Signs of lack or excess batteries. Leaves in grapes light green, pale: causes of the disease
Greetings to you, dear plants lovers.
Everyone knows that he has negatively affects the growth and development of plants, which naturally affects the quantity and quality of the harvest collected. Today I will tell you about how our most common favorite vegetables react to the lack of basic nutrition elements - nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium. And also on what needs to be done if you have identified the lack of one or another element on external signs.
Lack of nutrients. Nitrogen deficit.
It manifests the strongest in the presence of high soil humidity, especially when there are long rains, as well as during drought or long cold.
With a lack of nitrogen, plant leaves become small, pale green with a yellowish tint, and the fruits are crushed and, as a rule, falling before the deadline.
Consider a specific reaction of a vegetable plant for a lack of nitrogen:
Carrots are small leaves, very slowly grow, become yellow and die away.
Onions - slightly growing, narrow short leaves of light green color, often begin to blush from the tip of the sheet.
Cabbage - Loan in growth, becomes dwarf, small leaves, first pale green with a yellowish tint, and later are made orange, quickly dry and soon fall.
Beets - cares, lagged behind in growth, has a reprehension, thin leaf stiffs. Color leaves from pale green, up to yellow-red.
Tomatoes - the general growth is strongly depressed. Small leaves become light green with a purple or yellow tinge on the veils. Very quickly die old leaves. Stems tough and thin. The roots are darker and will soon die. Tomatoes with a lack of nitrogen have woody, small fruits, which first have a pale green color, then become bright red and often fall prematurely.
Cucumbers - in growth lagging behind, have a pale green with a yellow tint of a small leaves. Especially quickly dropping and yellow lower sheets. Steel fibrous, thin, tougher, with pale color. Cucumbers develop with a lack of nitrogen very and very slowly.
What to do the gardener, if he noticed the appearance of signs of a lack of nitrogen in the soil?
The scheme is very simple. It is necessary to urgently hold the plant with a solution of urea. For this, 1 tablespoon of urea is bred in 10 liters of water. The flow rate of this solution is 3 liters per square meter.
Phosphor deficiency
Phosphorus is needed by plants to increase regenerative (regenerative) properties of tissues to accelerate their development. The lack of phosphorus plants suffer most of all in hot and dry weather, when the temperature of the soil is raised. At the same time, the growth of the stem is slowed down, purple or reddish strips or stains on the leaves appear. Roots and shoots are developing slowly, weakly, and therefore slows down the formation of rootepodes, kochanov, fruits.
Carrots - the leaves acquire a reddish tint, all the plant lags behind the growth, dwarf root roots are formed.
Onions - on old leaves fade tips, after which they black and soon die away at all.
Cabbage - the growth of young leaves slows down. Explicit sign \u003d Dark green color of young leaves.
Tomatoes - plants have an oppressed look. The leaves acquire a dark green color from the upper side, and with the bottom, their color becomes purple-lilac. This is especially noticeable when growing. The flowering of tomatoes and the ripening of their fruits with a lack of phosphorus is noticeably delayed.
Cucumbers - young leaflets become dark green, then begin to fine, shriveling, their edges begin to spin up. The plant at the same time significantly lags behind the growth, flowering and fruit formation is also delayed.
What needs to be done when the first signs of phosphoric failure are detected?
It is necessary to make superphosphate in the soil (1 square meter - 1 tablespoon), or phosphorous flour (1 square meter - 2 tablespoons), or any other fertilizers containing phosphorus. It should also be noted here that the advance lime of soils with an acidic reaction improves the phosphoric nutrition of plants.
Lack of nutrients. Potassium deficiency
The main tasks of potassium in soil nutrition of plants are: ensuring normal photosynthesis, an increase in plant resistance to various infectious diseases. In the phase of intensive growth, plants especially need potassium.
Especially needed potassium vegetables on light soils, as well as during arid weather. The lack of potassium may occur in the soil when making magnesium and calcium in it. During the lime of acidic soil, the need for fertilizers containing potassium is always increasing.
With potassium deficiency, the growth of vegetable crops is depressed, stalks and shoots are weakly developing, often being twisted, they dry up the tops. The leaves acquire a dark green color, but already with a bronze or bluish tint. On the leaves you can see the location of the fabrics. The edges of the leaflets are first yellow, and then dry out.
