Calculation of the needs of drinking water. Water expenses at industrial enterprises
Industrial enterprises are large consumers of water. Water is used for industrial, economic and drinking and fire aims. The largest manufacturing consumers are metallurgical and oil refineries, heat-power plants station (TPP) using water for cooling, enterprises of the pulp and paper and mining industry, where a significant amount of water is used to flush raw materials and producing products. These costs reach 80 ... 90% of the total water consumption of the enterprise.
Water is also used to obtain steam and its condensation, hydrotransport (removal of ash and slag from furnaces), dust collecting and for other industrial purposes.
Depending on the purpose of water in the production of water, various requirements are presented. For example, water used in thermal power engineering (TPP) should have minimal pickling, water for the textile industry should not contain iron and manganese, for the food industry and economic and drinking needs of workers water must meet the requirements of GOST "drinking water" and Sanpin. For fire extinguishing, water is suitable for almost any quality.
Huge volumes of water consumption in industry require special attention to their savings and rational issues. One of the most important factors to reduce water consumption is the introduction of fees for water resources And limited vacation of water to industrial enterprises.
For revolving water supply systems of industrial enterprises
it is necessary to maximize the costs of recycled water, and the costs of fresh water closed from the source to minimize.
Determination of water costs for production needs
Water consumption for industrial needs of enterprises is determined based on the standards of water consumption or specific water consumption per unit of products.
Daily consumption of water is determined, m 3 / day:
where N.- the amount of products produced per day;
q Udo - Water consumption rate per unit of products, m 3.
The norms of water consumption or water consumption per unit of products are determined:
● the nature of production, the composition of the raw materials and the product obtained;
● the role of water in the production process;
● water supply system;
● quality of water used;
● Water use conditions (heating temperature, degree of contamination).
For various enterprises, water costs per unit of products change widely, q Udo , m 3 / t:
● coal industry enterprises - 3 ... 5;
● Metallurgical plants - 150 ... 200;
● non-ferrous metallurgy enterprises - 30 ... 40;
● Oil refineries - 100 ... 120;
● Plastics production - 200 ... 250;
● Synthetic rubber plants - 600 ... 1000;
● Light industry enterprises - 40 ... 80;
● Cellulosic and paper industry enterprises - 500..800;
● Food industry enterprises - 10 ... 20.
Significant water costs are characteristic of both thermal power plants (TPPs) that produce about 80% of all electricity consumed in the Russian Federation.
| Power, thousand kW | |||||
| Water consumption, m 3 / h |
With those large expenses Water on TPPs is usually applied water supply system With freshest water from a source within 3 ... 5% of the total daily water consumption.
In addition to these costs of water consumption for individual enterprises, there are its departmental norms for individual production cycles, operations and types of equipment used, which are given in the appropriate literature. For example, in the enterprises of railway transport, "norms of water consumption and drainage in the technological processes of the industry", it is 016-01124328-2000, defining both the specific costs and the quality of water quality.
Water consumption mode. Water spending mode in industrial enterprises mainly depends from the features of the technological process And maybe: uniform during the day, uneven or episodic.
In many cases, the uneven water consumption is caused seasonal changes in water consumption. Seasonal changes in water consumption are recommended to consider with coefficients K yearsand K winters.
Using large number Water for cooling water consumption in summer will be larger in winter - less, because In winter, the cooling water temperature is lower. Former, for metallurgical plants K years = 1,15; K winter= 0,9.
The irregularity of water consumption is also characterized by the coefficients of daily K Sut.and clockwise K C. unevenness. On the the coefficients of daily unevenness The seasonality of production and water quality affect K Sut.= 1,1…1,3, optional coefficients are the result of the replacement of production and unevenness of production of shifts, K C.= 2,0…3,5.
Determination of water costs during water and
Evaporating cooling
Water expenses on cooling They are significant, but for many enterprises, the determining part of water consumption for industrial needs, reaching 90-95% of it.
When cooled an aggregate having a heat load A (kcal / h), water consumption Q in, (m 3 / h) required for the discharge of highlighting heat at the temperature of the outgoing heated water t 1.and incoming cold t 2.depends on dependence:
![]() , (12)
, (12)
where from - Water heat capacity, kcal / hail kg.
