Art styles in architecture. Architecture, its concepts and directions
Gothic is one of the most prominent architecture styles, causing any feeling of awkwardness and trembling. The terrific majestic structures admire everyone who saw them.
Gothic architecture began to develop in the Middle Ages based on Romanesque architecture. For gothic structures, which most of the cathedrals and temples are characterized by huge arches with pointed riding, the facade decoration with various carved details, high towers, narrow columns and, of course, beautiful stained glass windows.
The most famous monuments of gothic architecture
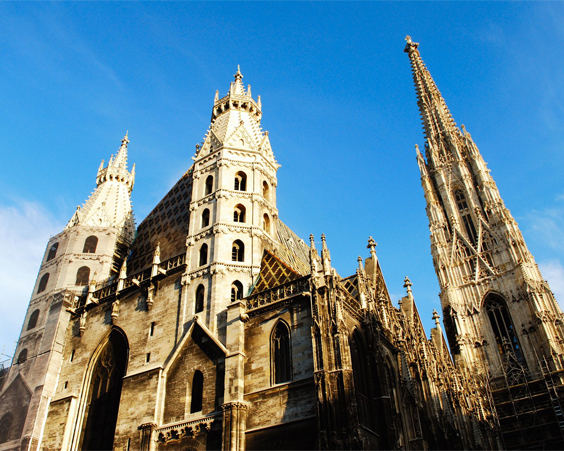
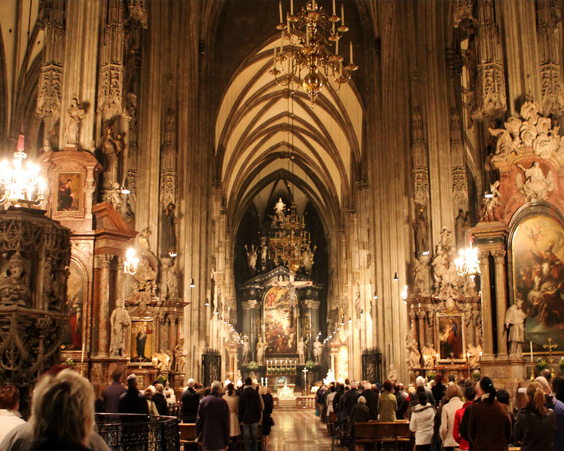


St. Stephen's Cathedral in Vienna is considered one of the most monumental buildings. The construction of the cathedral began at the beginning of the XII century, but the fire of 1258 destroyed the cathedral almost to the ground. Only in 1511, the Cathedral of St. Stephen was completed due to the efforts of Anton Pilgram.
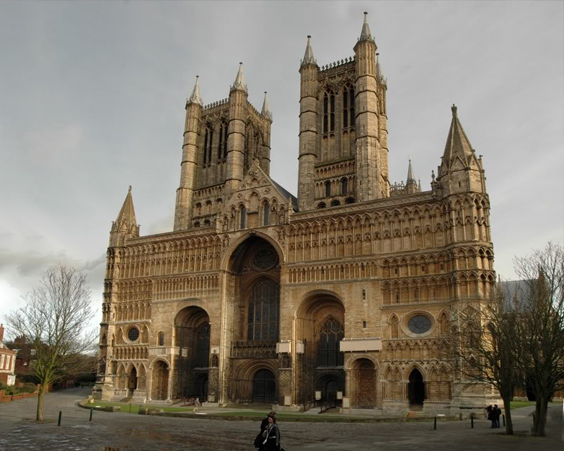
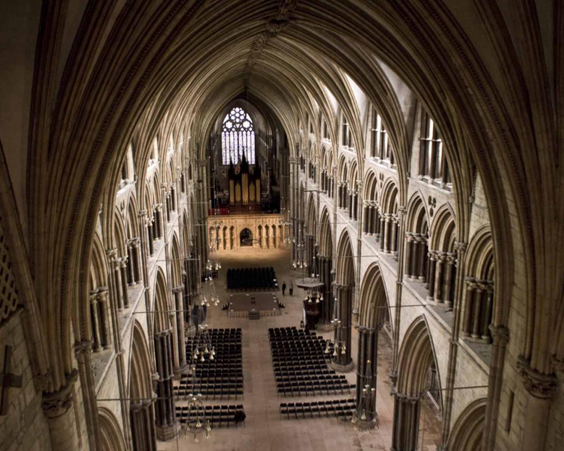


The cathedral in Lincoln was rebuilt from the Norman Cathedral. The construction of the cathedral took more than one hundred years, some parts of the cathedral still retained the features of originally the building. After the earthquake of 1185, the cathedral was rebuilt.
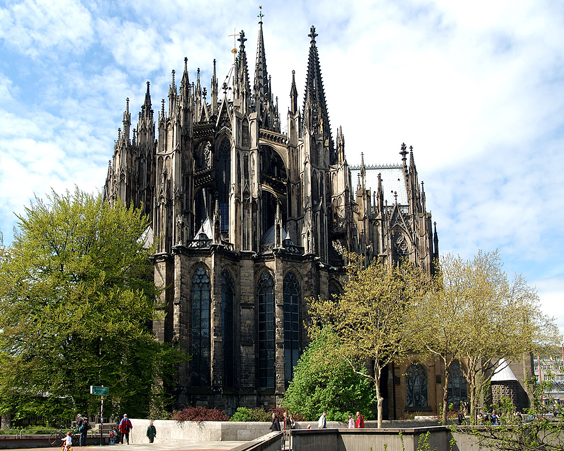
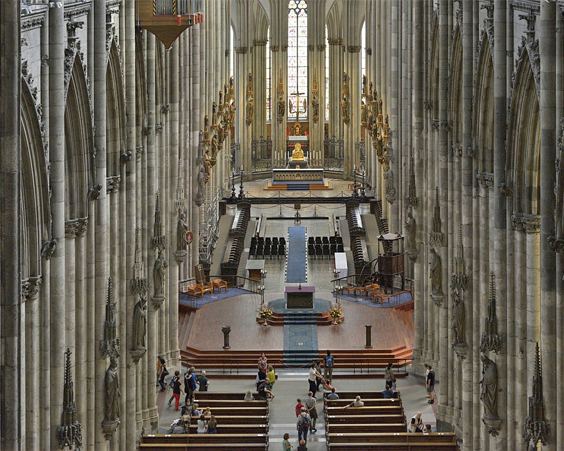


The Cathedral in Cologne was laid in 1248. The cathedral was built incredibly slowly, and in 1450 its construction and was stopped at all. Only in 1842 it was decided to resume construction, which was completed in 1880. It is worth noting that the cathedral is difficult to call perfectly complete, it is completed so far. This is largely due to an unusual legend. The architect of the Cologne Cathedral, realizing that he is unable to complete such a monumental structure, invited the devil to help. The devil agreed to help the architect, but when the cathedral will be completed and the last stone will fall into place, the end of the world will come. To avoid the implementation of the threat, the cathedral is constantly reworked.
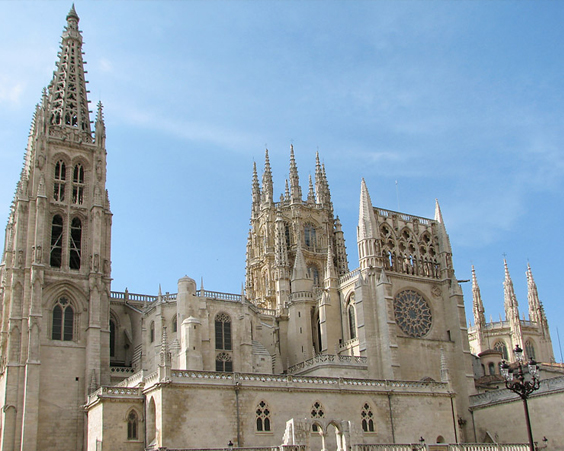
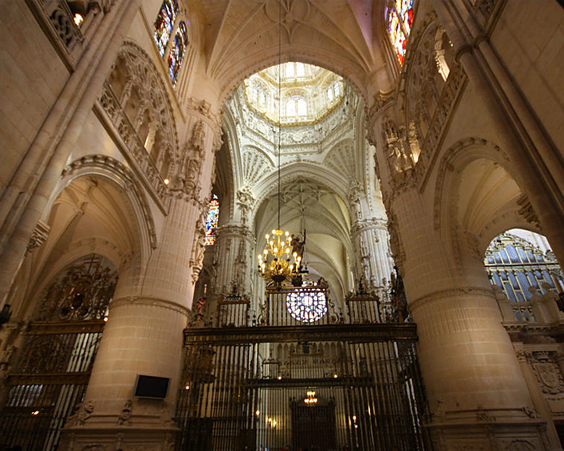


