Vegetative reproduction with cuttings and leaves. Reproduction and landing: vegetative reproduction
Today we will talk about the vegetative reproduction (rhizomes, bulbs, clubnellukov, cornklubs, grain and cuttings) - the most common method of reproduction of floral perennials.
Vegetative reproduction
Vegetative reproduction has a number of advantages: it allows you to obtain plants identical to the maternal (with a seed method, the characteristic features of the variety are often not preserved at all or are not fully maintained), reduces the juvenile (young) period of plant development. Some perennials preferably propagate only in vegetative way, because It significantly reduces the deadline for entering new plants in the most decorative phase - flowering. With seed reproduction, such plants like saffron, peony, a dress, and others. She often comes on 4-6 years of life.
Vegetative reproduction can be carried out. rhizomes, bulbs, tubers, roots, grains and cuttingsused to obtain a new plant. Methods of reproduction for some plants are listed below.

Decision root
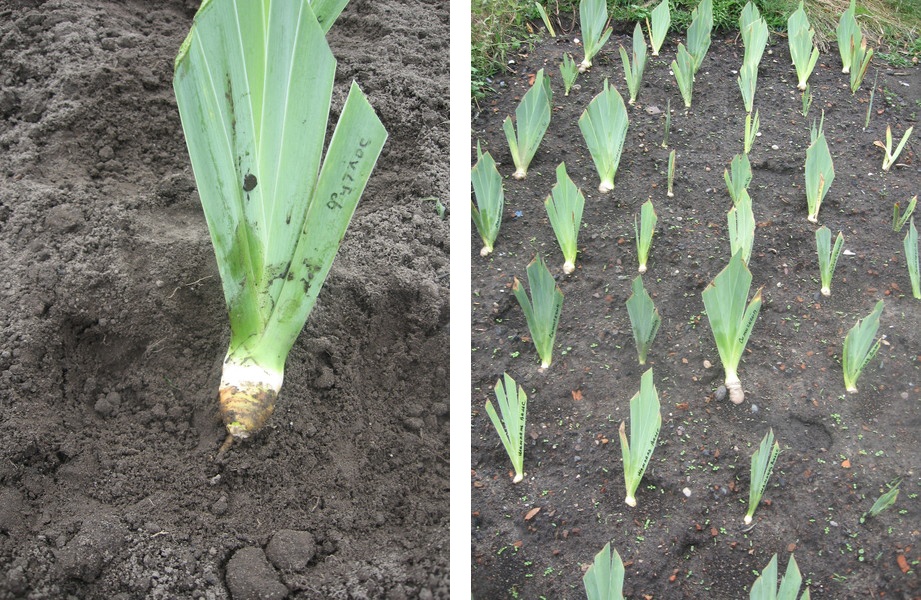
The most common method of vegetative reproduction is decision root. Rhizome is an elongated underground part of the plant, carrying the remains of leaves, kidneys and apparent roots. For reproduction of plants, the deceives are used **, obtained from the periphery of the old bush. To obtain high-quality planting material of irises, peonies, leafers, etc. It is better to multiply the plants aged 3-4 years. With age on rhizome develops a large number of The renewal kidneys, which eventually begin to compete for living space. As a result, the kidney bush is weak, and on the periphery are stronger and viable. Therefore, when dividing old bushes is better to use the material from the outer part of the root, and the central - delete. Some gardeners are the central part of the old bush, and after a while re-divide.
Most rhizuy plants have a loose rhizome, which is divided by hand or sharp knife. A very old plant or plant with a dense root system is cut in a shovel.