Water consumption increases with increasing thermal load A. and reducing the temperature difference Δt..
For increase Δt.need to increase t 1. Or decrease t 2. Value t 2. Depends on the temperature of the water in the source or on the cooler (pool, cooling turret). In summer, cooling conditions are worse, it means again. Value t 1. Depends on the design of the cooling system and the conditions of the technological process. For water cooling systems, the temperature of the outgoing heated water is usually within t 1. ≤ 40 ... 50 0 S.
With a significant content of stiffness salts and heating to 40 ... 50 o C and more abundant scale of scale. This limits the water heating limit. Given the relationship Δt.and Q B. For different objects, you can define economically the highest temperatures. t 1. and t 2. Considering the above, with optimal design and operation of cooling systems, it is possible to improve the efficiency of industrial enterprises.
3.3. Determination of water costs on economic and drinking and fire prevention needs of industrial enterprises
Drinking water expenses. General expenses of economic and drinking water at industrial enterprises can be determined by the consolidated norms of water consumption and quantity wastewater per unit of products for various industries. To calculate the system of economic and drinking water supply of an enterprise, it is necessary to know the cost of water in separate administrative, economic and household and production buildings. In this case, expenses are determined in accordance with SNiP.
Water expenses for economic and drinking needs of workers for workshops with significant heat generation (more than 80 kJ per 1 m 3 / h) take 45 L. for the rest of the workshops - 25 L. for each workflow in shift, while the clock non-uniformity coefficient is taken respectively By hour\u003d 2.5 and 3.
The water consumption in the shower is determined at the rate of 500 l / h per shower grid for 45 minutes after the end of the shift. The number of shower grids in the company's workshops depends on the nature of production.
In the workshops, in which there is no pollution of clothing and hands of the workers 1 Shower mesh (1 D.S.) is envisaged on 15 people if production processes lead to pollution and hands - 1 D.S. for 7 people, for strongly dusty workshops, where water is applied - 1 D.S. for 5 people and for workshops with allocating particular pollutants - 1 D.S. on the 3 persons .
Basic change is insignificant, but at the end of the shift it increases. Therefore, to reduce the diameters of the supply pipelines and reduce the costs taken from the urban network on the territory of the enterprise, spare tanks are arranged, which are gradually replenished during the shift and empty at the maximum water intake.
Water expenses for landscaping Industrial enterprises are: on the irrigation of advanced coatings of space 1.2 ... 1.5 l / m 2, travel - 0.3 ... 0.4 l / m 2; Polishing of flower beds and lawns - 4 ... 6 l / m 2. Moreover, for these purposes, water from industrial water supply networks is allowed if its quality corresponds to sanitary and agrotechnical requirements.
Water consumption for fire fighting. In industrial enterprises, the fire fighting water pipe is usually designed by combined with industrial or economic and drinking.
The number of simultaneous fires and water consumption is accepted according to SNiP. Estimated fire time at the enterprise accepted 3 hours . Water expenses on the watering of the streets, souls wash the floors and the equipment washing should not be taken into account.
On average, fire-fighting costs of water at an industrial enterprise are 3 ... 7% of the total water consumption. Including the prophylactic wood waters in warehouses, wetting peat, irrigation of tanks for storing flammable liquids (oil, kerosene, diesel fuel, etc.).
However, the limiting factor is, as a rule, not water costs, but water pressure because Most fireproof water pipes in enterprises are designed high pressure . This is one of the reasons for the combining of fireproof water supply with economic and drinking, and not industrial, since for production purposes usually the pressure is usually 20…40 m.
To preserve the necessary firefare stock of water in enterprises, special containers are arranged (tanks).
3.4. Water balance of industrial enterprise
When designing water supply systems of an industrial enterprise is drawn up water balance which indicates the cost of water for all categories of consumers, as well as water loss. Water consumers are usually grouped at their location, heads and quality of water. Then the water use scheme is compiled, i.e. Expenditures entering consumers, water loss by consumers and expenses drawn from them (designated).
Water balance An industrial enterprise is required when designing and calculating water supply facilities (pumping stations, water pipes, sewage facilities, cooling devices, etc.).
In the process of exploitation of the industrial enterprise, the water balance has an impact on the enterprise economy and the real cost of products.