The first stone was laid in 1221, but fully completed the construction of a monument of Gothic architecture only in the XIX century. The cathedral is a mighty ship, crowned with stone lace.
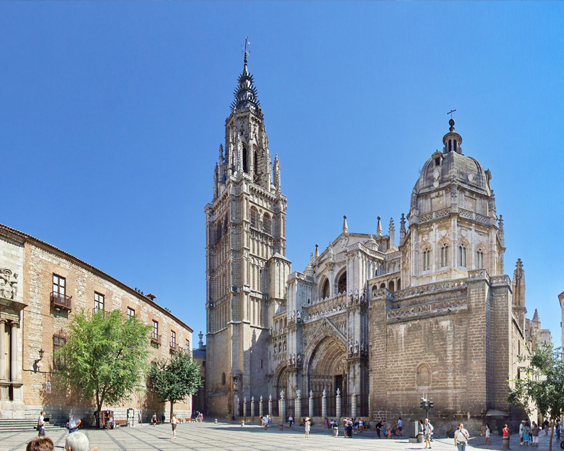
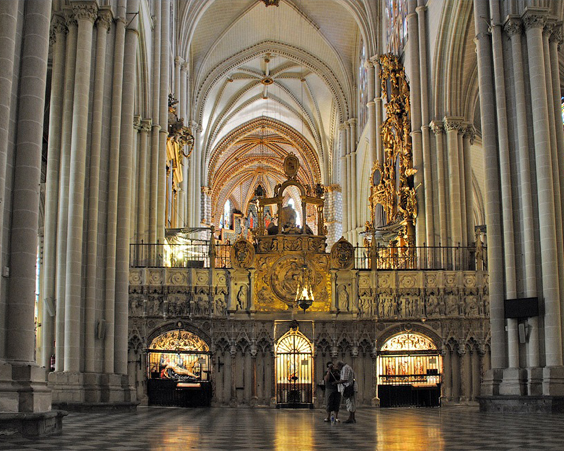


The Cathedral in Toledo is one of the largest in Europe. Built in 1226-1493, the Cathedral became the center of Catholic faith in Spain. In many ways, it is why the cathedral lost some features of the Gothic style, but acquired many unusual elements from other architectural styles.
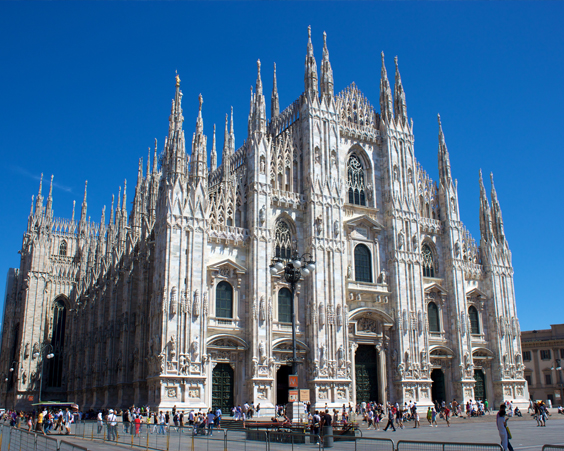
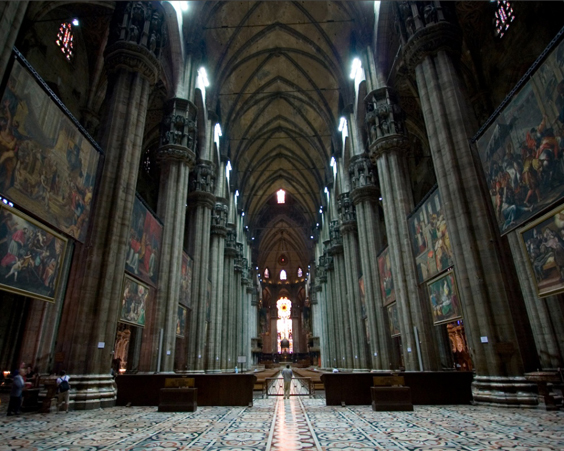


Milan Cathedral is considered one of the most significant creations of gothic architecture. The first stone was laid in 1386, the construction of the cathedral was completed in the XIX century. Interestingly, the cathedral was erected from the most valuable Candolian marble, and not from the usual red brick.
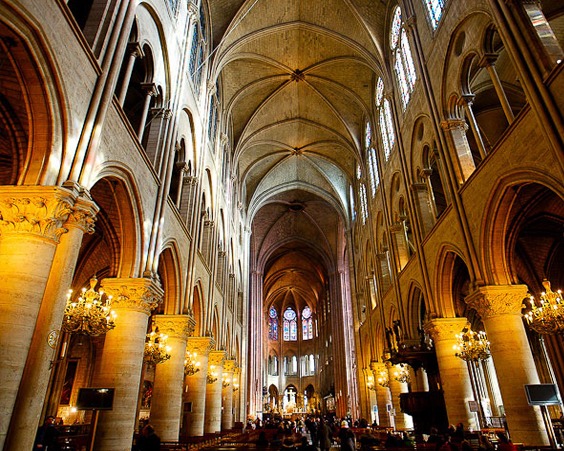


The Cathedral of the Parisian Mother of God is considered one of the most famous monuments of gothic architecture, and the Hugo himself. Construction of the cathedral began in 1163 and ended in the middle of the XIV century. One of the greatest relics of Christianity is stored in the Cathedral - the crown of Jesus Christ. The cathedral was built on the money of the king, bishops, ordinary citizens and even prostitutes that promised that their gift would remain in secret.


Reimi Cathedral can be called the top of the French gothic architecture. The perfectly preserved Cathedral is proudly demonstrates visitors initial decoration and magnificent stained glass.


The construction of the Gothic Cathedral began in 1344 and ended in the XX century. The first temple on the site of the cathedral was built in 925, the little church was devoted to Saint Vita.
Bidermeier
Style Bidermeier (Biedermeier) - the first style of the middle class, arose in Austria between the Vienna Congress (1815), which crossed the map of Europe, and the revolution of 1848. Vienna becomes the city in Europe by the legislator in the field of fashion and art. The style of the bidermeer expresses the lifestyle of a typical burger - sentimentality, cleanness, the functionality of life and Protestant moderation in external manifestations. Biedermeier is the name of a typical Austro-German average man, a fictional literary character from poet Eichrodta poems (Biedermaiers Liederlust - "Miscellaneous Songs of the Glorious Meyer") (it. BiedErmeier - Words Game: "Nice (kind, honest) Mayer" from BiedEmann and Meier). Bidermeier is the style of succeeding bourgeois, primarily German and Austrian. It is characteristic of safety, intimacy, comfort and moderation.
Renaissance
heritage and return to antique forms in art - ordinary forms in architecture, realistic manner in painting with the development of linear and light prospects, round realistic sculpture and sculpted relief based on studying proportions human body and plastic anatomy. The ancient heritage in a new way was understood, first of all, in Italy, where the ruins of the ancient Roman monuments literally were lying under their feet.
Gothic
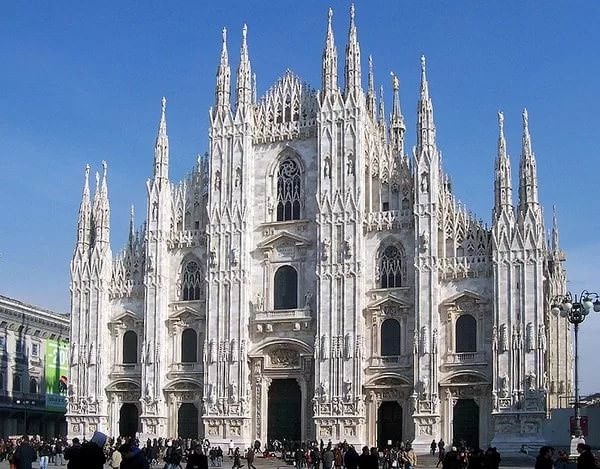

The main stimulus of the formation of art Gothic was the unique combination of the Christian worldview, the traditions of ancient culture, primarily the architecture of Rome, Latin writing, book miniatures, Roman-Celtic artistic crafts. The development of new style contributed to the rapid growth of European cities and trade. The focus of spiritual life was the city cathedral. The paradoxical feature of the Gothic style, the perfect forms of which demonstrate irrationalism, dematerialization and the highest, mystical expression, is that the occurrence (but not the reason) of its occurrence technical achievements - rational improvement of the construction structure.
Moorish style
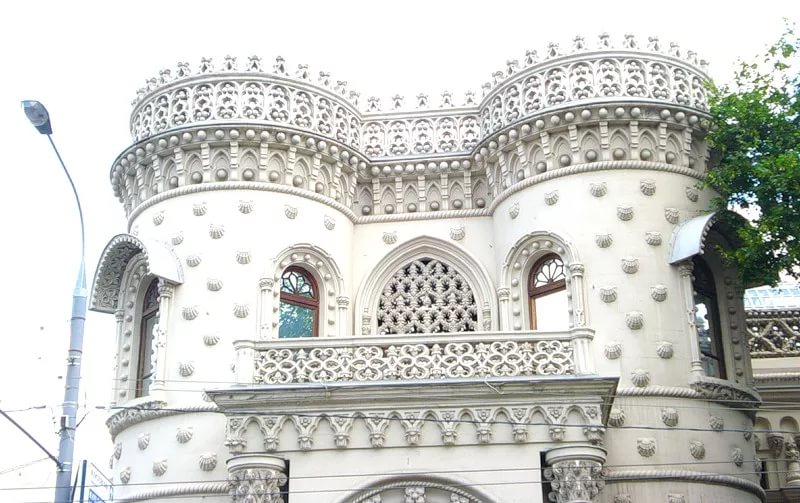

