nervous system is called ortogon.
- Blood and respiratory system are missing; Gas exchange occurs directly through the body surface.
- The excretory system is represented by protonfritis - paired thin channels, beginning with starfish cells with a seating flame in a parenchym on the sides of the body and ending excretory pores on the dorsal side of the body.
- Sex system: Flat worms - hermaphrodites:
- Men's sexual system: numerous seeds, seeding tubes flowing into seeds, seed bubble. From the seed bubble, a seed-residual canal departs, opening into the cooler ( zirrus);
- Women's sexual system: ovaries, eggs, yolklinks, shell glands and a copulative bag. - Reproduction:
- Miscellaneous: fragmentation;
- Paul: internal fertilization. - Regeneration well developed
Class Classified Cherry
About 3,500 species.
Fig. Sea flat worms
All free-live predators.
Live in aquatic environment, less often on land.
The body is covered with a solicified epithelium containing numerous mucous glands.
Representative: Dairy Planaria.
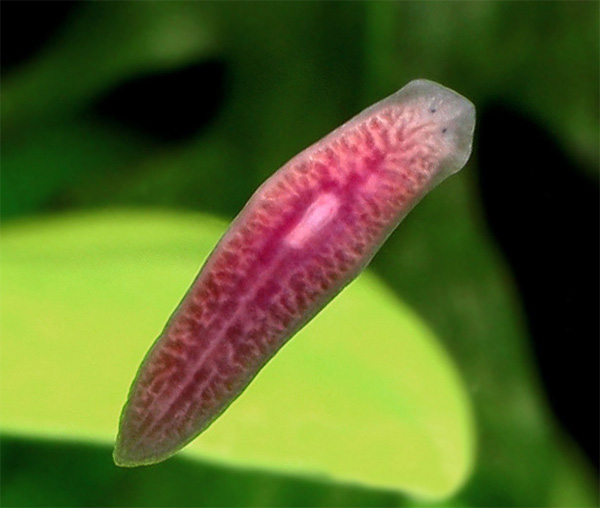

Fig. White (dairy) plane

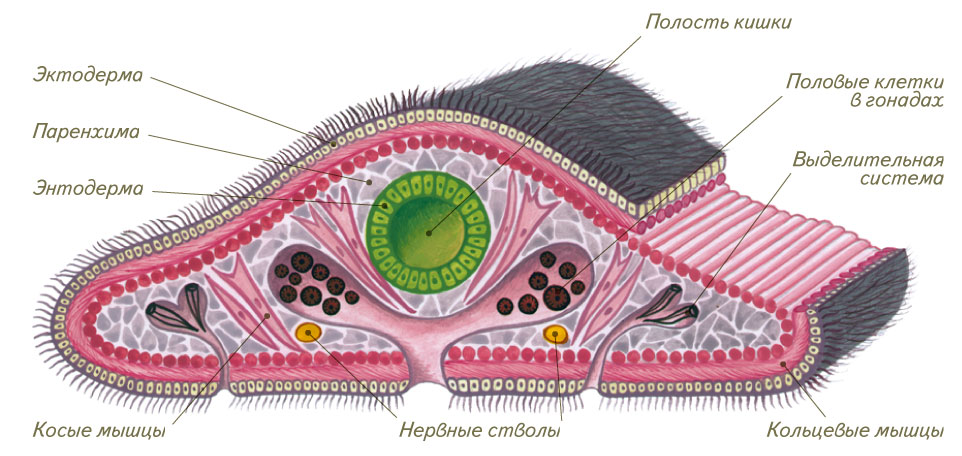
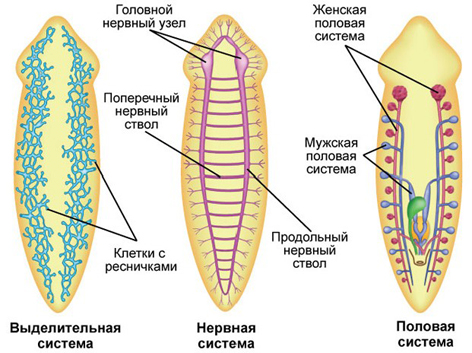
Fig. The internal structure of the planarium Fig. Regeneration
class of seashers, or trematodes
Cause diseases - trematodose.