The basic principles of water balance of an industrial enterprise:
1. The amount of water in the industrial water supply system is maintained constant, while water loss in the system is reimbursed by water from the source.
2. Install the sources of water intake into the system.
3. The quantitative characteristics of each source are determined.
4. Determine consumer groups requiring water of one
quality.
5. To reduce the number of fresh water taken from the source, the possibility of sequential use of waste water of one group of consumers for water supply to another group is detected.
In general, sources of receipt and decrease of water from the water supply system of the enterprise are shown in Table. 3.1.
To comply with the water balance, a condition is necessary:
ΣQ post \u003d ΣQ UB, (13)
where ΣQ post - the amount of water costs enrolled in the water supply system,
ΣQ UB - The sum of water costs decreasing from the water supply system.
In addition to the water balance of water supply systems, the maintenance of water balance is important in quality, thermal stability, cyaogenic waters, etc.
The main types of water consumption are: Economic and drinking water consumption of residents of settlements; water-consumption of industrial enterprises; Water consumption related to the improvement of territories (watering streets, green plantings, etc.); use of water for fire extinguishing; Own needs of the water supply system.
Economic and drinking water consumption.The norms of drinking water consumption in settlements are accepted by SNiP 2.04.02 - 84 (Table 1.1).
For the development areas of buildings with water use from watershed columns, the specific temperature (per year) water consumption for one inhabitant should be taken 30 ... 50 l / day.
Specific water consumption includes water costs on economic and drinking and domestic needs in public buildings, for excluding water expenditures for holiday homes, sanatorium and tourist complexes and recreation camps.
Select specific water consumption within the limits specified in Table. 1.1, must be carried out depending on the climatic conditions, the power of the water supply and water quality, the degree of improvement, the storeinities of the development and local conditions.
The amount of water for the needs of the industry, providing the population of products, and unaccounted costs with the appropriate substantiation is allowed to be taken in addition in the amount of 10 ... 20% of the total water consumption for the economic and drinking needs of the settlement.
Specific water consumption in settlements with the number of residents over 1 million people is allowed to increase when substantiating in each individual case and coordination with state supervisory authorities.
Average daily (per year) volume of water consumption, m 3 / day, on economic and drinking needs are determined by the formula
where q z1 is the norm of specific water consumption, l / (day of course) corresponding to i.-y.the degree of sanitary and technical improvement of residential buildings and the table received. 1.1; N. I. - The estimated number of residents living in residential areas with the I-th degree of improvement, at the end of the construction queue under consideration.
The calculated number of residents can be determined by the formula
where r J. - j-I population density, people; F.iJ., - The area of \u200b\u200bthe residential building area with the I-th degree of sanitary and technical improvement of buildings and the j-th population density, ha.
To correctly calculate water systems, it is necessary to know the sequence of their development and the water consumption corresponding to these sections. The growth of water consumption during the development period is due to an increase in population and increase the degree of sanitary and technical improvement of buildings. Accounting for water consumption growth is carried out by determining the calculated water consumption at the end of the corresponding development queue.
Water consumption on the economic and drinking needs of the settlement is uneven during the year. There are fluctuations in daily flow: seasonal, associated with a change in temperature and humidity in certain seasons, butalso weekly and daily, due to the features of water consumption on various days of the week (weekdays, weekends, pre-holiday and holidays). Water supply systems should be designed to skip the maximum daily water flow, M 3 / day equal
where ksut Max = 1.1 ... 1.3 - the maximum rate of daily unevenness of water consumption, taking into account the lifestyle of the population, the mode of operation of enterprises, the degree of improvement of buildings, change in water consumption for the season of the year and the days of the week, is the estimated (average per year) of water flow rate, M 3 / SUT, defined by formula (1.1).
In some cases, the operation of the water supply system is required at minimum daily water flow, M 3 / day, determined by the formula
where TOsut.mIN.\u003d 0.7 ... 0.9 The minimum coefficient of daily irregularity of water consumption.
Water consumption of industrial enterprises.In industrial enterprises (including agricultural enterprises), water is spent on the technological needs of production, economic and drinking needs of working, as well as on the use of the shower.
The norms of water consumption on technological needs depend on the adopted technological process, the type of water supply system, water quality, etc.