Mauritan style - (from Lat. Mauritania is an ancient Roman name of the area in North-West Africa from Mauri, Greek. Mauros is dark) - Neostil in European art of the second half of the XIX century. Unlike
the arts of the Moors (black people, Arabs and Berberov, so they were called in the Middle Ages) The term "Mauritanian style", to avoid confusion, should be attributed to the era of historicism and nonostille XIX century. The emergence of the Moorish style (more correctly - Neomavritsky is associated with the movement of national romanticism, which covered the country of Europe in the period after Napoleonic wars, and its roots can be found in the hobby of the Egyptian period of the Napoleonic Ampire. Architectural facilities: Prince A.Muruzi , Sintra, Portugal; Mansion A.A. Morozova on ul. Vozdvizhenka in Moscow. 1894-1898. Architect V.A. Mazyar.
Ancient Greece
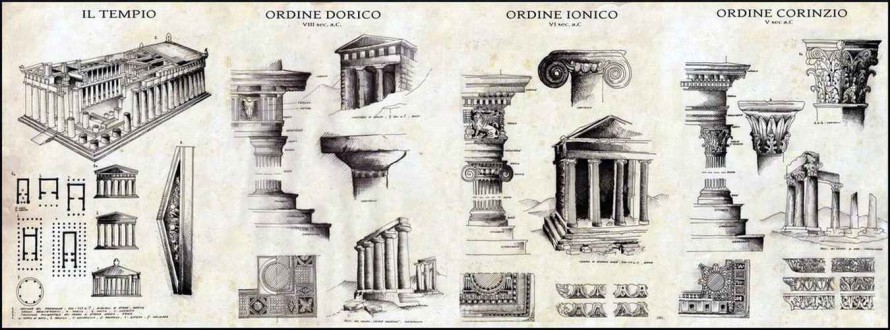
Overview of architecture and art Ancient Greece. Periods for the development of ancient Greek art. Styles of ancient Greek architecture. Doric order. Ionian order. Corinthian order. Architectural
ansumps of ancient Greece. Types of ancient Greek temples. Athenian Acropolis. Parthenon. Portico Caryatid. Ereheheton. The temple of Poseidon in Pestum. Temple of Zeus in Olympia. The influence of ancient Greek architecture on the architecture of Malaya Asia. The tomb of Malsol. Sculpture of ancient Greece - Miron, fidium, policlet. The stylistic unity of the architectural and objective environment of ancient Greece. The influence of democracy and mythological perception of the world on the architecture of ancient Greece.
Ancient Rome

General overview of architecture Ancient Rome. Buildings, facilities and architectural ensembles of ancient Rome. Composition of the characteristic Roman city ensemble. Forum Romanum. Forum Trajan. Column trayana. Arch
Title. Arch Constantine. Roman aqueducts. Aqueduct Marcy in Rome. Bridge Trajan in Alcantre. Aqueduct in the city of Nimea. The Imperial Palace on Palatine. Villa Adrian in Tibur. Roman theaters. Marcello Theater in Rome. Roman collosses (Colosseum) is the largest amphitheater. Roman terms. The terms of Caracalla. Diocletian terms. Pantheon in Rome. Ancient Roman basilica. Three-spoke Basilica Constantine.
Second ampir
The second ampir is one of the uncomplications in France after the second Rococo. The patrons of the new artistic style were the emperor and empress Evgenia, who wanted to betray the second rococo period of restoration of Bourbon and breathe life into the solemn and pompous art of the first empire of his great predecessor of Napoleon Bonaparte. The artistic symbol of the second empire was a huge building of a large opera ( Grand Opera.) In Paris, erected by the project Sh. Garnier in 1860-1875
Ampir

power) - a historical artistic style, first developed in France at the beginning of the XIX century, during the first empire of Napoleon Bonaparte. The chronological framework of the original French "Empire style" of a narrow, they are limited, on the one hand, the end of the board of the directory (1799; the style of the directory) or the year of the Coronation of Napoleon (1804), and on the other, the beginning of the restoration of Bourbon (1814-1815). Nevertheless, in such a short historical period, French neoclassicism, which has grown on natural interest in antiquity and enhanced by the ideas of enlightenment, civilian ideals of the beginning of the revolution, managed to be reborn in a cold, pompous, pompous, artificially embroidered by the imperial authority. Its basic elements, hoped from ancient art, were already kept in the classicism of the "style of Louis XVI" and were crystallized, in the "Style of the Directory".
Victorian style
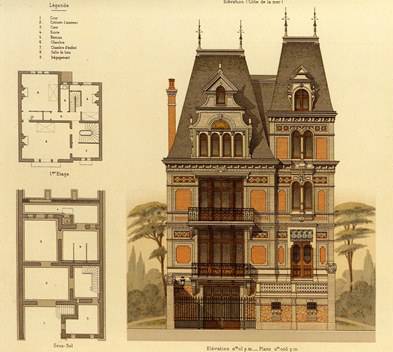
Victorian style - (English. "Victorian style") - the conditional name of a long period in the history of England's art of the second half of the XIX century, associated with the years of the rule of Queen Victoria (1819-1901) and Prince Consort (English, Consort - spouse) Alberta (1819- 1861). Victoria became Queen in 1837. This is a rare duration and sustainability, the Board covered more than half a century and turned out to be a "bridge" in the twentieth century. It was characterized by the "balancing between traditions and reforms" in economics and politics, which was reflected in the development of art. The British call this period briefly: "Victorianism" and believe that in aesthetics, he meant the triumph of pragmatism and materialism, which, however, is generally characteristic of "English style".
Colonial style

Colonial style - (from Lat. Colonus - Colon, Ancient Roman settler, land tenant, resident of the province). Colunt - the attachment to the land of the provinces settlers - consisted in the ancient Roman Empire in the III century. In the history of art, the term "colonial architecture" began to call the result of the construction activity of francs on the lands of Byzantium after the capture of Constantinople's crusaders in 1204. The colonists created a kind of architecture, in general, features a repeating Western European romance and gothic, but in a simplified and hardened form. Another example of "colonial style" is the art of the Catholic countries of Latin America of the XVII-XIX centuries. - Argentina, Chile, Peru, Uruguay, Brazil. The spanish and portuguese conquerors and missionaries the Baroque style with the elements of Mauritan art characteristic of Spain, the elements of Moorish art, Isabellino and Plater styles were gradually assimilated and under the influence of local ethnic traditions accepted fantastic forms.
Art Deco

AR Deco. ART Deco. - Reducing from the title of the exhibition "L" Exposition International Des Arts Decoratifs Et Indu-Striels Modernes "-" International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts ", held in 1925 in Paris). Artistic style of interior design, decorative and applied articles, Jewelry, clothing modeling, as well as industrial design and applied graphics.
Constructivism
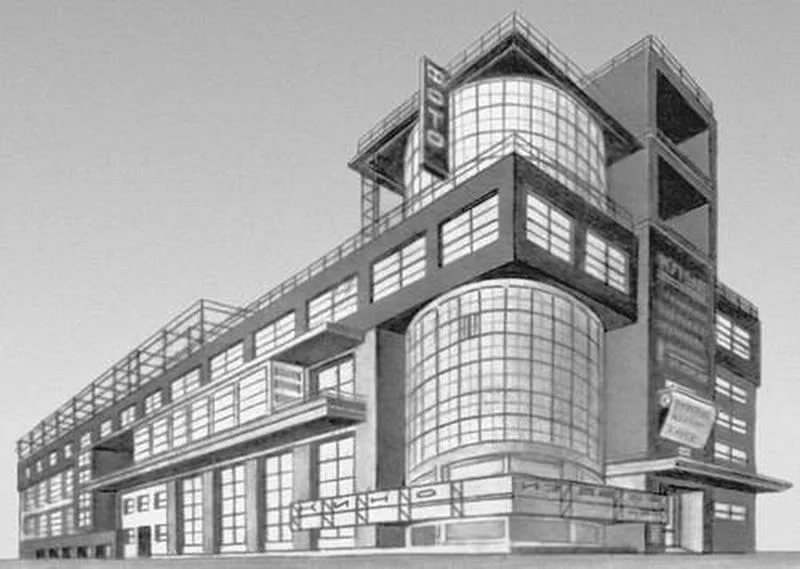

