Who for the first time a secondary body cavity appeared. Primary body cavity is
Why is it interesting?
In the school year of zoology, the issue of body cavities in invertebrates is "difficult" and "incomprehensible" according to the reviews of both students and many teachers. In training manuals on zoology for high school, the material is set forth in the "systematic" order, and for each group of animals, the body cavity is usually described in one phrase: "There is no body cavity", "there is a primary body cavity", "there is a secondary body cavity (whole)" , "Body cavity is mixed." The content of the concepts of the "body cavity", "whole" and other associated with them are not disclosed. The morphological nature of the primary, secondary and "mixed" body cavity, the functional connection of the body cavity with other bodies is not discussed.
The question of the schoolchild "Why am I should know this at all?" natural and justified.
When transferring information in the chain "Scientific publications-manual-textbooks for universities-textbooks for school" the volume of facts is inevitably reduced. If any information remained even in the "science filings", of which the average school textbook is likely to be of great importance for scientists. For example, the problem of the morphological nature of the body cavity in animals from different taxa, its formation in ontogenesis and phylogenesis is actively discussed in the "scientific" zoology over the course of two centuries and is still of great interest. Why? The body cavity is anatomically and functionally connected with blood, excretory, respiratory systems. Understanding these ties allows to comprehend many patterns of the structure and physiology of animals. From what ideas about the emergence of the agencies and evolution in philogenesis we will add, the choice of one of possible options Reconstruction of the phylogenetic tree of animals.
What is body cavity?
Body cavity They call the space in the body of the animal between the body wall and the intestines, not filled with cells.
The body cavity is a closed space, communicated with the external medium only through the pores of the excretory and sexual systems. The body cavity can occupy a significant amount (for example, in multi-pectic and unauthorized ringed worms), and can be represented by very narrow slightly gaps between the organs (for example, in small round worms). It is filled with a strip fluid, which is one of the components of the inner environment of the body and washes internal organs located in the body cavity. In the curb fluid, cells involved in gas exchange, isolation, immune reactions, etc. can be located, but they do not form dense tissue and swim freely in the strip fluid.
Some typical errors Pupils:
- « In the intestinal body has a body cavity - this is an intestinal cavity».
- the cavity of the digestive tract is not considered an internal cavity of the body. It communicates with the external medium through the oral hole (and through the anal hole in those animals that it has).
The space between the intestine and the body wall (where the body cavity could be located) in the stringing is filled with a sufficiently dense extracellular substance - mesoglya, and there is no body cavity.
- « Flat worms body cavity is filled with parenchyma cells».
If the space between the organs is filled with cells is not an cavity.
What is the difference between the primary body cavity from the secondary (organizer)?
Secondary body cavity (Overall, nominal cavity)has its own wall of mesodermal cells. This is a "cavity in mesoderm." It is surrounded by a nuclear epithelium ( siftlee), which swears on one side the muscles of the body wall, and on the other hand covers the internal organs. Cells of a nuclear epithelium are arranged in one layer. Their basal (facing the wall of the body or intestines) surfaces are isolated by a layer of extracellular matrix - basal plate* The apical surfaces of the cells of the nodium epithelium are drawn as a whole and often march. Thus, from the tissues of the body wall of the cell of the nominal epithelium are separated by a basal plate, and from the nuclei cavity is not separated by anything, besides its plasma membrane.
Primary body cavity
(In English-language manuals, it is commonly called pseudocel)does not have its own continuous wall of mesodermal cells. All cells bordering the primary cavity are separated from it with basal plates. Four options for organizing a body cavity in multicellular animals, a scheme (left to right): "Acelomic" animals, "primary"; "nominal"; Arthropod (body cavity - hematocula). In primary and fragrant cloths are separated from the body cavity to the basal plate (designated by points), the body's oxytic animals are not seduced by a basal plate. Red marked intestine, Blue - Etoderma, dark green - Mesoderma, light gray - the primary body cavity, dark gray - hematcell, light green - whole, brown - Cuticula.