The average volumes of water consumption are determined by the type of water used (revolving, capital) by multiplying the corresponding specific costs of its performance on the performance of the technological process in the adopted units of values \u200b\u200b(1 ton, 1000 kW, etc.).
In accordance with SNiP 2.04.01-85, the requirements of the water consumption for economic and drinking needs of employees of industrial enterprises are taken equal to operating in workshops with a heat generation of more than 84 kJ per 1 m 3 / h (hot cages) q.r. = 45 l in shift per person; For other shops q. H. = \u003d 25 liters.
The volume of water consumption in shift, m 3 / cm is determined by the formula
QX / N. = q. R.n.r. + q. X.n. X., (1.5)
where pr., P H. - The number of more than 84 kJ per 1 m 3 / h, respectively, on 1 m 3 / h and in the rest of the shifts under consideration.
Water consumption for the use of the shower is determined based on the time consumption of water
 on one shower grid 500 l with the duration of use of the shower of 45 minutes. At the same time, water consumption for the adoption of the shower after the end of the shift, m 3 / h is determined by the formula
on one shower grid 500 l with the duration of use of the shower of 45 minutes. At the same time, water consumption for the adoption of the shower after the end of the shift, m 3 / h is determined by the formula
where N. shower- the number of shower in this shift; but -the number of people per shower grid.
Water consumption associated with the improvement of the territories of cities and industrial sites.The norms of water consumption on the polishing of green spaces, as well as washing streets of settlements and territories of industrial enterprises adoption on SNiP 2.04.02--84, depending on the type of territory coverage, the method of its watering, the type of plantings, climatic and other local conditions (Table 1.2) .
The daily volume of water consumption, m 3 / day, on the watering of streets and green spaces is determined by the formula
where quill is the water flow on the watering, L / m 2, received by table. 1.2; F. - Square of the territory of the Grutto settlement (including streets, squares, etc.), ha; A - the proportion of the territory of the settlement,%.
In the absence of data on areas by type of improvement (green plantings, passages, etc.), the average daily watering season water consumption on watering, m 3 / day can be determined by the formula
where q.well p - The specific rate of water consumption on the watering in the calculation per resident of the settlement, taken equal to 50 .. 90l / day per person, depending on the climatic conditions, power, source of water supply, degree of improvement of the settlement and other local conditions; N -the estimated number of residents in the village.
Total daily water consumptiondetermine by individual groups of consumers supplied with water calculated water supply system.
For a single water supply system serving all of the listed consumer groups, determine: the average daily water consumption, m 3 / day,
maximum daily water consumption, m 3 day,
In formulas (1.9) and (1.10) QTEFT Water consumption on the technological needs of industrial enterprises.
Water supply systems are calculated on the maximum daily water consumption and check for skipping the estimated fire consumption.
Use water for fire extinguishing.In accordance with SNiP 2.04.02-84, water consumption for outdoor fire extinguishing (per fire) and the number of simultaneous fires in the village for calculating the main (calculated ring) lines of the plumbing network should be taken in Table. 1.3.
With zone water supply, water consumption for outdoor fire extinguishing and the number of simultaneous fires in each zone should be taken depending on the number of residents living in the zone.
The number of simultaneous fires and water consumption per fire in settlements with the number of residents more than 1 million. Man should be taken according to the requirements of the state fire supervision bodies.
For a group water supply, the number of simultaneous fires is taken depending on the total number of residents in settlements connected to the water supply.
Water consumption for outdoor fire extinguishing housing and production buildings for calculating the connecting and distributed lines of the plumbing network, as well as a water supply network inside the neighborhood or quarter, should be taken for a building that requires the greatest water consumption in Table. 1.4.
Water consumption per fire for outdoor fire extinguishing on industrial and agricultural enterprises should be taken for a building that requires the greatest water consumption according to Table. 1.5 and 1.6. The calculated amount of fires depends on the area they occupy: one fire - with an area of \u200b\u200bup to 150 hectares, two fires - more than 150 hectares.



The estimated duration of fire extinguishing 3 hours; For buildings of I and II degree of fire resistance with non-aggravated supporting structures and insulation with the production of categories G and d - 2 h.
The definition of the total fire consumption of water in the settlement is carried out depending on the location of industrial or agricultural enterprises.