Constructivism - Soviet avant-garde method (style, direction) in visual art, architecture, photographs and decorative and applied arts, developed in 1920 - NAC. 1930s.
It is characterized by rigor, geometrism, laconic forms and monolithium of appearance. In 1924, the official creative organization of constructivist workers was created, whose representatives developed the so-called functional design method based on the scientific analysis of the features of the functioning of buildings, structures, urban planning complexes. Characteristic monuments of constructivism - factory-kitchens, palaces of labor, work clubs, house-communes of the specified time.
Rococo
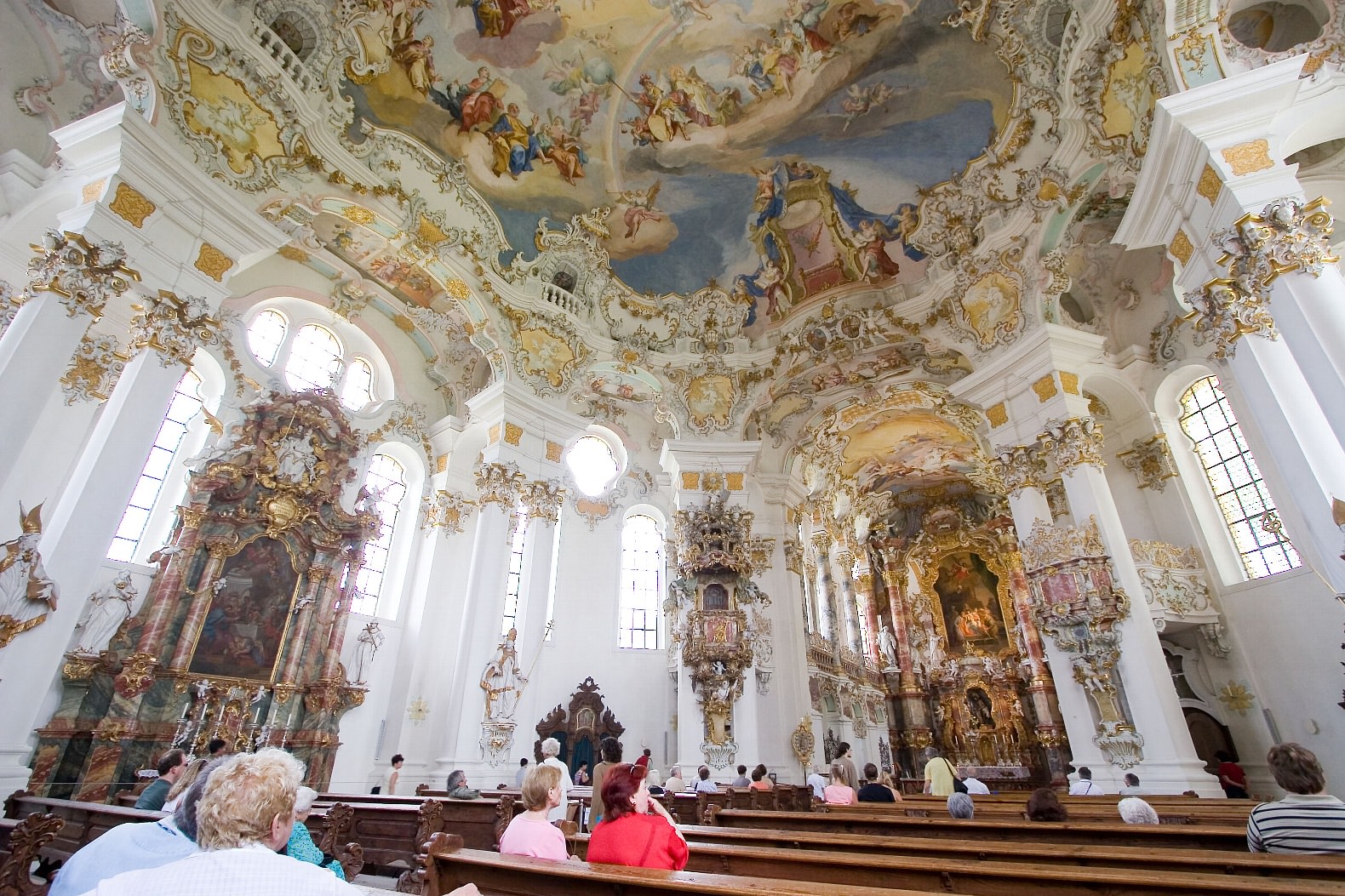

external forms and in its inner mood, this style is very different from the noisy and grand baroque. Rococo often reproaches in vague and lightness, but the highest refinement is hiding behind these external impressions, the brilliant artistic taste and perfection of the form. Rococo - the first lackless style, playful and elegant, considered non-serious and frivolous, who has become nevertheless very popular and has enormous influence on the development of all types of art, especially decorative. This is the first in the history of architecture and design of premises "cozy and carefree style".
Post-industrialism
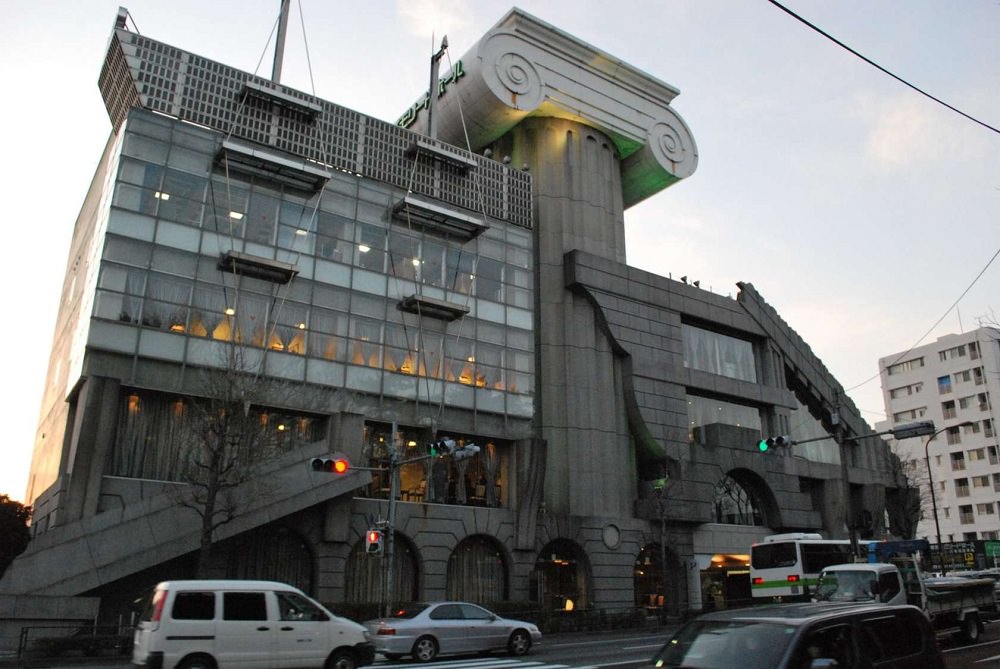

The term "postmodernism" in the current sense means a new direction, which in reality is part of the modernism continuing. In fact, almost all modern architecture can be attributed to postmodernist.
Russian retrospectivism
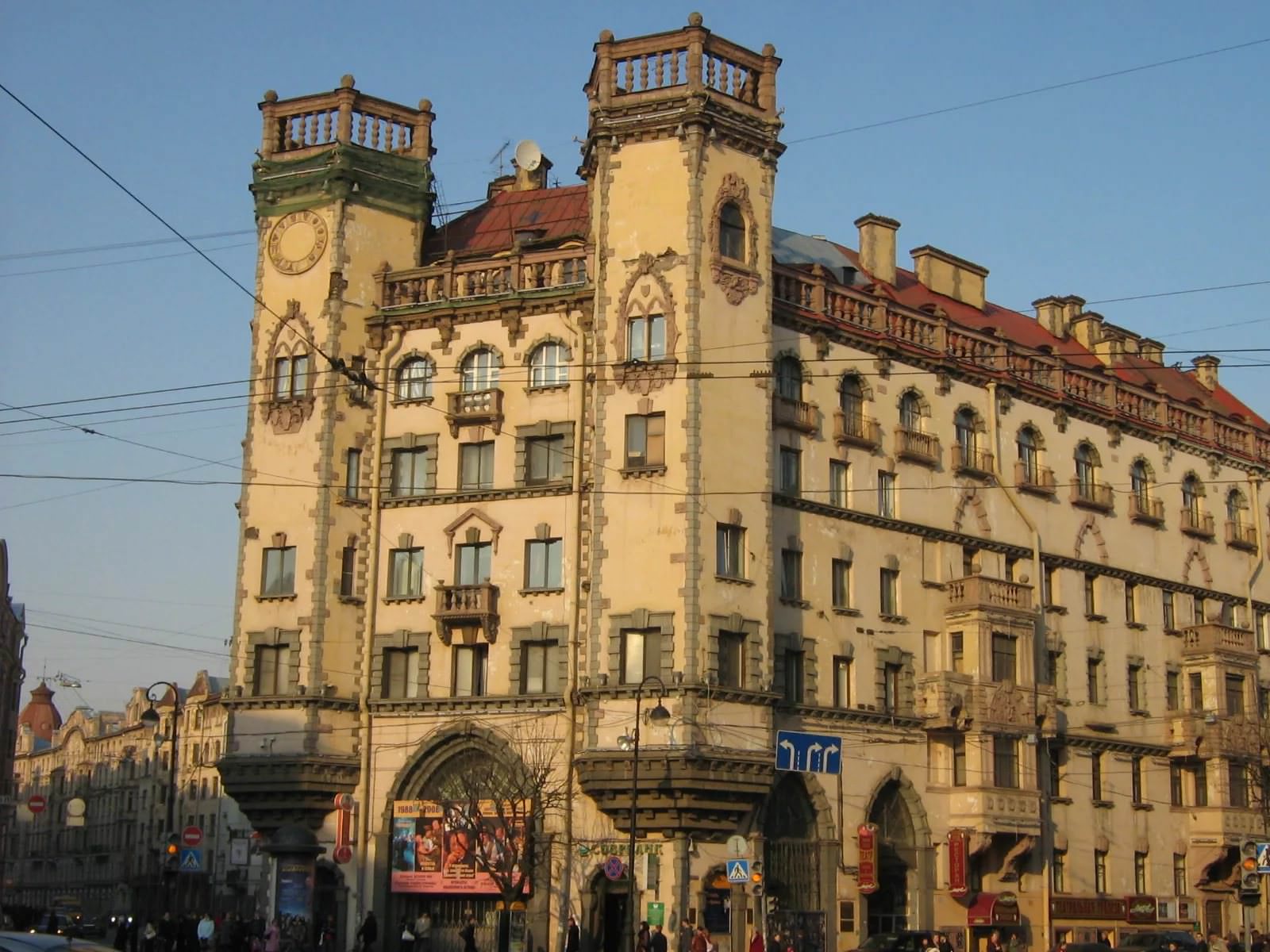