There were from the cilia worms.
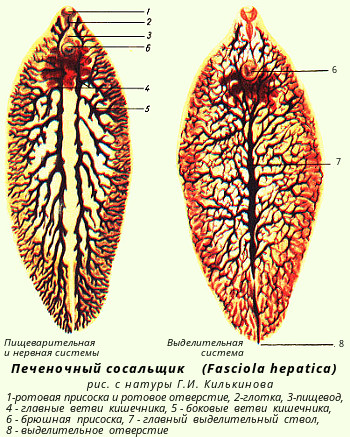
Representative: Liver Slerk.
- Small pondovik - an intermediate owner (non-reproduction of larvae);
- Man, large and small horned cattle and other herbivores - final owners.In the body of the final owner there is sexual reproduction of the worm.
- Infection: raw water from small water bodies, plants in swampy terrain, water swallowing when bathing.
- Huge fecundity: many eggs + parthenogenetic reproduction at the stage of the larvae (neural).
Stages of the liver sequer development cycle
Adult hepatic loseller ( Fasciola Hepatica.) It is in the bile ducts of the final owner. Adult feast worm called marita. Marita hermaphroditic, but usually exchange sperm during cross-fertilization. The eggs of the liver loser fall into environment Together with the excrement of the final owner. For the further development of the eggs must be in full with reservoirs. In the water out of the egg comes out actively floating larva, covered with cilia - miracidium. Miracidium has two eyes, protonfrites and germinal cells. Miracidium floats for a while, then finds an intermediate owner - freshwater brying mollusk small ( Lymnaea Minor) And actively introduced into his body. In the liver of Mollusk Miracidium loses cilia, acquires a capsule and turns into the next larval stage - sporocyst. Due to the germinal cells that were present in Mirachydia, subsidiaries are formed inside the sporocysts - Finia.
When Sporocyst is bursting and dying, the fingest go out and begin to actively eat, absorbing the owner's fabrics. Finia has a mouth with a mouth suction cup, a muscular pharynx, turning into a bag-shaped intestine, two protonphridium, the primitives of the orthogonal nervous system, generative cells (egg cells) in the parenchyma and the generative time. The presence of the latter, as well as the oral hole, pharynx and the intestine distinguishes them from sporocyst.
Freedies multiply parthenogenetically, giving rise to a new generation - churches. The length of them is 0.3-1 mm. Their distinctive feature is the presence of a large muscular swimming tail at the rear end of the body (in some types of forked), as well as the infarded genital organs. Like adults, churches have a mouth and abdominal suction cleaners, a two-way intestines, a nervous system, sometimes eyes and well-developed protonphrideas.
Also, churchings have at the forefront of the body, which are involved in the dissolution of the cover of the owner, due to which they break through the body of the mollusk and go into water. Some time of the churches are floating in water, then attached to the incoming vegetation, covered with a thick shell and turn into adolescaria. Cattle, going on the water, eats grass with adolescari attached to it. In the intestine of the final owner, the adolescary shell dissolves, and the young hepatic sequence penetrates into the liver. Thus, the swallowing of the adolescary is the only way to infect the final owner. It is necessary to treat patients with fasciolaise animals in order to exclude the chips of the eggs in the environment.