Table 1.6 The norms of water consumption on the outdoor fire extinguishing of production buildings 60 m wide and more

If the enterprise is located within the city, in the estimated number of simultaneous fires (Table 1.3) included fires of this enterprise. At the same time, the estimated water consumption should be included in the estimated water consumption in these enterprises, if they are more specified in Table. 1.3.
At the location of the enterprise outside the settlement, the estimated number of simultaneous fires should be taken:
with the area of \u200b\u200bthe enterprise to 150 hectares and the number of residents in the village of up to 10 thousand people - one fire (at the enterprise or in the settlement of the greatest water consumption); The same, with the number of residents in the settlement of over 10 to 25 thousand people - two fires (one at the enterprise and one in the village);
with the area of \u200b\u200bthe territory over 150 hectares and with the number of residents in the settlement of up to 25 thousand people - two fires (two in the enterprise or two in the settlement of the highest consumption).
for the number of residents in the settlement of more than 25 thousand people, water consumption should be determined as the amount of demanding more consumption (at the enterprise or in the village) and 50% of the required smaller consumption (at the enterprise or in the village).
In all cases, water consumption for outdoor fire extinguishing in the village should be at least water consumption for fire extinguishing residential and public buildings specified in Table. 1.4.
Own needs of the water supply system.The water supply system should be considered as an industrial enterprise that consumes water to the household needs of employees, in technological processes and for fire extinguishing. The largest consumer of water used on its own needs in the water supply system is the treatment facilities.
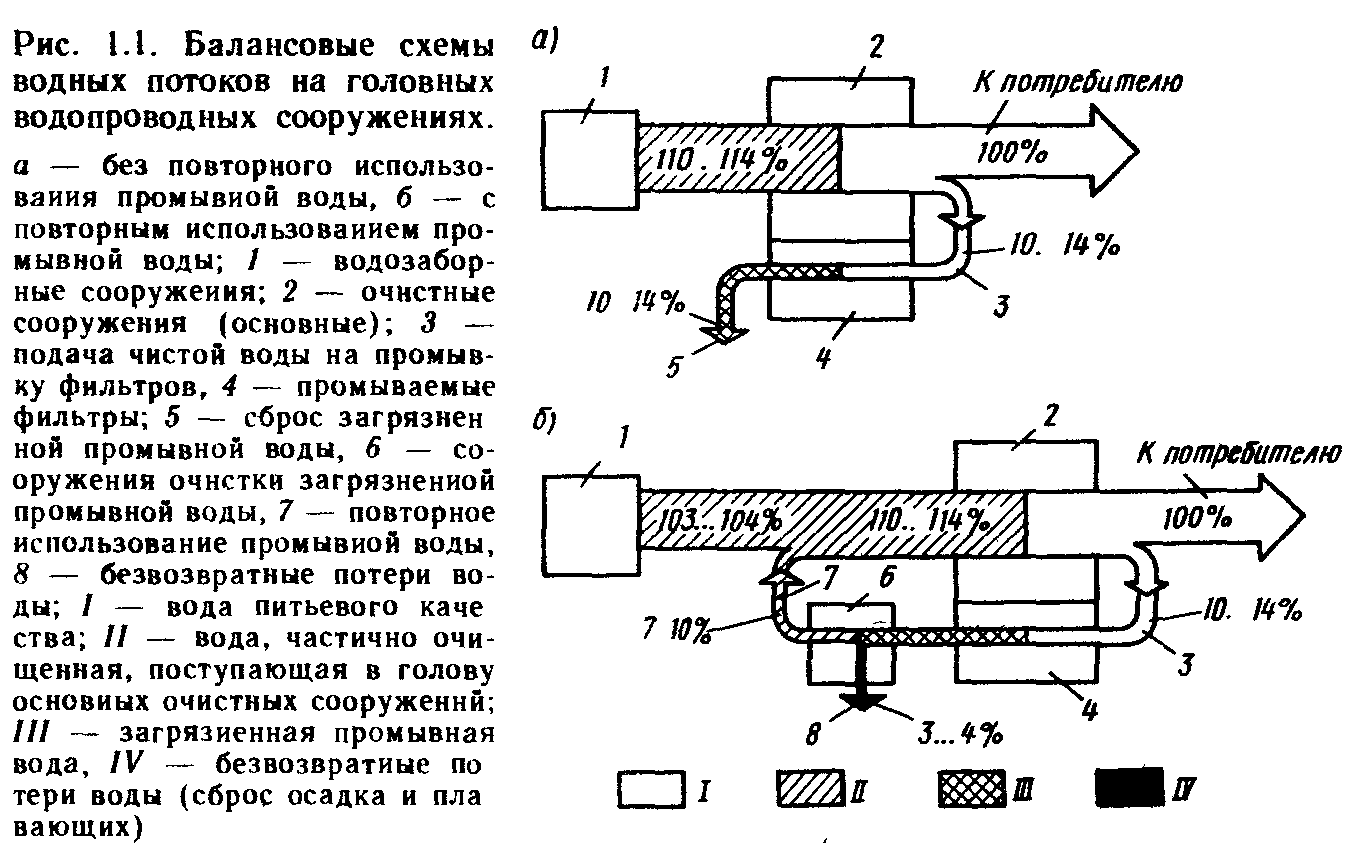
In accordance with SNIP 2.04.02-84, approximately average daily (per year) Water expenses on the own needs of clarification stations and disinfection should be taken: when reuseing wash water in the amount of 3 ... 4% of the amount of water supplied to consumers; without reuse - 10 ... 14%, for softening stations - 20 ... 30%;
The volume of water consumption on the own needs of the water supply system affects the calculated productivity, M 3 / day, water intake and treatment facilities (Fig. 1.1)
where
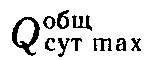 - maximum daily water consumption, M / day; α - coefficient, taking into account its own needs of sewage facilities; For water intake structures, and we accept equal to 1.03 ... 1.04 with reuse of water and 1.1 ... 1.14 without reuse at the station of clarification and dearness, at 1.2 ... 1.3 softening stations; For wastewater treatment plants, both when the water is reused and without it, 1.10 ... 1.14 at softening and deferrization stations and 1.2 ... 1.3 at softening stations.
- maximum daily water consumption, M / day; α - coefficient, taking into account its own needs of sewage facilities; For water intake structures, and we accept equal to 1.03 ... 1.04 with reuse of water and 1.1 ... 1.14 without reuse at the station of clarification and dearness, at 1.2 ... 1.3 softening stations; For wastewater treatment plants, both when the water is reused and without it, 1.10 ... 1.14 at softening and deferrization stations and 1.2 ... 1.3 at softening stations.