Carrots - all the plant becomes short, the leaves are painted pale, later acquire a bronze tint, slightly curly. The tips of the leaves become brown and dry. Gradually, such leaves completely die off, and in general terms, the above-ground parts of the plant are developing strongly, to the detriment of the corneal of carrots.
Onions - starting from the tip, old leaves are made with grayish and straw yellow, after which the sheet is completely yellow and slightly faded. If you do not accept the appropriate measures, the complete dry drying of the leaves will be observed.
Beets - in the growth heavily lags behind, leaves, instead of proper green, acquire dark crimson color.
Cabbage - you can see the sudden yellowing of the run of the lower, and sometimes the average leaves of the plant. Then this yellowing passes to the whole sheet, but the color of the vein remains green. Further, the amount of yellowed leaves quickly increases, towards the bottom up. The lowest leaves become brown, begin to blame and in the end, dry.
Tomatoes - in growth significantly begin to lag behind, shoots and stalks are weakly developing, often being twisted and made woody. The color of tomato leaves with a lack of potassium is bluish green, and old leaves are yellowish on the edges or pale gray. Later, the edges of the old leaves are twisted up and becomes kind of burnt. Treaty of tomatoes often fall, there is an unetended ripening of fruits. The roots are very poorly developed, often brown.
Cucumbers - the growth of plants slows down, the leaves become small, dome-shaped, dark green. A distinctive feature is the appearance of a light yellow kayma on leaves. Fruits become similar to the pear - fruitful and extended to the top.
What to do when there is a sign of a lack of potassium in the soil?
It is necessary to hold the plants with sulfur-acid potassium (1 square meter of beds - 7 - 10 grams of the drug) or potassium magnesia (1 square meter of beds - 15 - 20 grams of the drug), you can also use conventional wood ashes (for 1 square meter. - 100g).
Today it's all. Look closely to your green pets and then you can get them in time to prevent lack of nutrients In the soil and get a wonderful harvest.
See you, dear friends!
Causes when a leaf of grape acquires light green color
What conditions are needed by grapes so that the vegetation of the plant should be in normal conditions, which can negatively affect the course of the formation and growth of the vine, crop maturation and for what features it can be determined. First of all, full lighting required for growth, temperature, the desired amount of moisture and trace elements in the soil is required for photosynthesis and other processes. The shortage of listed components can adversely affect the growth of grapes and cause various diseases At the plant. One of the manifestations of grape diseases can be expressed in modifying the color of the leaves of plants.
Changing the color of the grape leaves can signal about the shortage of trace elements
Causes of cutting grapes color cut from dark green on light
Figure (5-8 days) Lightening grape leaves in agronomy is called chlorosis. Green leaves change the color on the pale green, with gradual yellowing. The cause of these manifestations is the inability of the plant to produce in the desired amount of chlorophyll. The accumulation of hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide in excessive amounts that grapes are not able to recycle, is a feature of the changing color of the leaves.
The manifestations of chlorosis may be manifested due to the following reasons:
- surplus lime elements on the site;
- solonechard soils (large percentage of salts in the ground);
- damage to rhizoma fungal diseases;
- infectious diseases;
- nonconformity of meteorological conditions;
- lack of trace elements in the soil.
Rainy, cold conditions can negatively affect plants by provoking the appearance of chlorosis. The oversupply of moisture in the ground contributes to a decrease in aeration, which disrupting the metabolism processes cause oxygen starvation in plants. The development of grape branches with possible booting is stopped.
The oversupply of water in the ground contributes to soliter in the lime ground, reinforcing its concentration with further provoking of the alkaline reaction. Minerals, which are necessary for further growth, when entering the metabolism in the plant in the plant are formed into insoluble elements. This in turn leads to carbonate chlorosis, which is why the first sign of these diseases brighten the leaves, modifying from the normal in the pale color.
The oversaturation of the soil lime can be balanced by the sulfuric acid ammonium made in the proportion of 3 kg at the rate of the addition of 1 bush. Some of the types of fertilizers can cause an alkaline reaction, they should not be used for feeding:
- superphosphate in large quantities;
- fresh manure;
- sodium and calcium nitrogen compounds.
The soil, susceptible saline microelements and carbonates, can be used under the planting seedlings with vaccinations, specially trained under such types of soils and resistant to listed factors.

Sulfuric acid ammonium will help solve the problem of chlorosis
Grape reaction for a lack of minerals in the ground
For normal growth, grapes requires about seventy trace elements, which stabilize the growth of the vine and the right development. The disadvantage or improper balance of minerals (oversupply of some and lack of others) provoke metabolic disorders in the entire plant, which in turn leads to diseases, reducing yield, and sometimes the death of vineyards.