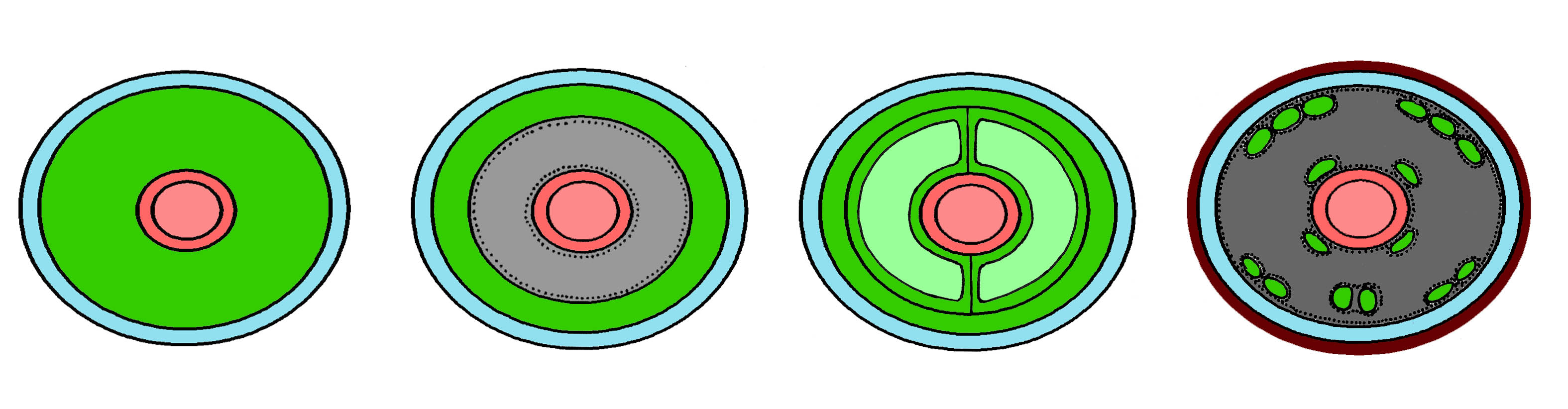
* basal plate - a layer of extracellular matrix, isolated by cells of epithelial, nervous muscular tissues, separates them from connective tissues and body cavities. It consists of proteoglycans, glycoproteins and structural proteins (collagen), contains cell adhesion proteins. Functions: Structural (reference), filtration (in protonethylidial, metanephridial excretory system and in renal gloms), regulation of the transport of ions and small molecules through the epithelium, determination of the polarity of epithelial cells, participation in the processes of tissue regeneration, morphogenesis, cell migration.
Why body cavities are called "primary" and "secondary", can be understood by knowing how they are formed during the individual animal development.
Formation of body cavity in ontogenesis
At the stage of Blastuly, the inner cavity is formed - blastocel. During gastullation, two layers of cells (two germinal leaves) are formed from one layer of units of blastuly cells - ectoderma and entoderma. At the same time, two extracellular spaces are formed:
1) the cavity of the primary intestine (Archentheron) is not related to the body cavity;
2) blastocel turns into space between ectoderm and entodermy - this is the primary body cavity arising from the earliest stages of embryogenesis. In an adult animal, it will be between the wall of the intestine of the body of the body.
Later, in one way or another, Mesoderm cells are isolated from the Entoderma.
Animals, in which mesodermal cells fill the entire space between the intestines and the conclusions, called parenchimatous (Aceksomatom - "honest").
In other animals, Mesoderma has the beginning of a part of the internal organs and a layer of muscle cells, which are part of the body wall (the muscles of the skin-muscular bag), but the cavities in the mesoderm itself is not formed. These animals are customary called primary-moving.
W. oulticians Closed bubbles arise, the walls of which consist of mesodermal cells - this is the descent of the aim. The nominal bubbles grow, gradually displacing the primary cavity of the body and occupying her place. That is why the whole is called the secondary cavity of the body. The number and method of the formation of nominal bubbles differ in animals from different taxa.