The parameters of the elements of the water supply system are in accordance with the amount of water supplied and with a mode of operation scheduled for them. To determine the total volumes of water used, the most comprehensive account of all types of consumers is required. The latter include: population of cities, towns, etc., consuming water to meet economic drinking needs; industrial enterprises using water in technological processes and sanitary and hygienic, drinking and economic needs; Fire extinguishing service using episodically, the supply of which should always be provided; Housing and communal enterprises that consume water to wash the streets, squares, etc., and also on the watering of green plantings. There are other consumers using water in smaller quantities compared to those specified. Requirements for water by various consumers regarding quality and quantity are extremely diverse. At the design stage, water expenses are determined on the basis of the rules obtained by processing statistical data on actual consumption or technological calculation.
Water consumption for economic and drinking needs of the population in the object as a whole depends on a number of factors. Knowing the flow per 1 person / day, which is called specific economic and drinking water consumption, you can determine the daily water consumption. It will be the greater the larger the number of residents in the village.
Specific water consumption takes into account the amount of water consumed 1 person. For economic and drinking needs not only at home, but also in public buildings. It depends on the degree of improvement of residential buildings. Obviously, with more comfortable conditions, the specific water consumption is higher. The climatic conditions are influenced by its magnitude to its magnitude: in areas with a hot climate of water, more is consumed than in cold areas. It also affects local conditions, water quality, building strokes. It is possible to determine the specific water consumption by analyzing the actual data on water spending in existing water supply systems. When designing water supply systems of settlements, the specific daily diquses (per year) water supply per resident is determined by SNiP 2.04.02-84 "Water supply. External networks and facilities »
For areas where water use is provided from watershed columns, the specific average water use by one inhabitant is taken equal to 30-50 l / day. The amount of water CL needs of the local industry serving the population of products, and unrecorded costs are allowed to be taken in the amount of 10-20% of the total water consumption for economic and drinking needs of the settlement. In the event that in the city the number of residents of more than 1 million people, the specific water supply is allowed to increase, but for this requires coordination with the state supervision authorities. Choosing a water consumption rate, it is necessary to provide measures to reduce leaks in the system and the irrational consumption of water in buildings. These include the organization of the zoning system, improving its operation, pressure regulation, etc.