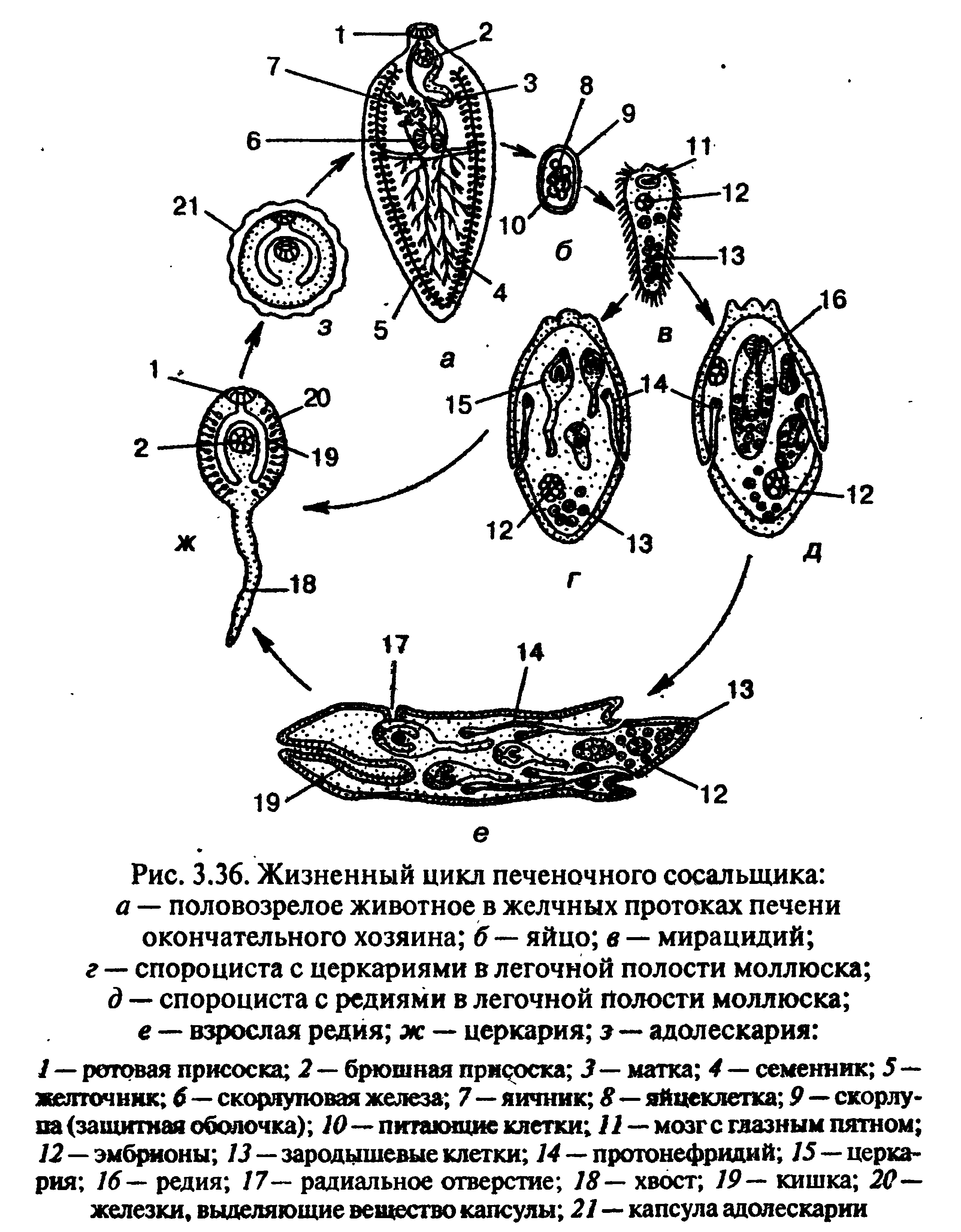
Ways of infection of man - Use of unwashed vegetables and fruits (water can be used with adolescarii), swallowing water when bathing in fresh reservoirs, where small strudes live.
Part of the trematode has a second intermediate owner, for example, a fish in which the church is introduced, loses the tail, is incinerated in the tissues and turns into a metaercaria. When using crude or uncomfortable fish (mostly carp fish), a person can become infected with these types of trematodes - this is, for example, Clonorkhis (Chinese duxtile), opistorhis (feline duxtile).
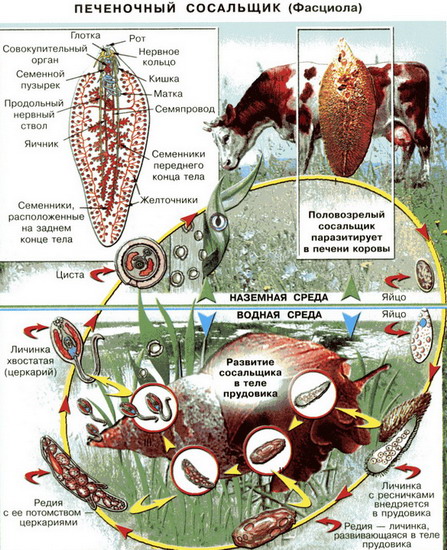
Fig. Life cycle Hepatic Soster
Class of tape worms
About 3,000 species.