Two ways to educate the organizer
1. Skizocel (TELLUSTIC)
In the nucleus in the primary body cavity, there are only two cells (mesodermal tallowes), each of which is divided and forms a group of cells. In such a cluster of mesodermal cells by their discrepancy (schisocetia), the cavity is formed. Such a method of bookmarking the agencies is observed in the ringed worms, mollusks. Even before the start of the scattering, the mass of mesodermal cells is divided into several paired groups lying on the sides of the intestine. Thus, in each larvae segment, its own pair of nominal bags is formed. In the rear portion of the body of the larvae there are two groups that are capable of dividing the cells, due to which the mesoderma is formed in the new segments (they appear in the growth zone during the metamorphosis, and often in an adult animal).
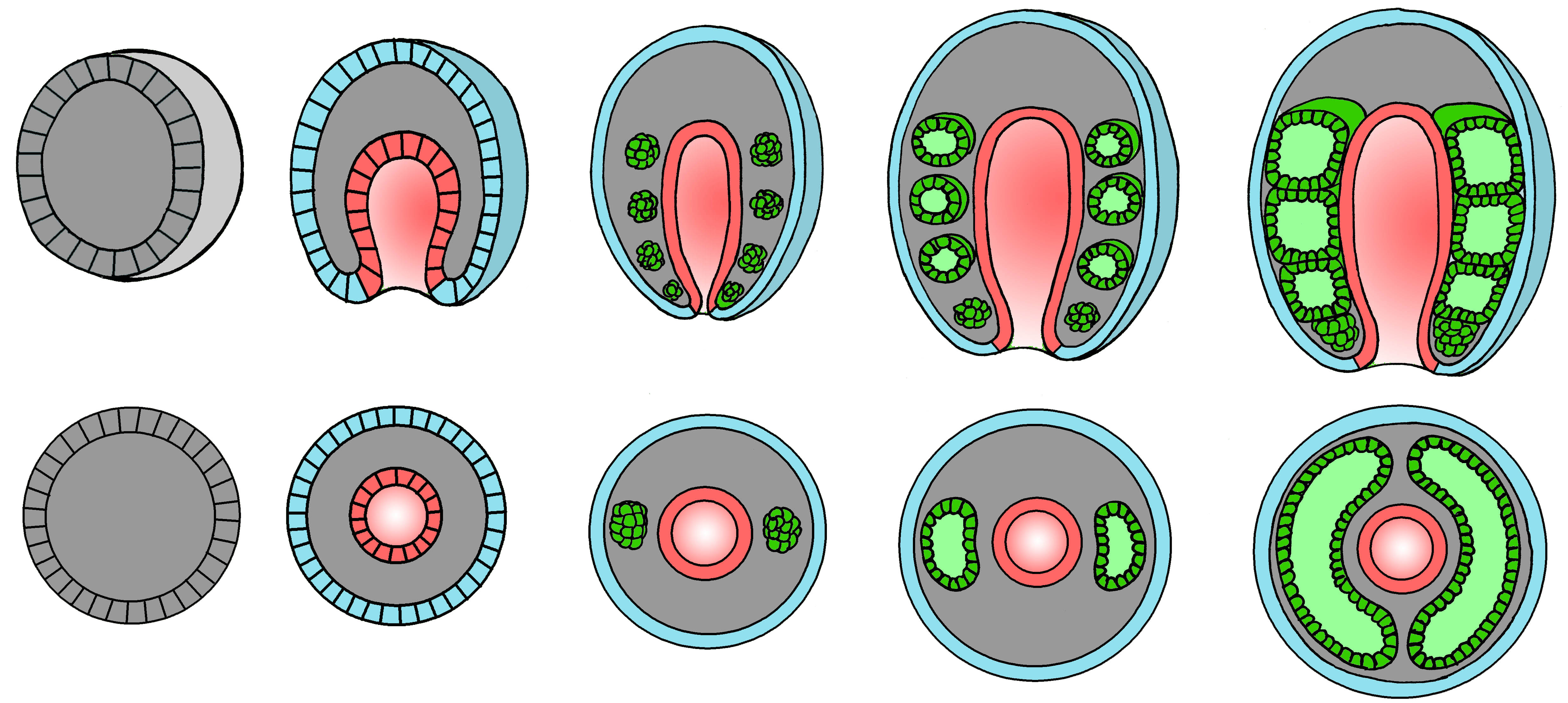 |
||
|
The formation of primary, and then the secondary (nominal) cavity in nullifying ringed worms. The whole "displaces" the primary body cavity. Top row - longitudinal (frontal) cuts of embryos and larvae, lower row - cross sections Red marked intestine, Blue - Ektoderma, dark green - Mesoderma, light gray - primary body cavity, light green - whole. Ektoderma cells and entoderms are drawn only to the gastraul stage. |
2. Enterocel
The nuclear bags are formed as the proportion of the intestine of the embryo. The protrusion is separated from the intestines and become closed nominal bubbles. It is so laid in oskulkin, chordovy.