Water consumption for industrial and household needs of industrial enterprises. Water expenses for technological needs depend on the type of production adopted by the technological process, the type of water supply system
water quality, etc. Water costs for production needs are determined by the specifications of water intake per unit of products. These norms are set on the basis of technological calculations by employees of a field of industry. They are appointed from the condition of applying the most progressive technologies providing for low-water processes, a device for revolving and closed water supply systems. In accordance with the existing standards, water consumption for economic and drinking needs of workers during their work is taken into account in addition to the economic and drinking costs, which were considered above. They depend both on the number of working and the type of production. Their values \u200b\u200bare determined in accordance with SNiP 2.04.01-85 "Internal water supply and sewage system". In addition, in production requiring a certain mode, water is spent on the reception of the shower.
Water consumption on watering and washing of streets and squares, as well as on the irrigation of green plantings depends on the size of the area of \u200b\u200bthe area, the method of watering, such as coatings IT. P. In SNIP 2.04.02-84, the following specific velocities of water consumption, L / m2, per wash or one irrigation are provided:
mechanized washing of improved coatings
trucks and squares
mechanized watering of advanced coatings of travel and squares
manual watering (hoses) improved
coatings of sidewalks and travel
polyberry of urban green plantings ...., »Polyvilny lawns and flower beds ,. .
In the absence of data on areas by type of improvement, the specific daily water consumption of water is taken equal to 50-90 l / day per inhabitant. When prescribing the norm, the climatic conditions, the power of the water supply source, the degree of improvement of settlements and other local conditions are taken into account.
Water consumption for fire extinguishing depends on the nature of the development of fire and the conditions of water supply to the bargaining center. The higher the fire danger of the object, the more water is required to extinguish the fire. Submitting a significant amount of water into the fire center, it is possible to eliminate it for a short period of time. However, for the construction of water pipelines, calculated on the passage of a large amount of water, significant material products are needed. Therefore, water consumption for fire extinguish is prescribed depending on the fire hazard of the object and its significance. Water expenditures to extinguish the fire are given in regulatory documents (SNiP 2.04.02-84). They are compiled based on the processing of statistical data on actual water flow rates, taking into account the creation of the required conditions for extinguishing fires at various facilities. Water consumption for extinguishing fires in settlements depends on the population and development nature (1.2).
The duration of the fire extinguishing in most cases is taken equal to 3 hours. Water consumption for external fire extinguishing in production buildings with lanterns and buildings up to 60 m wide without lights depends on the volume of the building, the degree of fire resistance of its building structures, and the category of fire
the dangers of production placed in the building (1.3).
Water consumption rate for external fire extinguishing in production buildings 60 m wide without lanterns and more than more different (1.4).
The number of simultaneous fires at an industrial enterprise is determined depending on the area occupied by them. At an area of \u200b\u200ban enterprise to 150 hectares, it is assumed to occur in the possibility of a single fire and two fires - with a larger area. For large industrial enterprises (for example, refineries and chemical combines), independent water supply systems are created that are not related to urban water supply systems. Water consumption for external extinguishing fires in such cases is determined in accordance with fire-fighting technical conditions for construction design (Pt PSUP). Film water pipelines of these enterprises are usually calculated based on the condition of supplying water into fire trucks, water supply with fire hydrants and beams, as well as extinguishing fires inside buildings with the help of internal fire cranes and stationary water or foaming systems.
Norms of water consumption. Determination of the need for water. The norm of water consumption is called the amount of water spent on certain needs per unit of time or per unit produced products.
The average (per year) daily water consumption by each consumer group is determined by the average periods given in the relevant chapters SNiP 2.04.02 - 96 "Water supply. External networks and facilities. "
For example, the average daily rate of consumption per resident in settlements depending on the improvement of residential buildings in the presence of sewage is as follows: no baths 125 ... 160 l; with baths and local water heaters 160 ... 230 l; With centralized hot water supply 250 ... 350 liters.