The development cycle occurs with the change of owners.
Representatives: bovine chain.
- It dwells in the small intestine of a person.
- It feeds on a semi-stealing food, sucking it with the entire surface of the body using the outer epithelium microwave.
- Structure: The body is flat, tanning, divided into segments. In each segment there is a segment of the hermaphroditic sexual system.
Fig. Bull chain
At the front end of the body, a small head (Skolex) is equipped with fixation organs: suction cups (bovine and pork chain) and hooks (available only at a pork chain). For this reason, the bull chain is also called non-equipped, and a pig - armed.
Next segment - neck,it occurs increasing new segments. Previous segments are gradually moved to the rear end, falling off, stand out with the host feces into the external environment. By this time, inside segments already occurs self-exploitation and maturation of numerous eggs.
Bull Chain Development Cycle: With the change of owners.
- final owner: human;
- intermediate owner: cattle.
A man is infected with chains, using uncompressed or uncompressed financial meat. The head of the head is turned out to be turned out and attached to the intestinal walls with suction cups or hooks. From the head begin to grow segregate.
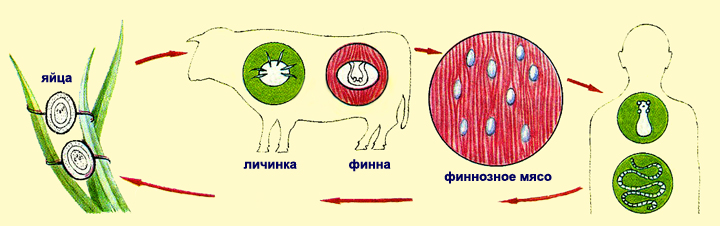
Fig. Bovine chain development cycle
Pork (Armed) Chain In addition to the sucker has hooks. Its intermediate owner is a pig.
All representatives of multicellular animals are distinguished by the level of the organization, characteristic features Life processes and are combined into special taxa - types. All of them are 7. Is one of them. These creatures have perfectly adapted to the conditions of existence and occupy their biological niche. How is the power of flat worms? Answers are looking for in our article.
General characteristics of flat worms
The representatives of this systematic group obtained their name due to the form of the body. A transverse section of flat worms resembles a sheet or tape. For these animals, bilateral symmetry and formed organ systems are characteristic. The musculoskeletal system is represented by a skin-muscular bag, which consists of a coating epithelium and several layers of muscles. The separation system consists of thin canals opening outwards.
Habitat

Features of the digestive system
The digestive system of flat worms of a closed type. It consists of a mouth and intestines. How is the power of flat worms? Food particles come through the mouth, digested in the branched intestine, and the residues are also removed through the hole located at the front end of the body.
Food of flat worms
Worms who live in various reservoirs are predators. They attack small bottom animals and with the help of a special trunk they suck their contents.

Food of flat worms and round worms Signally different because the last digestive system of through-type. It has a view of a tube with mouth and anal holes, so the metabolism is more intense. Free-lived ground flat worms are powered by insect larvae living in a wet forest litter.
Crymfish
Representatives of this class of animals inhabit the water. In this medium, the epithelium cells highlight a special secret to help keep small dress animals - racks, hydra, a variety of larvae. Food of flat worms of this class occurs very unusual.

For example, at the milk-white planarium, the river hole is located in the middle of the body on his abdominal side. The worm is cashing, thus holding it. Further, through the oral hole, trumps are turned out, with which the planaria sues liquid content from the body of production.