Body communication with blood and excretory systems
The most clearly showing the attitude of the body cavity and the circulatory system can be used by the example of ringed worms. As the larvae develops, the nominal bags increase in size until they start contact with the body wall, with intestines and each other. The left and right nominal bags, racing, closed over and under the intestines - are formed longitudinal partitions in the body cavity (mesenteria). The contacting walls of neighboring pairs of delicate bags form transverse partitions (dissipions) between body segments. Increasing nominal bags almost completely displacing the primary body cavity. Only narrow spaces 1) remain between the nuclear epithelium and the mesoderma wall of the body, 2) between the nuclear epithelium and intestinal epithelium, 3) in the mesenters between the two layers of the target. All these intervals
("Remains" blastocel \u003d primary body cavity) become blood vessels. The walls of the vessels are formed by the overall and its basal plate. The extracellular substance in them is liquid and performs blood functions.In this way, only oxygen animals have a circulatory system, and by origin it is the residue of the primary body cavity.
The selection organs in the nominal animals, as a rule, there are metanephridia.
Metanephridium - Unbranched canal, begins in a whole funnel with cilia - nephrostom, and ends with excretory sometimes.
Methanefridia function in close connection with a circulatory system and the whole. The liquid released by them is formed as a result of ultrafiltration, selective reabsorption and active secretion.1)
First, ultrafiltration occurs - filtering at the molecules level. Blood plasma, being under pressure, filtered through the walls of blood vessels in general. In some parts of the wall of the blood vessels are formed by special cells - undercatics. There are gaps between the undercitues, where the vessel cavity is separated from the ancient only the packaging plate - it serves as a filter. Large molecules (for example, respiratory pigments) do not pass and remain in the blood, and water with dissolved small molecules and ions comes in general. Thus, the nominal fluid is the ultrafiltrate of blood - primary urine.2)
Due to the work of the ciliates of the funnel metanephridium, the scholarship fluid enters the metanephridium channel, which is thickly braided with blood capillaries. In the process of moving fluid on the channel between it and blood is met. Water, many ions, soluble carbohydrates, etc. Return to blood (selective reabsorption), and metabolic products (ammonia, urea and others) are concentrated in the metanephridium channel (including active secretion), and then outward.
In the metanephridial excretory system, the filtration barrier is located on the border between the blood system (primary cavity) and the secondary body cavity
. Next, in the channel metanephridium, there is no filter. Therefore, non-sacomic animals cannot be metanephria (it would be a through canal from the primary body cavity to the external environment, and blood with breathing pigments would be output).In primary or parenchymal animals, the selection authorities are protonphridia .