Retrospectivism - The direction in the architecture of the first half of the 20th century, associated with the revival of styles and the spirit of the architecture of the past epochs.
In different countries, various schools appeared to various architectural periods, in connection with this, the exact interpretation of the term "retrospectivism" does not exist. For example, in Russia, retrospectivism implies both neoclassicism and non-Russian style. In America, about the same period there was a flourishing of the American Renaissance, as well as the revival of the colonial style.
In art historian studies, it is customary to talk about retrospectivism in relation to the Russian architecture of pre-revolutionary years. At this time, the architecture experienced a new stage of understanding Russian classicism, samples of baroque, renaissance architecture were also copied. Such buildings were more often built in St. Petersburg (famous architects - I. Zoltovsky, I. Fomin).
The second branch of retrospectivism is associated with the revival of interest in the architecture of the Doperer Times, while the desire to preserve the purity of the style without distortion was traced. Neorussky style is presented for the most part in Moscow (the largest architects - V. Pokrovsky, A. Schusev).
ABOUTraganic architecture

integrity in the philosophical sense, where the whole treats the part as
part to the whole, and where the nature of the materials, nature of the destination, nature
in total, it becomes clear, acts as a necessity.
In contrast to the functionalism, the organic architecture sees its task in creating buildings and structures that reveal the properties of natural materials and organically inscribed in the surrounding landscape. A supporter of the idea of \u200b\u200bthe continuity of architectural space, Wright offered to bring the line under the tradition of the deliberate release of the building and its component parts from the surrounding world, dominated in Western architectural thought since Palladio. In his opinion, the form of the building should each time flow from its specific purpose and the unique conditions of the medium in which it is erected.
Bionic architecture. Bionic Hi-Tech

Bio Tech (Architectural Bionics) - the modern direction of architecture, the main features of which are borrowing natural forms. Often it is opposed to high-flow. Contrary to the opinion of the majority of bio-tech, it does not simply copy natural forms, but it tries when designing structures to take into account the functional and fundamental features of living organisms - the ability to self-regulation, photosynthesis, the principle of harmonious coexistence, etc. Bionic architecture involves creating houses that are natural continuation of nature not entering it into conflict.
In architectural and construction bionics, much attention is paid to new building technologies. So in the field of developing efficient and waste-free construction technologies, a promising direction is the creation of layered structures. The idea is borrowed from deep-water mollusks. Their durable shells consist of alternating hard and soft plates. When the rigid plate cracks, the deformation is absorbed by a soft layer and the crack does not go further.
High-tack
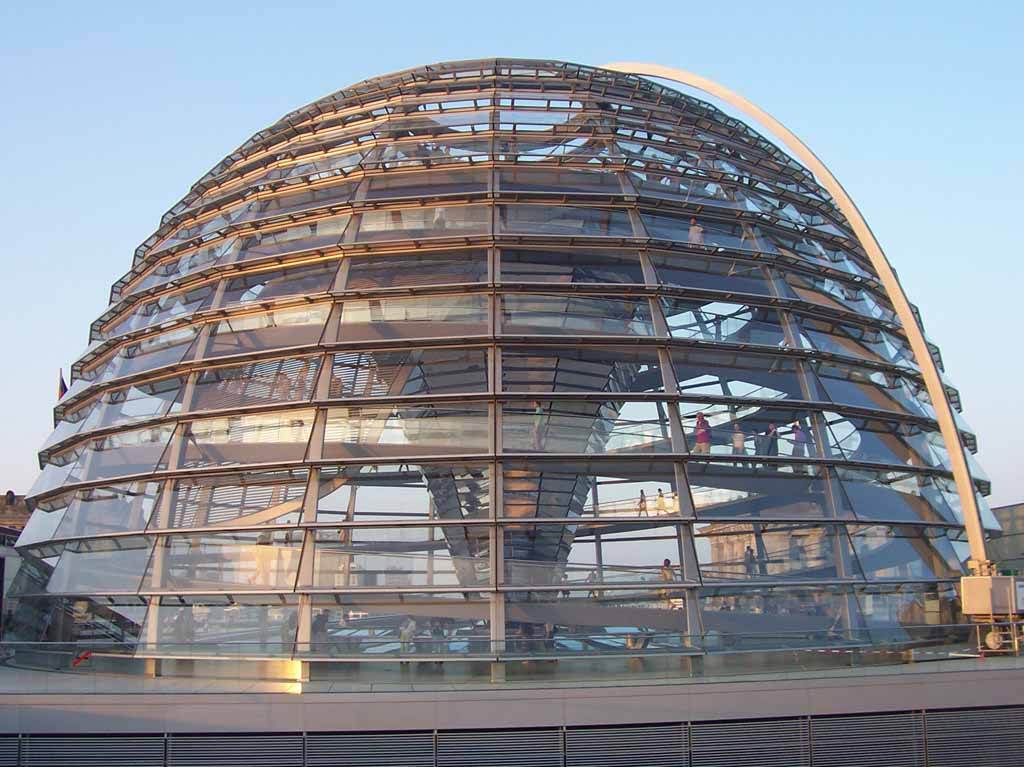

Modern High-tech is the synthesis of architecture and science. In the world, permanent
increasing speed Architecture High-Tek as far as possible
express the long-standing dream of a person - overcome the time and space.
Although the architect works closely with an engineer closely with an engineer, this direction actually lies outside the engineering tradition as such and is primarily a matter with experiments in the field of technological picture. However, on the threshold of the new millennium, the High-tech architecture solves sufficiently pragmatic tasks associated with the problems of combining energy and resources, the environmental situation and modern functional and architecture requirements. Hi-Tech is not so much a form how much content.
Roman style

The main objects of architecture and construction, which is obliged to architectural practice in Europe romanesque style- Feudal Fortress, Monastic Complex, Basilical Church and Fortress City. The architecture of ancient Rome becomes the object for imitation, but significantly changed (due to an orientation). Huge influence on the formation of a new style of life provided
the arrival from the east of the Turkic, German and North-Iranian tribes (Goths, Huns, Alans). All these tribes were exclusively military lifestyle under the laws of military democracy, then creating temporary unions with each other, then speaking in the role of federals on the side of the residents of the old Europe (ie, the remains of the Roman Empire). The feudal house was the fortress, and the Christian temple. A significant role in the occurrence, and especially in the spread of Romanesque art played monastic orders, in large quantities arising at that time. Features of the architecture of Romanesque temples. Planning decision of monasteries. Development of romance architecture. Specific traits Romanesque style architecture. Romanesque arch and crusade. Construction features of Romanesque architecture. Development of urban settlements.
Modern

The main content of the period Modern The desire for the synthesis of various
sources, methods, styles, shapes and techniques. In comparison with the previous eclectic period, the principle of formation, and not formal, ensuring the integrity of the external and internal, ornamental and structural elements of the composition was more common. The desire for such integrity is the main quality of art of modern. Neorokokok, Neojet, neoclassicism, "Mauritan style", the non-Russian style or constructivism of the model of modernity are different from styles under the identity names of other historical periods. The term "modern" should be distinguished from the general meaning of the word "modern" and from the concept of "modern art", as well as from modernism. In the mode of modern, there was no single historical artistic style with the necessary integrity of formal signs. Therefore, under the word "Modern", it should be understood primarily a specific historical period, which includes various currents, schools and styles associated with common ideological aspirations. The phrase "Modern Style" is more specifically and denotes a separate stylistic flow in which the ideas of synthesis are most fully manifested.
Minimalism

postmodern art. Used in different values. Minimalism in the architecture is a direction striving to the extreme simplification of the composition and neglect of the decor for the sake of searching for ideal proportions and color ratios in basic forms. Minimalism developed in the United States in the 1950s as a reaction to expressionism with its emotional approach. Accents the chance of the ability to form (mainly geometric shapes), the rhythmic repetition of its elements. The most fully expressed in the works of Carl Andre, using modular building materials.
Pseudorussian style
Pseudorussian style It originated in the framework of the general lift of interest in the national architecture that reigned in Europe XIX century, and is the interpretation and stylization of the Russian architectural heritage. Currently, pseudorussian style is often mistakenly called Russian or ancient Russian architecture, although it does not directly inherit a Russian architectural tradition. Presenting a skillful stylization, the pseudorussian style was consistently combined with other, international styles - from the architectural romanticism of the first half of the XIX century. Up to the style of modern. It is one of the directions of eclectic architectural style historicism.
Modernism
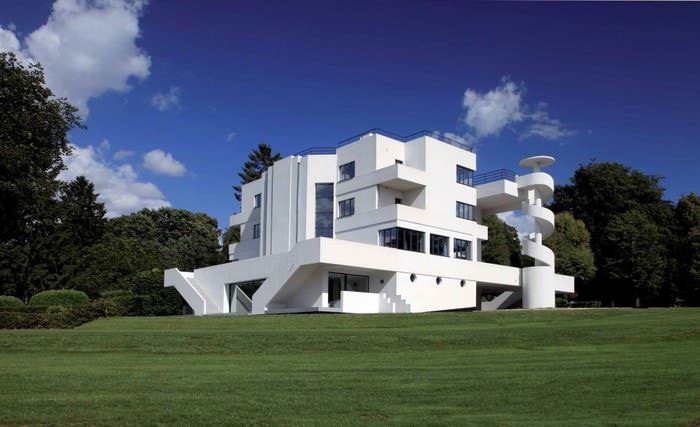