Why green leaf Plants so rapidly change the color, and from the lack of which of the trace elements they brighten. All the color changes that the sheet carries the sheet comes from an insufficient amount of minerals, they feed from the soil grapes. The list of the most popular trace elements that affect the color of the leaves of the grapes includes:
Nitrogen is vital for plants, since this element activates growth stimulation, but being in the soil, it is not available to rhizomes due to insoluability in compounds that are saturated with soil. The ability to get nitrogen compounds occur due to organic fertilizer. Bacteria that are in the ground contribute to the transformation of nitrogen into plants affordable for plants, the first sign of an insufficient number of nitrogen compounds - the grape sheet has changed its color.

Changing the color of the leaves begins with the bottom of the vine
Not only the color of the leaves may change with the lack of nitrogen compounds, it is reflected in the revealed kidney, the weakness of shoots, the absence of launches. First of all, there is a bottom sheet of grapes, dark lightweight colors are gradually brighten, moving to yellow. Why it is from below that the process of modifying the color of the leaves begins. The bottom leaf of the plant reacts to the lack of nitrogen first, as it is closer to the root system, the pet is also changing the color, it becomes red. In the near future, the bottom sheet completely dies and crept. If the situation does not take control in a timely manner, all the leaves are brightened on the grapes, and the berries become small.
Zinc problem - restoration of oxidation in the body of plants and in carbohydrate production. The same trace element participates in the exchange of nitrogen compounds.
The zinc deficiency leads to the accumulation of nitrogen, which disrupts protein synthesis, the leaf of the plant loses symmetry, becomes brittle, and appears in the form of light spots with a metal tint. The situation with the lack of zinc is a common phenomenon, it is easy to fix with extractive treatment by adding a zinc oxide solution, or zinchete.
The reproductive function provides a boron, with its lack of a sheet resembles a mosaic, only in a discolored form, the pale starts with the tissue between the streaks, then the color of the leaves will raw and falls, pre-twisted outward. These are not all problems caused by the shortage of boron - the marking can be very weak, and by the beginning of the flowering point can disappear. Roots weaken, with severe frost grapes dies. The problem of boron deficiency is filled with feeding drugs containing item.
The shortage of molybdenum phenomenon is rare, when it is short enough in the ground, the sheet becomes pale and dim on color. This element is directly connected to the sugartyness of grapes, and its lack affects the root formation, the ability to regenerate damaged places. Upborn molybdenum superphosphate compensates for the deficit of the element.
A manganese deficit makes a spot spotted, its surface resembles finely sprinkled points of various tonalities.
Next, the leaf becomes almost monophonic, since the stains are increasing, connected with each other. Mineral is involved in photosynthesis, regenerates damaged tissues, is directly related to the formation of juice. The disadvantage is compensated for manganese sulfate.

Manganese sulfate compensates for the deficit of this substance in the vine
Types of grapes, methods of treatment
The changed color of the plant leaves may be the cause of infectious diseases that almost all grape varieties are exposed. Characteristic manifestations of chlorosis are the yellowing of the residences. The leaves change the color, twisted, dry and fall.
Plants affected by spotted mosaic are doomed to death, with the detection of this disease, experts recommend to irrigate the entire section of the vineyard and in no way use to reproduce the cuttings. Not only grapes are subject to this disease, so after irritation, it is necessary to clean the area by disinfection. In the next six years, it is not recommended to plant a vine on the site.
Fungal diseases are the result of the galant attitude of the gardeners, which did not proceed the plants with antifungal drugs on time. Trootheral processing contributes to the full protection of vineyards from diseases of fungal diseases.
Many of the drugs can be purchased in the network of garden-garden stores, but some of them can be cooked independently. In order for the vineyards to be healthy and brought abundant yields, careful attitude to the plant is required. The first signs of diseases is the change in the leaves of the plant to which it is required to respond immediately.
More information
In natural conditions, each plant is involved in the cycle of substances in nature. Rain worms, mushrooms, bacteria and insect living in the soil decompose dead organisms into composite elements. At the same time, important minerals needed to feed plants are obtained. They are absorbed by the plant with roots and are used as a building material for new cells.When the plant dies, insects living in the soil and microorganisms are processed; Mineral compounds from which their fabrics consisted, decompose on the component elements and become available for other living organisms.