Protonfridium - This is a thin channel, walking deep into body cavity or a parenchyma, where he blindly ends terminal cell. This is a large cell with one or more long flagellas facing the cavity of the Canal ( the bundle of the oscillating flames under the microscope resembles a flickering flame of the candle, so the terminal cells of protonphridium are called "clinical flame cells"). There are gaps formed only between the terminal cell and the first cage of the tuba - it serves as a filter. The fluid from the primary body cavity (or tissue liquid in parenchymal animals) is filtered through these intervals to the cavity of the channel. The beating of the harness of the terminal cell creates a current of the fluid in the tubing, directed outside. Cells of the tubule can perform reabsorption or secretion of ions, due to which protonfritis can participate in osmoregulation. In parenchymal animals (for example, flat worms) Protonnefrial tubules are branched and form a complex network, draining the whole crowd of a parenchyma. Small tubules merge into large excretory ducts.
Functions of body cavity
TO functions Komotom You can attribute:
- 1 . Functional separation of body walls and digestive tract. Due to the presence of ancient, for example, the reduction of somatic muscles does not affect the operation of the digestive system.
- 2 . Formation hydrostatic skeleton and participation in movement Animal. The muscles of the skin-muscular bag, reducing, have pressure on the nominal fluid. Since it is incompressible (like any liquid), then under pressure, serves as a support for the muscles themselves and maintains the body shape of the worm, that is, plays the role of a hydrostatic skeleton. In some animals, movement is carried out by pumping a nuclear fluid (hydraulic locomotion). For example, at the reepulide when digging the soil, the liquid is first injected into the front body of the body ("trunk"), it is protruding and fixed in the ground with cuticular hooks, and then the animal is tightened forward. Ambulacral system of Ichalkinski also has a nuclear origin.
- 3 . The participation of the nuclear fluid in transport of nutrients, exchanging products, dissolved gases. The nominal fluid is in constant motion, which provides transport of substances - not only diffusion, but also convective. Overall performs a function gas exchange. A number of animals have nuclear gills or other body grows, which comes in a nuclear cavity. Through the thin wall of such growths there is gas exchange between the external environment (water) and a nominal liquid (starfish, msnok, brachiopods and others). In the nominal fluid, respiratory pigments may be (both dissolved in the nominal fluid and in cells).
- 4 . Overall takes part in osorgulatory, temporary accumulation and selection Metabolism products (see above).
- 5 . Sexual function. Gonads (sex glands) are a nuclear origin. Gamets are differentiated from the nominal mesoderm (target) and ripen in net. Hydrostatic skeleton, as well as related to the presence of a kommelation, the development of the transport (blood and the most soda) and excretory systems allows the delicious animals to achieve relatively large sizes.
Reduction Komatoma
The support function of the organizer, apparently, is the initial and one of the most important. If it proceeds to other structures, the volume of the wellness decreases, only small nominal bags are preserved in the composition of the isolation and gonad.
The reduction of the Kommemy is observed in two basic cases.
1. Powerful muscles development - then the whole-filled whole interfered the body shape and move.
For this reason, leeches and non-nertine are reduced. Both those and other worms are capable of strong body cuts due to the work of powerful and multilayer muscles. Overall, they have decreased and turned into vessels that perform the functions of the circulatory system, that is, the transport of substances in the body.
2. The emergence of a solid exoskeleton - it removes the reference function from the organizer.
For example, the mollusks solid sink performs the role of the skeleton, and therefore they are reduced and is represented only by the gonad and pericardium cavity. The remaining functions, besides the reference, the organizer is saved. For example, the kidneys of mollusks are arranged and operate according to the principle of metanephridium: they remove the primary urine from the alert (in this case, the ispericard, where it is filtered from the blood), modify it and allocate secondary urine. The kidneys are associated with pericardium (whole). Funthno, so always arranged next to him.
Gemocel Clavistonogich
Traditionally, the body cavity of arthropods was determined as mixcela - "Mixed cavity." In embryogenesis, a nominal mesoderma is laid and the descendant of nuclear bags, but then they disintegrate, and the closed bags are not formed in most segments. The primary and secondary body cavity is not lifted with a solid epithelium and "mix" with each other. The nominal fluid is mixed with the fluid of the primary body cavity (blood), so the liquid, filling body cavity of arthropods, is customary called hemolymfoy, not blood. Hemolymif performs many blood functions: transport (including often respiratory), immune, etc.