Wide space for architecture in modernism style opened in
the result of the consequences of World War II. Many European cities were destroyed. Wound the world of new formation. There was a fundamental ability to design whole quarters without a special binding to the "old" architectural ensemble of cities. The largest modernist construction areas occurred in cities with the largest destruction - Berlin and Gavr. On these giant construction sites, great international teams of famous modernist architects were worked - Hans Sharun, Walter Gropius, Le Corbusier, Alvar Aalto, Oscar Nimeier, Pierre Luigi Nervi, Marseille Breier, Auguste Perre, Bernard Zhrhusus and many others. The expression "modernism in architecture" is often used as a synonym for the term "modern architecture", but the last term is still wider. Modernism in the architecture covers the work of pioneers of modern architecture and their followers in the time interval since the beginning of the 20s and 70-80 years (in Europe), when new trends arose in the architecture.
Expressionism
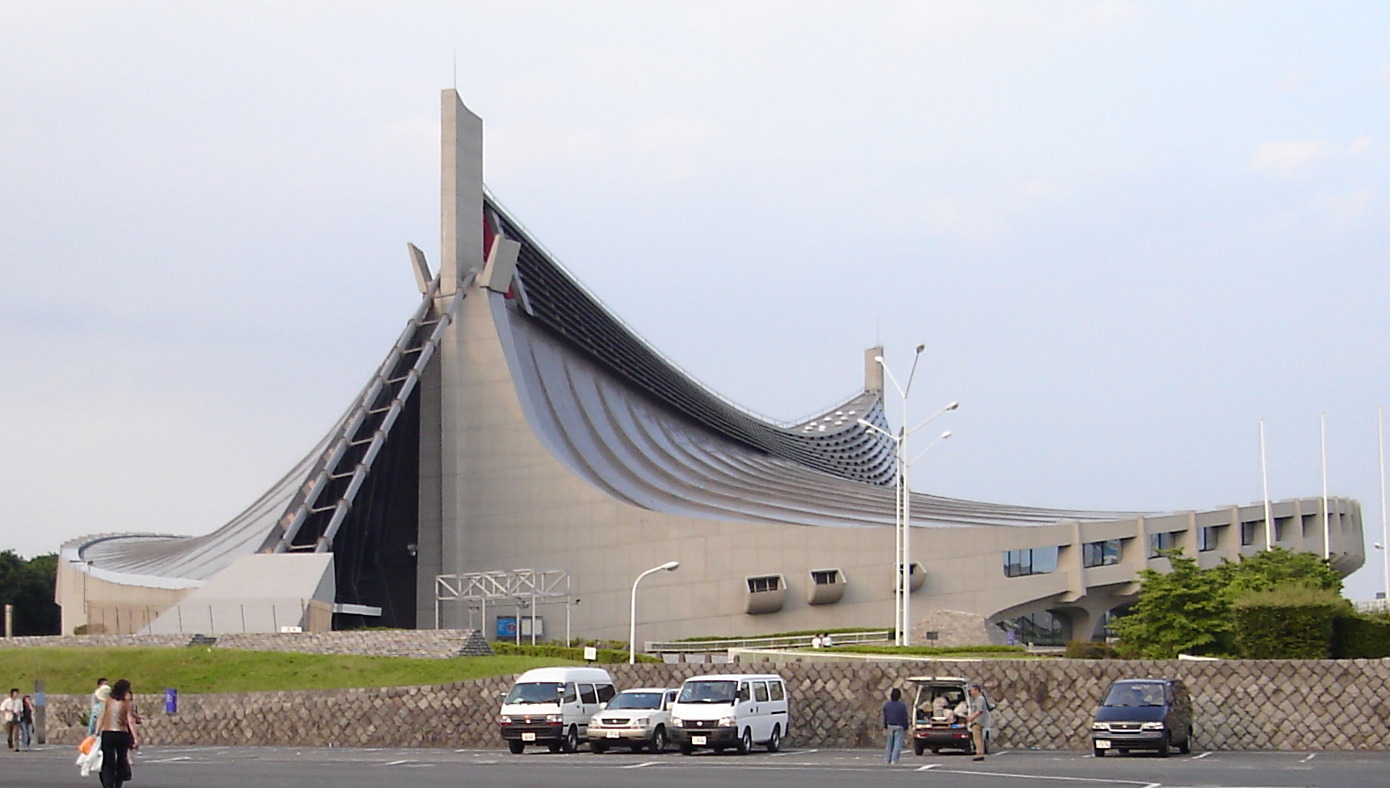

Expressionism - Another modification of architecture and interior, which came to us from the past. This style is expressed in distortion of traditional forms. Thus, the maximum emotional effect was achieved.
The homeland expressionism in architecture is considered Germany and the Netherlands. The birth of this style began at the end of the First World War. Then expressionism reflected a severe economic situation.
Expressionism in architecture is characterized by bright emotional expressiveness. It is achieved in the composition due to the pointedness, the detractive distortion of traditional forms in architecture. The most vivid representatives of this flow are E. Messelson, G. Sharun, Höring.
Among the most significant buildings built in this style can be called the "Enstein Tower", Church of Grundtvaig and Chilihaus.
Interior in the style of expressionism is already part of avant-garde, where there are no specific frameworks. The main thing is that the interior is not standard. Expressionism in the interior is achieved at the expense of furniture of bizarre forms, large sculptures, acute lines, bright colors, combining materials.
Expressionism in the interior is emotionality and grotescia.
Incoming

In the late 70s. interest in modernism is revived, and in the 80s he again
it turns out in the arena of the world architecture under the name of non-modestism. Keeping the advantages of modernism, inadenerism is exempt from a number of shortcomings of the latter. The works of non-modestism are not included in the traditional confrontation for the modern movement with the medium, and thoughtfully and organically fit into the context of the building. Keeping commitment to orthogonal forms, inadenerism is less ascetic in relation to color: this is not always a "white architecture", other colors of the spectrum are actively used, although, for example, an outstanding master of inadenerism Richard Meier (Richard Meier.) Stores dedication to white color, believing that " white color - Illusory symbol of continuity of development. " The following in the 70s began to be crucial for the formation of non-modestism. Penetration on the West of the information about the architecture of the Soviet avant-garde of the 20th year, which led in the 80s to serious hobby in his images and ideas, sometimes to direct borrowings.
Structuralism
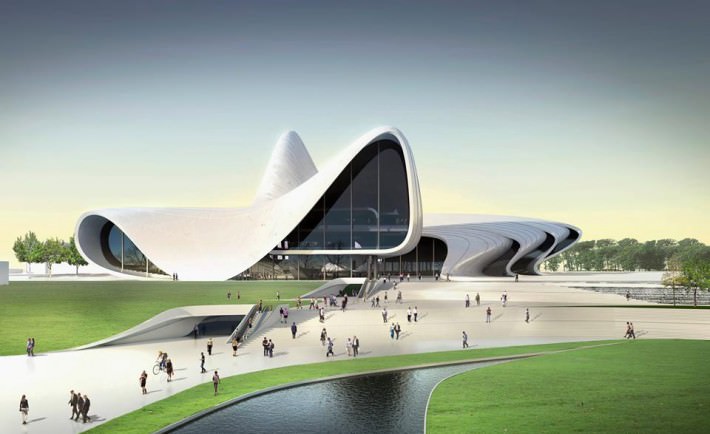

Structuralism in architecture - The current in modernism, which came to replace the international style in the middle of the 20th century. It is a bit from expressionism and organic architecture. This style combines the constructivism of the 20s and the style of Hi-Tech the end of the 20th century.
The architecture of structuralism creatively applies the bright possibilities of not yet tried, but carefully analyzed various structures. Architects, when designing buildings in the style of structuralism, are constantly used by already proven materials, such as wood.
Typical signs of structural style have become a non-standard idea, uniqueness, romanticism of past years, the accuracy of bends and lines, as well as the use of naturalistic outlines. The largest creators working in the direction of structuralism are architects who have created key structures in Finland, Saernin Ero and Aaalto Alvar from Finland. If we consider examples of the most bright buildings in the field of structuralism, this is the building of the Opera House in Sydney, as well as the Olympic Center in the capital of Japan - Tokyo.
Functionalism