Indoor plants are turned off from this cycle of substances, and therefore they have to be content with only those minerals that we provide.
Since the soil volume in the pot is not particularly large, quite often plants suffer from a shortage or excess of nutrients.
Essential nutrients
Typically, nutrients depending on the needs of the plant are divided into micro and macroelements.
Macroelements are needed most of the plant: nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, as well as sulfur, magnesium and calcium. Microelements include boron, iron, copper, manganese, molybdenum and zinc. Each elements of mineral nutrition performs in a plant at least one, and sometimes several important functions. Microelements are needed by a plant in small quantities, but their lack of negatively affects its viability.
Below is a list of the main nutrients and describes the functions that they perform in the body of the plant.
Nitrogen (N)
It is considered the most important for the plant, because it is the main component of plant protein joints. Nitrogen is necessary for the growth of leaves and shoots, as well as for the formation of green leaf cells (chlorophyll).
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus affects the growth of roots, kidneys and buds. In addition, it is necessary for ripening and painting flowers, fruits and seeds.
Potassium (K)
This item is necessary primarily to maintain the water balance of the plant, because potassium contributes to the holding of water in cells. In addition, potassium increases the resistance of plants by pests and the ability to transfer adverse conditions.
Sulfur
Just like nitrogen, it is a building material for the formation of protein vegetable compounds and chlorophyll. The latter refers to another element - Magnesium (MG).
Calcium (SA)increases the strength of plant tissues and also, as well as potassium, contributes to increasing the endurance of the plant.
Signals talking about disadvantage or excess minerals
Typically, the plant receives a sufficient amount of nutrients if we do not forget to regularly feed it in the period of growth, and the long-term plants are transplanted from time to time to a new land.However, sometimes flowerflowers notice the growth of growth or painting from their pets and cannot find this cause. Although they cannot detect any pests, but just in case, perhaps, a special protective agent is used.
 |
|
| This chrysanthemum suffers from lack of magnesium. |
ABOUT lack of nitrogen You can learn from a slowdown in growth: decorative plants form quite a few new shoots. The leaves are pale, they become a light color, and reddish shades are also possible. First of all, it is manifested in older leaves, which in the next stage are prematurely falling.
Excess nitrogen manifests in a dark green color of leaves and a porous soft plant tissue. Resistance to diseases and pests decreases. If the flowers are not formed or pale painted, it means that lack of phosphorus. At the same time, the lower, older leaves become dirty-green, in addition, other colors can also be present in their color, from blue to red and purple. Young leaves remain small, and their tips bend up.
A plant suffering from lack of potassium, becomes sluggish, especially in warm and sunny days. It remains small and squat, often the leaves will pale around the edges and fall. With a lack of potassium, the resistance of the plant various diseases and pests.
A typical sign speaking about lack of iron, It is the so-called chlorosis of the leaves: the streaks are becoming dark green, and the surface of the sheet between them is pale and acquires a yellowish tint. Especially often, plants suffer from lack of iron when the light day decreases or when the level of soil acidity decreases.
The level of acidity is soil
In connection with the filtering of plants, it is also worth saying a few words about the level of soil acidity. Under the level of acidity, the ratio of acids and alkalis is understood. For greater clarity, we introduce a scale from 1 to 14. At the level of acidity 7, the soil is considered neutral. If the pH is less than 7, then the soil is acidic, if more is alkaline.
The capacity of plants absorb nutrients depends on the level of soil acidity. Best of all, they are absorbed if the soil is a weakly acidic or neutral (pH from 5.5 to 7). If the pH is deflected in one direction or another, the plants may show signs of lack of nutrients, although in the soil they will be contained in the required quantity.
The more lime is contained in water for watering, the faster the level of soil acidity decreases (the pH value increases). The plants begin to yellow leaves (lack of nitrogen) or chlorosis of leaves develop (lack of iron).
Especially often these signs are manifested in plants that prefer acidic soil. These include Camellia (Camellia Japonica), Kattleya (Cattleya Labiata) and Azalei (Rhododendron Simsii). These plants feel better if pH \u003d 4 - 5. In their cultivation, they can use special ammonium containing mineral supplements that increase the soil acidity or support it at the desired level. We mean oxidizing additives.
In addition, we will also remind that water for watering must necessarily be soft to prevent accumulation of alkalis in the soil.