On the nature of the body cavity arthropods can be glanced otherwise
.In the event of a dense chitinium cuticle, the whole is reduced because it loses the role of a hydrostatic skeleton. With a decrease in the nominal bags, their place again occupies the primary cavity of the body once. The bandwidth fluid performs the functions of the blood, and the body cavity is a circulatory system, and from the point of view of a comparative anatomy, it is all the same primary body cavity. These views are not yet generally accepted even among specialists in comparative anatomy, but look a logical continuation of the above ideas about the body cavity and the bloodary system of invertebrates.
Closed and unlocked blood system
The body cavity of arthropods functions as an unlocked blood system
therefore it can be denoted by the term " hemocel». Children's bags in adult arthropods can be maintained in the composition of the allocation bodies And perhaps gonad. For example, crustacean antennal glands (green glands at river cancer) begin with nuclear bags where primary urine is filtered from the blood.Unlocked They call such a circulatory system in which the capillaries are not developed, there are (and it is not always) only large vessels, and of them, blood flows into extensive lacuna and wash the body organs. Closedthis is called such a circulatory system, where the blood flows everywhere in thin vessels, including capillaries.
Secondary body cavity and blood system
(by origin - blastocel, primary body cavity)form and function together. The primary and secondary cavity can mutually "crowd out" each other. Based on the presentations outlined above, we can formulate some patterns of the ratio of these two internal environment systems.· Only nominal animals may have a circulatory system.
· Only in animals with an extensive whole sometimes a closed circulatory system.
·
In animals with a reduced whole blood system unlocked .The hypotheses relative to the origin and evolution of the organizer can be found in Article: V. Malakhov. Revolution in zoology: new system Bilateria // Nature. 2009. №3. P. 40-54 ( full version Articles are open on the Internet:
Tests
24-1. In the ringed worms in the process of evolution appeared
A) diffuse nervous system
B) blood system
C) bilateral body symmetry
D) abdominal nervous chain
Answer
24-2. What system of organs in the process of evolution first appeared from representatives of this type of animals?
A) nervous
B) digestive
C) blood pressure
D) sex
Answer
24-3. Are the following judgments about round worms true?
1. Round worms include a white planarium and a liver loser.
2. Round worms have an end-to-end intestine: they have a robust and anal holes.
A) right only 1
B) right only 2
C) orders both judgments
D) both judgments are incorrect
Answer
24-4. In what of the above types of invertebrates for the first time during the evolution appeared body cavity?
A) in segmental
B) mollusks
C) at round worms
D) in flat worms
Answer
24-5. Round worms, unlike flat,
A) no longitudinal muscles
B) no free-lived species
C) through digestive channel
D) well developed organs of feelings
Answer
24-6. Honors ringworms from round is that the first has
A) skin-muscular bag
B) through intestines
C) body cavity
D) Blood System
Answer
24-7. In the process of evolution, the circulatory system first appeared from the ancient class representatives
A) amphibians
B) cartilage fish
C) insects
D) ringed worms
Answer
24-8. The type of invertebrates, the representatives of which for the first time in the animal world appeared a through digestive system, -
A) flat worms
B) ringed worms
C) clansistonogy
D) round worms
Answer
24-9. Are the judgments about the structure of flat and round worms?
1. Under the skin and muscles of flat and round worms are the body cavity.
2. The intestine in flat and round worms through: in the front end there is a pole hole, at the rear end - anal.
A) right only 1
B) right only 2
C) orders both judgments
D) both judgments are incorrect
Primary body cavity Primary body cavity
schisopel, space between the body wall and the intestines in some multicellular animals, in K-Rom lie ins. organs. P. p. T. Appears in primary worms and is characterized by the absence of their own. Cell chill. Mollusks P. p. T. is represented by the Lakun and Sinus system, and the higher multicellular animals (for example, the ringed worms and chords) are ousted by the secondary body cavity, or the whole. In the articulated residues of P. p. T., Merging in the process of embryonic development with a reduced whole, form so-called. Mixed body cavity, or mixtal. In the embryos P. p. T. Represented by the cavity of Blastuly (blasting).