Functionalism - Direction in architecture, characteristic of the 20th century. Originated in the mid-1920s. The main advantage of buildings built in the style of functionalism is considered the rapid of construction. In the USSR, his introduction was dictated by the desire to settle the Stalinist communals (low-seamy hostels).
"Five signs of functionalism":
- The use of lapidary rectangular shapes.
- The main material is a monolithic and precast concrete, glass, less often brick. The use of large unintended planes of one material. Hence the prevailing color gamut - gray (color of inactive concrete), yellow (beloved color Le Corbusier) and white. Lack of ornamentation.
- "Flat, if possible, operated roofs" - the idea of \u200b\u200bLe Corbusier.
- For industrial and, partly, residential and public buildings, the location of the windows on the facade in the form of solid horizontal bands is the so-called "belt glazing" - the idea Le Corbusier .
- The widespread use of the image of the "house on the legs" is the ideas of Le Corbusier, consisting in full or partial release of the lower floors from the walls and the use of space under the building under public functions.
Rationalism
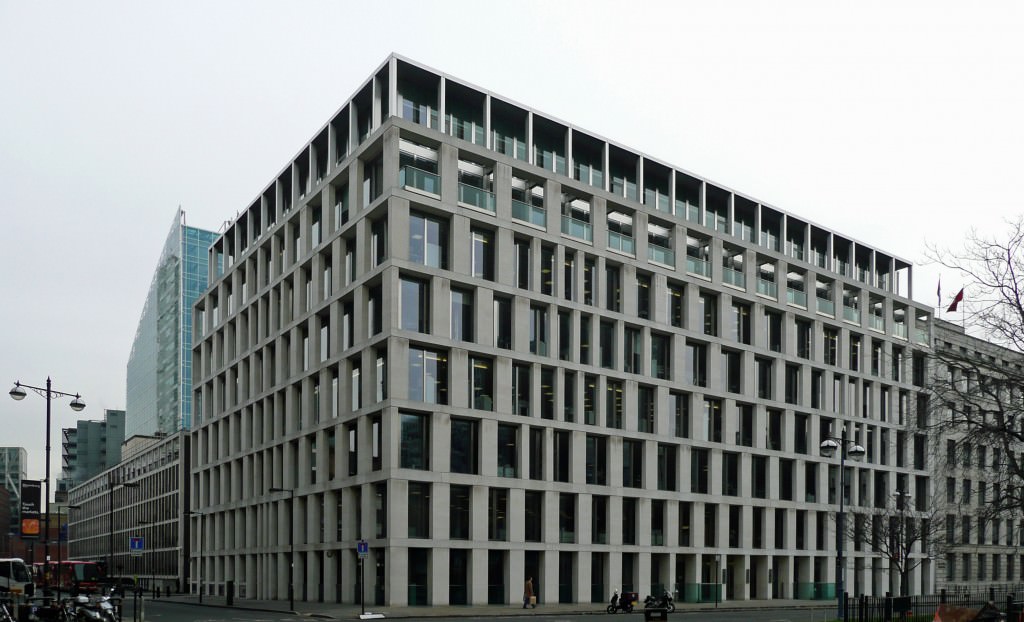