If you suspect that the cause of the growth of your plants is an incorrect soil acidity level, check the pH value using a special pH tester, which can be purchased in a flower or garden shop.
The need of indoor plants in minerals
The need of plants in nutrients depends on a number of factors. It is especially high in the period of growth, that is, from March to September.
Most plants during this period must be picked up at least once a week. Otherwise, it is the case in winter, when the feeding mode is installed for each plant. Plants wintering in a shaded or cool room are feeding every three or four weeks. Plants whose winter comes in winter, they stop feeding at all. The need for various mineral substances varies greatly depending on the plant development phase.
For a young plant, fertilizers are needed with a large content of nitrogen, which contributes to the growth of stems and leaves. Later, during flowering, phosphorus-containing mineral supplements should be made.
Potassium is always needed by a fair amount, regardless of the development phase.
Proper feeding of plants
During the growth period, the feeding should begin two or four weeks after the purchase. If you planted the plant yourself, start feeding it only after the sprouts are shown. At the same time you have a choice between mineral and organic fertilizers. When using mineral fertilizers, nutrients are available at once. As for organic fertilizers, the nutrients contained in them are absorbed by the plant slower.

The most common organic fertilizers are compost and manure. However, they are suitable for the garden or flower beds than for indoor plants. In the improvisedly made compost, the content of mineral substances cannot be determined, and this can easily damage the sensitive indoor plants due to incorrect feeding. Other organic fertilizers, such as a horny chips, bone and blood flour, guano, best add to the soil during transplantation.
In specialized stores, organic fertilizers can also be purchased, which also contains microorganisms, which are beneficial to the composition of the soil and preventing the excessive evaporation of water and the formation of the crust on the surface of the soil.
The easiest way to feed indoor plants to use mineral fertilizers, because In this case, the plant can get all the important nutrients in the desired proportion.
Liquid mineral fertilizers
This is the most common way to feed plants. In this case, a concentrated nutrient solution is used, containing all the necessary micro- and macroelements. There are special mixtures with an increased nitrogen content - for decorative substrate plants. In contrast to them for decorative flowering plants, mixtures with an increased phosphorus content are used.
The method of applying this type of fertilizer is quite simple. The concentration of fertilizers should not be higher than that recommended on the package, even if your plants detect symptoms indicating the lack of nutrients. Too high fertilizer concentration can damage gentle roots.
Soluble mineral fertilizers in the form of salt
They contain all the necessary substance plants, including magnesium. The corresponding number of fertilizers is dissolved in water. Usually required not at all a large number of Salts are best to measure it using weights.Tablets and sticks
This method of feeding is easier, but less accurate compared to those described above. Depending on the size of the pot and plants, a certain amount of nutrient sticks or tablets is introduced into the soil.
The plant assimilates the mineral substances in them gradually, and the risk of oversaturation decreases.
Special fertilizers
Some types of plants, such as cacti, bromelia or orchids, make their special requirements for feeding. For such plants, there are special nutrient mixtures on sale.
Assistance in an emergency: feeding plants through the surface of the leaves
Plants, especially acutely suffering from lack of mineral substances, can be fed through the surface of the leaves. This method is used, for example, with a lack of iron in the soil, when chlorine leaves appears. Very often, he is observed in Bougainvilia, Hydrangees, Brunfeels and citrus. If the reason for this is the increased pH value, then the introduction of liquid fertilizers in the soil will not help the case, since the plant will not be able to assimilate them.
In this case, we advise you to purchase chelate iron in a specialized store (i.e., intracomplex iron compound). Dissolve it in water, and then spray the plant by this solution - best on some washing surface, otherwise ugly stains may remain. This method of feeding is recommended, first of all, for the plants mentioned above. In no case should it be used for plants that do not like when water gets on their leaves.
Recently rooted cuttings are very useful to feed through the surface of the leaves with nutritional mixtures with a high content of nitrogen. However, feeding plants through the leaves is only an additional measure.
What to do with an excess of minerals?
With a small excess fertilizer, the plant may well handle independently; Just stop feeding for a while. The soil should be constantly wet, so that mineral salts do not damage the roots.
If the content of mineral substances in the soil is much higher than the norm, then you have two possibilities: to transplant the plant or rinse the soil. Put a pot on a quarter of an hour under a stream of water in the sink. Water should not be too cold and go well through the drain hole. You can also immerse the pot in a bucket with water to about the soil level and wait until all the soil is impregnated with water. Then remove the pot and let the water drain.