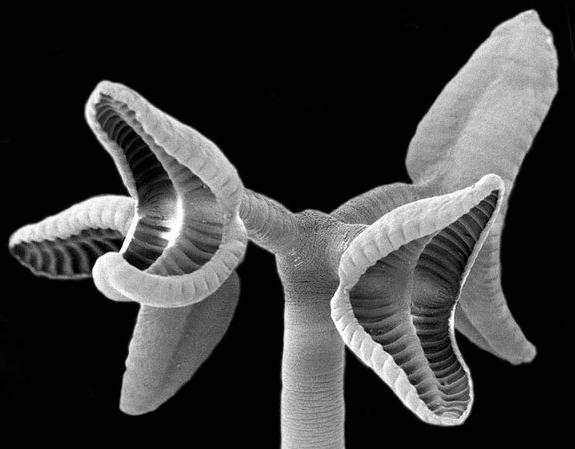
It is at this stage that the worm is powered. At the bottom of the first sucker there is a mouth opening opening in the intestines. The digestive system has a view of a bag or two channels that blindly end. Since these helminths have no body cavity and a circulatory system, the gastrointestinal tract also also performs the function of supplying the entire organism with various substances. Salers feed on blood, mucus and cells of the epithelium. Helmint exchanging products are highlighted through the oral hole, while poisoning the body of the final owner.
Ribbon worms

animals. The length is from 0.1 mm to 20 m. Their elongated, the bilateral almetrical body is flattened in the spin-abdominal direction and resembles the form of a plate or tape. Most species are deprived of all traces of segmentation, but the ribbon worms are divided into segments. Many parasitic species develop a variety of attachments: rounded or elongated suckers, troughs and chitin hooks.
Flat worms are three-layer animals. They in the ontogenesis between the ectoderm, from which the covers develop, and the Entoderma, which gives rise to the intestine, is formed by Mesoderm. Cells of parenchyma develop from it, filling the entire space between the internal organs. Flat worms are developed a powerful skin-muscular bag consisting of skin epithelium and underlying ring, longitudinal and diagonal muscles under it. In addition, separate beams of spin-abdominal muscles are located between the dorsal and abdominal sides of the body. Thanks to such a variety of muscles, flat worms are capable of making complex movements: cut and pull the body, narrow and expand it, as well as twist and wave bent.
Due to active movement, flat worms have bilateral symmetry, the head end is the senses (equilibrium, photosensitive) and several nerve nodes, from which nerve trunks with transverse jumpers are departed.
The excretory system consists of protonphridium - pear cells, in the cavity of the bunch of cilia. The bias of the cilia is driven by liquid into excretory channels in which the reverse absorption of water and beneficial substances occurs. Channels merge among themselves and open out with one or more holes.
Almost all IFs - hermaphrodites, i.e. Have both men's and female sexual systems. The men's field system consists of the seeds, the seeds, the focus. Women's - from ovaries, eggs, sexual cloaca. Internal fertilization, usually cross.
Tests
1. How the nervous system of flat worms is arranged
A) nervous network from individual cells
B) nervous nodes interconnected in chains
C) nervous nodes from which trunks are departed back
D) nervous tube
2. The process of reverse absorption of water and useful substances occurs at the IF in the system
A) bloodstream
B) digestive
C) gender
D) excretory
3. Fertilization in flat worms
A) occurs in water, one worm fertilizes the other
B) occurs in water, one worm fertilizes another
C) occurs inside the body, one worm fertilizes another
D) occurs inside the body, the worm fertilizes himself
4g. What type of animals, the scheme of the nervous system of which are shown in the figure?
A) flat worms
B) arthropod
C) shepherds
D) chordovye
5g. The nervous system in flat worms consists of
A) Occonditioning nervous ring and abdominal nervous chain
B) two head nodes and nerve trunks with branches
C) Occollectric nerve rings and nerves derived from him
D) nervous cells forming a nervous network
6g. Are there any judgments about flat worms?
1. The excretory system in flat worms is absent.
2. The nervous system is represented by stard cells connected with each other.
A) right only 1
B) right only 2
C) orders both judgments
D) both judgments are incorrect
7g. With which organs, a free living worm white planearia is exempt from harmful metabolic products dissolved in water?
A) mouth and pharynx
B) skin and muscles
C) excretory channels
D) intestines and anal hole