The lower limits of the norms belong to the northern regions, the top - to the southern one.
Also the costs of water on watering streets and sidewalks, green plantings, lawns and flower beds, greenhouses and greenhouses are normalized.
Water consumption standards animals depends on the conditions of the content and equipment of livestock facilities. For example, the average daily water consumption rates of animals, in liters per day: milk cows 100; Cows meat 70; Young cattle up to 2 years 30; Horses adults 80; Sheep adults 10; Pigs adults 25; Birds 1 ... 2.
Water consumption rates by machines depend on their design and power. For example, 400 ... 500 liters of water, a tractor 300 ... 600 liters, etc., is required to wash the car.
Water consumption for industrial needs is determined on the basis of technological data. Thus, when recycling 1 ton of raw materials is necessary at the dairy plants 10 ... 15 m 3 of water, on canned - 10 ... 15 m 3, on the cheered - 35 ... 40 m 3, etc.
In addition to the regular support of economic and drinking needs, the water supply system should provide water extinguishing fires. The norm for exterior fire exterior is used depending on the number of residents according to SNiP. For example, with the number of residents up to 1000 people - 5 l / s, from 1000 to 25,000 people - 10 l / s, etc. The calculated number of simultaneous fires is also established depending on the number of residents: up to 10 thousand people - 1 fire, from 10 to 100 thousand - 2 fires.
Water consumption for internal fire extinguishing usually does not exceed 2.5 l / s. The estimated duration of the fire is three hours.
Having established the number of each group of water consumers and the average daily water consumption rates of each of them, determine the average daily costs of water M 3 / day:
![]() .
.
Water consumption mode. Water consumption by the population is uneven during the year. So, in the summer it is spent more than in winter, in prehending days more than the other days of the week. The ratio of the daily flow rate in the days of the greatest water consumption to the average daily flow rate is called the coefficient of daily unevenness of water consumption:
 .
.
The value depends on the degree of improvement of buildings. With an increase in the degree of improvement, the coefficient decreases. So, for example, when consuming water from columns ![]() , with convenience
, with convenience ![]() .
.
In industrial enterprises, the coefficient is taken equal to one, i.e. It is believed that water consumption is evenly during the year.
During the day, water consumption is also uneven: at night it is less than the day. The fluctuation of water consumption by hours of day depends on the estimated number of residents. The smaller the population, the themes of this unevenness. Water consumption changes and within an hour. However, to simplify the calculations, it is conventionally believed that during the hour, water consumption remains unchanged.
The ratio of the hourly expense in the watches of the largest (maximum) water consumption q max The average hourly consumption is called the clocking coefficient of water consumption:

For populated areas ![]() Depending on the rate of water consumption. For industrial enterprises
Depending on the rate of water consumption. For industrial enterprises ![]() .
.
Water consumption mode, i.e. Changing water spending by hours of day, it is customary to submit in the form of tables or graphs. Water consumption graphics are stepped and integral.
The water supply should be calculated so that the throughput of its structures is sufficient during the entire estimated period of its action. For the calculated, the expense of the maximum water intake hours with the highest water consumption takes.
The estimated consumption of economic and drinking water supply in the settlement is determined by the formula
![]() ,
,
where q is the rate of water consumption, l / day; n - the calculated number of residents.
The estimated water consumption for production needs is accepted according to technologists.
Free head. The pressure in the outer water supply network should provide water supply with some reserve (residual pressure) to the highest and most remote water-removable water treatment point inside the building (dictating point). This head is called free n or necessary:
H SV \u003d H + ΣH + H 0,
where n g is the geometric height of water supply from the surface of the Earth to the highest water treatment point, m; Σh- pressure loss in the internal network, in water and water meter, m; h 0 - residual pressure at the dictational point, m;
H g \u003d H pl + (n - 1) h et + h pr,
where H pl - excess of the floor of the first floor above the surface of the Earth; n is the number of floors in the building; h et - the height of the building floor; H PR - height located dictating device above the floor, m.
Free pressure in the outer water supply network of settlements under preliminary calculations is assigned from the flood of buildings: with one-story development - 10m; With a two-storey building - 12m.