Repeat this procedure several times.
Danger signals
|
Rules of subcord
If the plant in the soil or a special soil mixture is not recommended strongly. At some points, the plant simply does not need feeding, to others - the amount of nutrients is determined by the size of the plant and the size of the pot. Most often feed simultaneously with watering during the growth or flowering period. During rest, the plant does not feed or reduce the dose of fertilizer.
Readers are often referred to as a question: changes the color of the leaves of plants - what to do? We decided to get ahead of such questions and publish symptoms of lack or oversupply of nutrient elements in plants. Completing the changes in the leaves with a "visual manual", you can identify the problems yourself and start acting. For ease of perception, the symptoms are shown on the same leaves.
The use of fertilizers is directly related to the status of plants. If they have a healthy appearance, they are fruit and do not show signs of mineral starvation, then the feeder can be postponed. But if you have noticed that the leaves begin to change the color, the plants sharply slow down their height, cease to bloom, it means that measures must be taken - to make fertilizers.
With a lack of nitrogen New shoots on the plant are almost not formed, and the size of the leaves is reduced. In the absence of nitrogen in old leaves, chlorophyll is destroyed, and as a result - they take a pale green color, then yellow and die away.
The formation and development of flowers and flowing fruits are worse.
What to do? The plants are fed by ammonium nitrate (20-30 g / m2) or null-grade (up to 1 kg / m2). For a quick effect, it is possible to make an incorrect feeding (spraying) with urea solution (30 g per 10 liters of water).
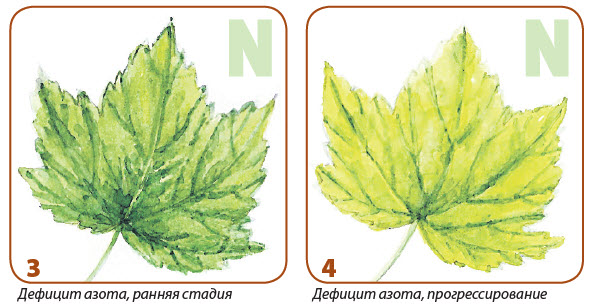
However, it is not necessary to get involved in nitrogen fertilizers. Excess nitrogen Especially in the second half of the vegetation, it delays the formation of reproductive organs of plants; They form a large green mass. The quality of the harvest is greatly worsen: the concentrations of sugars are reduced in berries, fruits and vegetables, the nitrates are accumulated. With an obvious rebupping of nitrogen in the soil, the leaves on plants acquire a dark green color, a large number of young shoots appear, the stalks of grassy crops are thicker than usual.
What to do? It remains only to "disappear" plants, leaning nitrogen from the soil by abundant irrigation.

Phosphorus It is necessary in the early periods of the life of plants and in the formation of a crop. The plant is capable of using this power element re-from the old leaves it can move to the growth zones, young shoots and leaves. therefore exterior signs His drawback will be manifested primarily on old leaves. They will begin to acquire a characteristic red-purple or bluish tint, sometimes a dark green color. Flowering and ripening of fruits in plants is delayed, leaves the leaves early. The growth of shoots and roots is slowed down, the leaves are minced, the winter hardiness is reduced. The symptoms of phosphoric starvation of plants are most often observed on acidic soils, in which the organications made little.
What to do? It is necessary to make a solution of superphosphate (50 g per 10 liters of water). Superphosphate is a poorly soluble fertilizer, so the granules should be soaked for a day, periodically stirring. Strain through 2 layers of gauze, and the opportunity to spray plants. After 2 weeks, it is advisable to feed the plant with complex mineral fertilizer (1 tbsp. Spoon on 10 liters of water, spending solution per 1 m2 landings).

With potassium deficiency The following symptoms appear on the plants: the edges and tips of the leaves will boil, they acquire as if burned out, on a leaf plate there are small rusty stains. Cells grow unevenly, therefore the corrugation of the leaves appears, they acquire a dome-shaped form. The plant becomes short with short interstices, shoots grow thin. Especially sensitive to the lack of potassium such vegetable cropslike potatoes, root, cabbage, corn.
What to do? Plants are fed by chloride potassium (10 g / m2) or ash (up to 100 g / m2). For non-believers, 50 g of potash salt in 10 liters of water is breeding.

Do no harm
Nitrogen is spent the last substrald of July and no later than the first week of August. Otherwise, young shoots of trees and shrubs will not have time to grow, there is a threat to freezing in winter.