.(Source: "Biological Encyclopedic Dictionary." Ch. Red. M. S. Gilyarov; Radric.: A. A. Babaev, G. M. Vinberg, G. A. Zavarzin, and others - 2nd ed., Focused . - M.: Sov. Encyclopedia, 1986.)
primary body cavityThe space between the body wall and the intestines in which the internal organs are located. Unlike secondary body cavity. Does not have your own shell. Well developed at round, or primary, worms.
.(Source: "Biology. Modern illustrated encyclopedia." Ch. Ed. A. P. Gorkin; M.: Rosman, 2006.)
Watch what is "primary body cavity" in other dictionaries:
Large encyclopedic Dictionary
The space between the body wall and the intestines in some multicellular animals in which the internal organs lie; Does not have its own cell wall. Well developed in non-malemintes. Most multicellular in the development process ... ... encyclopedic Dictionary
The space between the body wall and the intestines in some multicellular animals in which the internal organs lie. P. p. T, well developed only at primary worms (see primary worms) and is characterized by the absence ... ...
The space between the body wall and the intestines in some kind of multicellular, in rum lie ins. organs; Does not own. cell wall. Well developed at the heatersmints. In most multicellular in the process of development, the whole is supplanted ... Natural science. encyclopedic Dictionary
Animals and humans, space bounded by the inner surface of the body wall, in which the internal organs are located. The primary body cavity is distinguished (see the primary body cavity), which does not have its own wall, and secondary ... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
Or the cavity of crushing the cavity observed between the segmentation balls of a crushing egg. With full, but equal to the surface discoid crushing (see) this cavity appears, but is not observed in most cases on eggs with ... ...
Body cavities - body cavities. Comparative anatomy and embryology. In the intestinal animals, as well as the flat worms there is only one single inner cavity of the intestinal, which in these cases is commonly equipped with outgrows or even goes into ... ... Big medical encyclopedia
- (Schizocoelom) body cavity formed through the discrepancy between the elements of the middle reservoir or primary, which it is at Rotatoria, Nematodes, AcanthoCephali and in general at primary worms. The secondary-haired it is presented with blood ... Encyclopedic Dictionary F.A. Brockhaus and I.A. Efron
- (Coeloma), or secondary body cavity, lined with an epithelial layer of mesodermic origin, or amendment, or, otherwise, peritoneal (see) epithelium. The difference between the primary and secondary cavity of the body, for the first time with proper clarity ... ... Encyclopedic Dictionary F.A. Brockhaus and I.A. Efron
- (primary worms), type of invertebrates. Between the body wall and the internal organs primary body cavity. Respiratory and blood systems are missing. Classes: Hair, gastrotrikhi, campactosis, cineryns, provicrats, nematodes, ... ... encyclopedic Dictionary
Type of ringed worms (Annelida)
We will get acquainted with a very interesting group of animals, the structure and behavior of which did not leave even Charles Darwin. He devoted a lot of time to studying the ringed worms and wrote several scientific works about them.
Among the worms, the ringed are considered the most progressive group. This conclusion is done primarily on the basis of the structure of animals.
Type of ringed worms Includes secondary-haired animals whose body consists of repeating segments, or rings. Ring Crafts have closed circulatory system .
Secondary body cavity , or whole (from Greek. koiloma - "Deeperation", "cavity"), develops in the embryo from the Mesoderm layer. This space between the body wall and the internal organs. In contrast to the primary body cavity, the secondary is wiping with its own inner epithelium. The secondary body cavity is filled with a liquid that creates the constancy of the body's interior. This liquid participates in the metabolism and provides the activity of digestive, blood, excretory and other organ systems.