Rationalism - The direction in the architecture of the 20th century, for which the simplicity and rigor of forms are characterized, refusal of decorativeness, underlined interest in functionality. The heyday of rationalism is considered the twentieth - fifties, but certain features of this style are visible in later architects. For example, the main motives of rationalism - the use of straight lines, squares and rectangles, a game with proportions and color - are widely used by modern architects around the world.
The basic principle of rationalism is the unity of the architectural image and its functional conditionality. "The new architecture, real, should be based on logic, at a rational principle. New forms will receive aesthetic value only to the extent that they are advisable, "the outstanding Italian architect-rationalist Giuseppe Terrani in his manifesto.
In addition, representatives of rationalism from different countries of the world - from Italy and the Netherlands to the USSR, it was believed that modern architecture should be a tool for the upbringing and restructuring of society, the creation of a "new person", free from the heritage of the past. For the impact on the psyche, rhythmic repetitions of simple geometric forms were used, a game with color on large planes was used, the search for expressiveness in the field of architecture synthesis with other arts was searched. Also among the main techniques - asymmetry and the bet on such purely urban materials such as reinforced concrete, metal and glass.
About the bottom of the main properties of God - his omnipresents, so you can pray to an Orthodox Christian everywhere, anywhere.
But there are places of the exceptional presence of God, where the Lord is in a special, fertile way. Such places are called the temples of God or churches.
The symbolism of the temple explains the believing the essence of the temple as the beginning of the future kingdom of heaven, puts the image of this kingdom to them, using visible architectural forms and means of pictorial scenery in order to make the image of the invisible, heavenly, Divine.
The architecture is not able to adequately recreate the heavenly primise, at least because only some holy people were awarded the vision of the heavenly kingdom, the image of which according to their explanations cannot be expressed by any words. For most people, this is a mystery, which is only slightly ajar in the Holy Scriptures and the Church Tradition. The temple is also the image of the Universal Church, its basic principles and devices. In the Faith Symbol, the Church is called "Unified, Saint, Cathedral and Apostolic".
In some way, these features of the church can be reflected in the temple architecture.
The temple is a consecrated building in which the believers weak God, thank him for the benefits received and pray to him about his needs. Central, most often the most majestic temples, in which the clergy from other closest churches about common solemn services are called cathedral, or simply cathedrals.
By subordination and location of the temples are divided into:
Stavropigial - Temples located in the direct administration of His Holiness Patriarch and Synod.
Cathedral - are the main temples for the ruling bishops of this or that diocese.
Parish - Temples in which the services of local parishes are accomplished (the community is called the community of Orthodox Christians, consisting of clergy and laity, united at the temple).
Cemetery - either on the territory of the cemetery, or in close proximity to them. A feature of the cemetery temples is that funeral services are constantly committed here. The duty of local clergymen is the commission at the request of relatives of Lithium and Panir about those who are buried in the cemetery. The temple building has its own, established over the centuries, an architectural appearance with its deep symbolism.
European classification of architectural styles.
About renovy architectural styles:- Architecture of the ancient world
- Egypt
- Mesopotamia, etc. Antique architecture
- Greek
- Roman Medieval architecture
- Byzantine
- Roman
- Gothic New Time architecture
- Renaissance
- Baroque and Rococco
- Classicism and ampir
- Eclectic or historism
- Modern, he is art nouveau, Yuggendistil, Setsion and others. Architecture of the Newest Time
- Constructivism
- Art Deco
- Modernism or International Style
- High tech
- Postmodernism
- A variety of modern styles
In fact, there are practically no clean styles in architecture, they all exist at the same time, complementing and enriching each other. Styles are not replaced by a mechanical one for others, they do not become obsolete, they do not arise anywhere and do not disappear without a trace. In any architectural style, there is something from the previous and future style. Related building to a specific architectural style, we must understand that this is a conditional characteristic, since each work of architecture is unique and unique.
In order to attribute the building to a specific style, we need to choose the main, in our opinion, a sign. It is clear that such a classification will always be approximate and inaccurate. Medieval Russian architecture in the European classification does not fit into anything. Moving to K. russian temple architecture.
Rus took from Byzantium the established Orthodox religion, in which there were already a variety of types of temples. The lack of a stone construction in Russia did not allow to take as a basis the complex metropolitan system of Dome Byzantine Basilica. The sample for Russian temples was the four-and-six-star cross-dome type of provincial Byzantine temple.
Below are examples of a certain classification of Russian temple architecture with examples.
Architecture, its concepts and directions
Architecture (Lat. Architectura from Dr. Greek. αρχι - Senior, Main and other Greek. τέκτων - builder, carpenter) - art design and build buildings and structures (also their complexes). The architecture certainly creates a materially organized environment necessary to people for their lives and activities, in accordance with the modern technical capabilities and aesthetic views of society.
The architecture also call the appearance of buildings and structures, as well as the buildings and buildings themselves.
Architectural works are often perceived as cultural or political characters as works of art. Historical civilizations are characterized by their architectural achievements. Architecture allows you to be carried out by the life functions of society, while at the same time directs life processes. However, architecture is created in accordance with the possibilities and needs of people.
The subject of work with space is the organization of the settlement as a whole. This was separated into a separate direction - urban planning, which covers a complex of socio-economic, construction and technical, architectural and artistic, sanitary and hygienic problems. For the same reason, it is difficult to give the correct assessment of the architectural construct, not knowing urban planning. Almost all famous town planners had an architectural education.
Architecture - this is an art whose task is to form surrounding man Environments, the creation of functional structures in accordance with the requirements dictated by the concepts of aesthetics and beauty. Architectural structures must meet the three main requirements: Benefit, strength and beauty. Artistic images embodied by modern architects play a large role in human spiritual life, and the design, functional and aesthetic qualities of architecture works are closely related to each other.
Each historical period is inherent in certain types of buildings, which were determined by the materials and technologies used. therefore each era is characterized by its own styleFor which, in addition to materials and technologies, the constantly changing concepts about beauty and feasibility have provided great influence.
6. The main directions of architecture. If we talk about the development of architecture in our days, many architects allocate two directions in it. Firstly - This is "eclectic" or traditional architecture. This direction is characterized by a constant appeal to various historical styles while creating architectural forms. The second direction The development of architecture consider "modern architecture", which in search of new images appeals to high technologies (both construction and computer), uses the latest achievements of scientists and the most modern building materials.
IN modern architecture You can observe the complete freedom of ideas and opinions: today there are no priorities and styles, and all development concepts are equal. In recent decades of the twentieth century, and at the beginning of this century, we see the rejection of the previous styles and forms, as well as the tireless search and the use of modern materials, such as iron, glass, plastic, reinforced concrete. Modern architecture uses a wide variety of styles: constructivism, postmodernism, minimalism, kitsch, "techno", "High-tech", etc., as well as their combinations, sometimes quite bold.
The first direction of modern architecture can be called constructivism , or how is it more often called - functionalism . The adherents of this direction believe that the aesthetic side of the structure should be completely submitted to a functional purpose. In this regard, the significance of the beauty and any achievement of the previous epochs is denied. Functionalism It is not focused on the inner world of man, his individuality, but on the averaged biological and social needs. Therefore, architectural structures of this direction differ extremely simple forms, minimal surface treatment, limited to the colors. True, the advantages of functionalism should include small material costs of building buildings, which made it possible to embody the principle: more housing for the same money. Most of the architectural solutions of modern cities, with monotonous gray, inexpressive boxes of residential buildings, can be attributed precisely to the direction of functionalism.
"Architectural postmodernism" Also denies the need for an artistic reference, but in contrast, this style is trying to revive such principles for constructing the composition, as proportionality, symmetry and perspective. Postmodernism is guided by the principles of eclectic, connecting into a single elements of a wide variety of styles. At the same time, different styles can penetrate each other, creating original, affecting the imagination of the building.
In some countries, such as in Japan, the main criterion for construction can be called "Polyfunctionality" . Architectural structures of this direction are performed not only the function of the bed, but also are an indispensable element in ensuring human life.
A vivid example of such a building can serve as a "media library" (architect Toyo ITO), in which there is a complete harmony between the natural and artificial component. Such libraries and museums make it much faster to receive new information and attract many visitors to themselves.
Today in architecture and design is becoming more and more distribution "high tech" (High-Tech), characterized by the use of high technologies and non-traditional for the construction of materials. High-Tech uses a lot of glass and metal. Often, architects include different engineering equipment (pipelines, elevator mines, air ducts, etc.), which gives structures a certain technocratic look.
In recent decades, we can observe an increasing development of the so-called "Bomorphic" direction In modern architecture. The development of this direction has become possible solely due to the active use in the architecture of the latest computer technologies. This area can be attributed, for example, the famous Museum of Goggenheim, which is located in Spain. An American F.Garya was designed by this Museum, who first applied modern computer technology in the architecture.
Outside, the museum resembles the spiral spiral, although some argue that it looks like a blooming flower. Complements this effect of titanium sheets. Inside the building is a labyrinth with curved walls, large windows and an abundance of chrome-plated accessories.
As we can see in modern architecture, many different styles, directions and schools that are not limited to the creative imagination of the architect, providing extensive opportunities to make our life brighter and expressive.
7. Building buildings, their volume planning and structural elements
The internal volume of the building consists of spatial cells (premises) of various purposes located in a certain order. Each such room (living room, kitchen, staircase, etc.) differs from another area, shape, and sometimes height.
Volume-planning solution - This is a system for placing premises in the building. Spatial cells are called volume-planning elements. In residential buildings such elements will be: rooms, kitchens, staircases and other rooms formed by the structural elements of this building (walls, overlaps, etc.).
Floors - Rooms located between overlaps.
Depending on the location of the floors, it is distinguished: overhead - at the location of the floor above the level of the soil (sidewalk), basements - when the floor is bleated, more than half the height of the room below the soil level; Semisillary (basement) - with floor bulk (below ground) less than half the height of the room; Attic indoors are located inside the attic.
Thus, the volume-planning elements shared the internal space of buildings on individual floors and rooms.
8. Building-planning structure A system of combining the main and auxiliary premises of the selected sizes and forms into a single holistic composition is called. According to the signs of the location and interconnection of the premises, there are several volume-planning systems of buildings.
ANNICULT SYSTEM Provides direct transition from one room to another through the openings in their walls. This system allows you to create a building of a very compact and economical structure due to the absence or minimum volume of communication rooms. All major premises in the building during an imbuilt system are passing, so it is applicable only in exposure buildings - museums, art galleries, exhibition pavilions, etc.
Horizontal Communication System Provides a link between the main premises through communication - corridors or gallery. This allows the main premises to design disadvantaged. The planning system with horizontal communication premises is widely used in the design of civil buildings of various purposes - hostels, hotels, schools, hospitals, administrative buildings, etc.
Section system It is the layout of the building from one or more single-character fragments (sections) with repeating floor plans, and the premises of all the floors of each section are associated with common vertical communications - a staircase or staircase and elevators. The sectional system is main in the design of apartment residential houses of medium and large storey.
High System It is based on the subordination of a relatively small number of utility rooms to the main hall, which determines the functional purpose of the building as a whole. The most common housing system in the design of spectacular, sports and shopping buildings is the gym, an indoor swimming pool, a cinema, an indoor market and other system use for buildings with one or more halls.
Atrium system - with an open or indoor courtyard, around which the main rooms are placed, associated with it directly through the open (galleries) or closed (side corridors) Communication premises. In addition to the traditional use in the southern housing, it is widely used in the design of low-rise buildings with large halls - covered markets, museums, exhibitions, as well as in school buildings, high-rise hotels and administrative buildings. The advantages of the system with open courtyards are a close relationship between the necessary and closed spaces necessary according to the technological scheme.
Mixed (combined) system, including elements of various systems, occurs mainly in multifunctional buildings.
The development of a volume and planning solution is carried out on the basis of the scheme of functional processes occurring in the building, and the most convenient links between the premises and their minimum volume should be provided.
Constructive building structure Call a set of interrelated structural elements - foundations, walls, overlaps, roofs, etc., performing various functions in the building.
The following requirements are presented to constructive elements of buildings:strength and stability; Functional feasibility; durability and fire resistance; architectural expressiveness; convenience of operation; manufacturability; economic expediency.
9.Public buildings and their complexes - This is an artificial medium in which one or more processes of public vital activity of people proceed; This is a limited space design space intended for a short-term or long stay in it and protect them from the effects of natural factors. The main factor, the basis of the volume-planning solution of public buildings and structures is the functional purpose, i.e., the social activity of a person for which the building is built. Any process as a single cycle is characteristic of the features that depend on its functional and technological nature, the number of people participating in it, the necessary improvement, equipment, furniture, and in general from the organization of internal space.
When designing major public buildings, public and socio-shopping centers, characterized by many different internal spaces, it is advisable to carry out the so-called functional zoning, that is, the breakdown on the zones from homogeneous rooms of the premises, based on the generality of their functional purpose and internal relationships. Public buildings are designed for temporary stay of people in connection with the implementation of various and diverse functional processes of rest, life and labor - training, sports, entertainment, spectacles, food, medical care, trade, management, etc. In accordance with the appointment, public buildings are divided into different kinds - educational, catering, spectacular, medical, etc.
10.Fast functions of public buildings:
1) creating conditions for a variety of types of communication and public service residents of cities and villages;
2) Ensuring the daily, periodic and episodic needs of the life of the population (leisure and rest, personal consumption of goods and services, spiritual needs).
Functional structure Public buildings consists of three main parts: recreational and wellness, household and manufacturing. The building should most fully meet the processes that are implemented in it. The compliance of the premises of one or another function is achieved only when optimal conditions for a person are created, that is, the space is responsible to the functionally and technological process performed in the room. The combination of all elements and conditions characterizing functional technological processes determines the spatial organization, the size and shape of buildings and structures. For each type of public buildings, its functional and technological process is characterized, on the basis of which certain requirements are presented to design. So, functional and technological process - This is an exercise in time and space of the main function of the building, in which it is divided into the system of main and utility functions at all spatial levels of the building (Fig. 1).
Fig.1. The architectural solution of the building and the functional and technological process (according to V. M. Preteaksky)
Functional and technological processes can be common and specific. Common functional processes are various types of serving, labor and household activities of people found in all types of buildings. Specific functional processes are inherent in only one specific kind of activity of people (therapeutic and wellness, educational and educational, etc.) in each public building there is a main functional and technological process and secondary (utility) processes. Functional processes in universal public buildings are characterized by a sequence of implementation depending on the purpose of using the premises.
Each process is peculiar to their internal features arising from the nature of the action, the number of participants, the necessary equipment and furniture. All this affects the definition of the size and spatial organization of the form of the building. One of the important tasks of architectural design is the leading of functional and technological processes occurring in the building into a certain clear system. At the beginning, it is necessary to analyze the functional and technological processes and their conditions, to establish a sequence (sequence) of these processes, to determine the relationship between individual premises or their groups on this basis and then the composite scheme of the building as a whole. The functional circuit provides information on the structure of the functional bonds of the object and the sequence of occurring functional processes, it discloses the functional content of the architectural object.