And potatoes and roots will be poorly stored. Cucumbers and tomatoes with acute nitrogen shortage can be fed and later.
What happens when they are undernourished
In plants, the need for trace elements is significantly less than in mineral and organic nutrients. However, they should not be underestimated - in the life of plants they play far from a latter role. With a lack of iron, manganese, magnesium plants, of course, do not die, but healthy fruits give them no power. For greater clarity, symptoms are given on the same leaves.
Microelements of the plant are obtained from the soil. But the lands that were given to gardeners are usually poor, therefore, timely feeding are required for the full growth and plant development.
there is important moment - Unlike the main elements of nutrition (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium), plants absorb trace elements only if in the soil they are in a moving condition. In other words - in plants available for plants. IN otherwiseEven if the feeding was carried out, landings may suffer from a shortage of a trace element.
Mobility of trace elements depends on the soil environment and, first of all, the pH indicator. For example, in acidic soils (when pH is less than 5.5) in the formations available for plants there are zinc, manganese, iron. And in neutral and alkaline, they, on the contrary, are sedimed and transmitted to unavailable compounds for plants.

Often as a result of improper agricultural equipment and the introduction of excess doses of phosphoric fertilizers of the bed garden sites There are "zafospheres". In the soil, excess of phosphates are accumulated, which form hard-soluble compounds with zinc and iron. This reduces the availability of these microelements for plants.
Symptoms of lack of trace elements
The lack of iron and manganese is manifested in young leaves and growth points. These trace elements are not capable of moving from one part of the plant to others, so when they are shortened in the soil, young shoots and leaves do not receive food in the desired quantity.
With a lack of iron, the leaf alkali is losing green color, shoots are covered with brown spots or dying.
With a lack of manganese, alkali remain green, the leaves become spotted, sections of dead fabric appear.

With magnesium deficiency, the root plant system suffers primarily, on the leaves of the vein remain green, and the other parts are brighten. Early leavefall is possible, which begins with the bottom of the plant. Sometimes the lack of magnesium leads to the appearance of a drawing on the leaves similar to the mosaic disease.
The symptoms of the lack of zinc are manifested first on old leaves. They are strongly expressed collity, corners of dead fabric appear. For fruit trees A characteristic symptom becomes a mumble of leaves and shortening of intersals.
What to do?
Organic fertilizers of good quality (manure, humus, bird litter, compost) contain the right amount of trace elements. If a sufficient amount of organic is brought into the soil in the soil, then, as a rule, the additional contribution of trace elements will not be required.
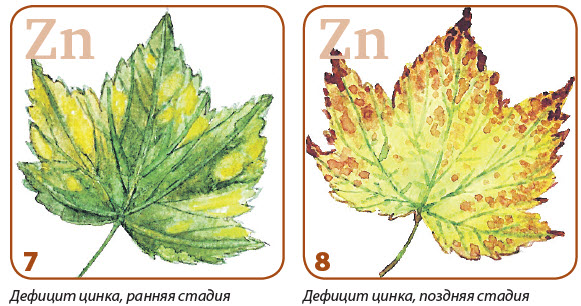
In case of acute shortage of trace elements, plants need to help non-rooting feeders (spraying). You can find individual trace elements in the form of simple chemical salts. But, as already mentioned, they are available to plants only on acidic and weakly acidic soils. On neutral and alkaline soils, trace elements in chelated form should be applied.
For non-smelly feeding, it is better to use solutions (2 g per 10 liters of water) of iron sulphate, zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate.
To replenish magnesium nice results Gives a spraying of plants with a solution with magnesium sulfate (10 g per 10 liters of water).
Let's continue our acquaintance with leaves. In the previous article, we learned how plants behave with the lack of basic batteries. In this article, you can find out how the leaves can determine the lack of elements such as iron and magnesium. After reviewing the basic signs of a shortage of one or another element, you can easily correct the situation and receive crops on any soils.
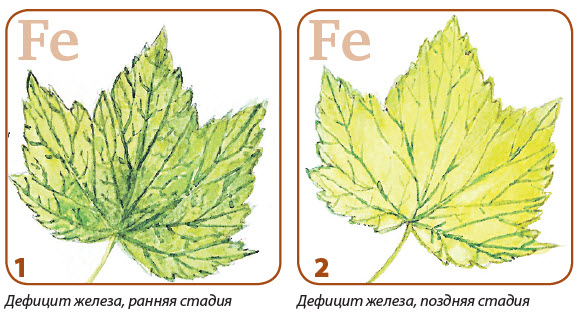
Iron
Disadvantage of such a microelement as iron, we have repeatedly could watch in our garden, it is yellowing or pale the upper leaves, and called it chlorose. Especially susceptible to chlorose of plants, in need of an acidic soil reaction, such as hydrangea, blueberries, rhododendrons, azalsa, all favorite petunias. But other plants may also lack iron.