In the ringed worms, the segmented structure of the body, that is, their the body is divided by For each other, the following sections -segments , or rings (Hence the name - Killed Worms). Such segments in individuals different species Maybe either a few, or hundreds. The body cavity is divided into segments by transverse partitions.
Each segment is to some extent independent compartment, because it has nodes of the nervous system, the selection organs (paired nephria) and sex glands. Each segment may have lateral growths with primitive limbs - parapodies armed with bristles.
The secondary cavity of the body, or the whole, is filled with a liquid, the pressure of which supports the shape of the body of the worm and serves as a support when moving, that is, the whole ishydravelope . The organic fluid carries the nutrients, accumulates and displays the substance harmful to the body, and displays sex products.
Musculature consists of several layers of longitudinal and annular muscles. Breathing is carried out by leather. Nervous system It consists of a "brain" formed by pair ganglia, and the abdominal nervous chain.
A closed circulatory system consists of abdominal and spinal vessels connected in each segment with small ring vessels. Several of the most thick vessels in the front of the body have thick muscle walls and play the role of "hearts". In each segment, blood vessels are branched, forming a thick capillary network.
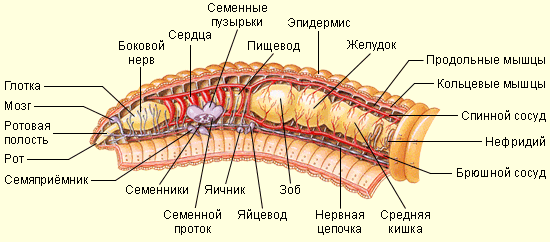
Some ringed worms of hermaphrodites, others differ males and females. Development direct or with metamorphosis. Occasionally digestive reproduction (budding).
Their sizes range from a few millimeters to 3 m. Total ring worms are 7,000 species.
Interactive Trial Lesson (Go away all the lesson pages and do all tasks)
Ring Worms - Progressive a group of worms. Their body consists of sets of ring segments. By body body is divided into internal ne roots, respectively, the number segments. Ring worms have different systems of organs. They have blood system appears and parry organs of movement - a presence of future extremities .
What animals for the first time during the evolution appeared body cavity?
1) Intestinal
2) flat worms
3) Round Worms
4) Ring Worms
Explanation.
Aromorphosis of round worms - body cavity - primary, filled with liquid under large than atmospheric, pressure. Liquid liquid gives the body elasticity and thanks to this actuates the role of the hydraulic. It also provides transport of nutrients and livelihoods.
The cavity of the body is called the space in which the internal organs lie. The only type of animals in which the primary cavity is preserved in an adult is round worms.
The correct answer is specified at the number 3.
Answer: 3.
Source: MiO: Training work on biology 28.04.2014 variant BI90801.
Natalia Evgenievna Bashtannik
Not. In the intestinal body, the body is a bag (intestinal cavity) of two cells of cells - ecto- and entoderms, between which the Mesogly mucosa is located.
The cavity of the body is called the space in which the internal organs lie.
The only type of animals in which the primary cavity is preserved in an adult is round worms.
Higher three-layer (ringed worms, mollusks, chord) have a secondary body cavity called the whole. Overall is always lined with epithelium of mesodermal origin. During the Bookmark of the Kommementary in the ringed worms, mesodermal cells lying in the primary cavity are divided, move and form a mesodermal bubble, which, increasing in size, displaces the primary cavity. The cavity formed inside the bubble is called secondary, since in ontogenesis it arose after the primary one.
There are animals, devoid of body cavities. These are flat worms. They have a space between the skin-muscular bag and internal organs filled with parenchyma cells.
In animals belonging to the type of arthropod, in embryogenesis, the primitives of the secondary body cavity are developing. However, the process does not reach the formation of a developed agencies, its primitives merge with the most existing primary body cavity. Therefore, body cavity is mixed.