Most often chlorosis occurs on lime soils. Iron, even if it is available in the limestone soil, cannot be absorbed by plants, because it is in the unavailable form. The cause of chlorosis can also be a lack of nutrition, too dry or too wet soil, freezing, various viral diseases, an excess of such trace elements as copper, zinc, manganese.


With just a beginner developing chlorose, the leaves of plants acquire a yellowish tint, and the grid remains even green. With severe chlorose, the leaves are even more brightened, become almost white, the lifts of the sheet will also be lightened (not to be confused with the volatile shapes of plants, whose leaves should by definition be yellow or white). The leaves begin to die the edges, boil tips.
Chlorosis begins to manifest first on young ones, and then on old leaves. Sometimes, with a lack of iron, young shoots or tops on the trees dry out. Sometimes with chlorosis, other plant diseases can be confused, for example, tomato ring spot virus.
Since most often chlorosis occurs on alkaline (lime) soils, then you need to make such fertilizers that acidify the soil, and thus iron becomes affordable and digested from soil by plants: ammonia nitrogen - ammonium salts, nitrate nitrogen - kalia, calciumor Sodium Selitra. Acidify the soil with a weak solution of sulfuric acid (no more than 10 ml per 10 liters of water) or add to the soil colloid sulfur. Do not forget to prepare such solutions only in plastic buckets.
To correct the situation, you can also use chelate Iron. Such a chelate solution can be prepared even at home, for this you need boiled water, citric acid, iron vigor.
In a three-liter jar, pour the cooled boiled water. Dissolve in this water about 12 grams of citric acid and stir up to the complete dissolution of acid crystals, then add about 8 grams of iron vapora to this solution. The result is a light orange "rusty" liquid that can be used for plant feeding.
Magnesium
The lack of magnesium is manifested quite often on light sandy or squealed soils. All plants with a lack of magnesium are growing very poorly.
Magnesium starvation Apple trees looks like chlorosis (iron shortage). Similarly, the leaves begin to shrust, and the veins and tissues of the sheet next to them remain green. Then, necrosis (die away) begins to form a sheet from the edge of the sheet, which is why the sheets of sheet begin to bend down, as if they worship, wrinkle, the leaves become dome. Gradually, the edges of the leaves are becoming torn. Only, unlike the "iron" chlorosis, magnesium starvation is observed primarily on old leaves, and not on young.
In the bone cultures, magnesium lack of magnesium causes premature yellowing of the leaves, after which they can crumble ahead of time. In pears from a lack of magnesium leaves black. The black currant leaves also acquire a dome-shaped form due to the fact that the edges of the leaves begin to bend the book.


Garden strawberries or strawberries lack magnesium can also be determined by changing the color of the leaves. The leaf fabric between the veins can get yellow, redden or become purple, purple, while the lodgings of the leaves still continue to remain green. With a very strong magnesium starvation, the leaves of the berries are premature.
In order to avoid magnesium starvation by plants on light soils, you need to perform feeding fertilizers containing magnesium.


For example, kalimagnesia. - Very effective potash-magnesium fertilizer, which contains 30% of potassium and 15% magnesium. Fertilizer is easily dissolved in water.
Dolomitic flourwhich contains calcium and magnesium, so the dolomite flour can be used not only for the limestone of the soil, but also as magnesium fertilizer, it all depends on the dose of application. If you use a dolomite flour as a fertilizer, then you need to bring it in spring and autumn during the main processing of the soil of a small dose - not more than 20-30 g per square meter. M, whereas for the lift of the soil dose of dolomite flour increases by almost ten times and depends on the acidity of the soil.
Magnesium sulfate, or Magnesium sulphate (magnesium content - 16%) - this fertilizer is also effectively both in root and non-rootful feeders.
So, you can make a small conclusion: chlorosis (yellowing of a sheet with remaining green streaks) on young leaves is caused by a lack of iron, chlorosis in the old lower leaves is a lack of magnesium.