If you do not need the task of getting as much planting material as possible, it is better to share a bush by 3-5 decene. Plants from such decene can bloom in the first year, from the second year they form powerful, well-developed and normally flowering bushes. If you need to get many plants from one mother's bush, it can be divided into smaller decenes (with one kidney), but in this case, in the first two years after dividing the plants will develop slowly and bloom only on the second or third year. In order for such a plant, it is better to go, it does not give to bloom in the second year, rushing color pains. In case of fine division, a complete renewal of the root system occurs and in the future this plant will be stronger and more durable to multiply by a standard defense.
![]()
Plant division is better to carry out in a cool, shaded place. In order to stimulate the growth of young side roots in the roots obtained, the roots are cut by approximately 1/3 of their length. Long, uncircumcised roots when landing is difficult evenly distributed in the landing point, which can lead to their twisting, reinforcement and death of the entire plant.
The division and transplant of perennials spend early in the spring (April-beginning of May) or at the end of summer (the end of August is the beginning of September). With the spring duration of the division, the kidney did not move into growth, only trimming the roots is enough. With summer-autumn transplants, it is necessary to cut and overhead part of the plants, leaving about 15-20 cm, because The roots will not yet be able to provide plants with everything necessary, which can lead to illness and tightening flowering time.
The division of certain cultures often has its own characteristics. So, for example, when the peony is reproduced, you should not use large deteen with a large number of kidneys and many long roots, as it will hurt long and weakly bloom.
For faster, a large Iris bush was formed, the decene sit down around the circumference or rows, taking into account the area necessary for the adult plant, etc.

In the division of the loyal, the old roots are cut, leaving no more than 7-8 cm, the sections of the sections are sprinkled with ashes.
Before boarding the deceit, it is desirable to dip in the clay tank. For its preparation on 10 liters of water, a small amount of clay is added (so that after foaming to the chattering on the hand, a thin layer of clay remained), 1 tablet of heteroacexin or Packet Korevin (you can any other stimulant of the root formation, according to the instructions) and 1 kg of fresh manure. Components add in the specified order. The root-processed roots are necessary for 30 minutes to dry outdoors, and then plant the decens into prepared, moistened pit.
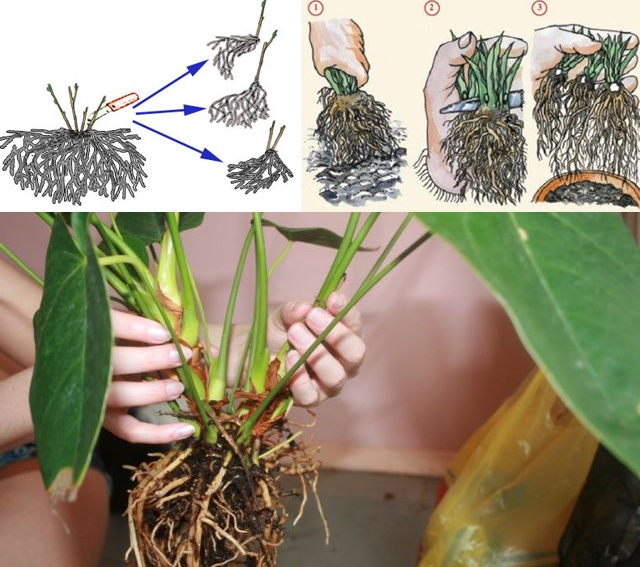
Division bush
Some Perennials (Priorices, Carnation, Perennial Lukes, Budrut Plude, Veronica, Oils, Ordinary, Bell, Pharmaceutical, Lily, Geranium, Major, Major, Margish, Medicinal Medicine, MEDODED Roofing, Customs Common, Peony Escape, Timyan, Sage, etc.) , forming subsidiaries, determine the division of the bush. If the bush is loose, then the rhizome is cut to the shovel, if a dense is, then all the plant is digging, inspecting, removing all dubious places, then sedient plants are separated by a sharp knife. When landing a decene in the landing pits add a compost or fertilizer of a long action. Dellets are planted immediately, on the same depth as before, but for a longer distance.

Reproduction of cuttings
Many decorative perennials reproduce with cuttings. You can use three types of cuttings:
- stems
- leafy
- root.
Best reproduce perennials stem or green cuttings, rooting them in open soil On shaded beds.
Terms of workpiece Chenkov
It is very important for success. the term of the billet Chenkov. It is determined by the nature of the growth and development of the uterine plant. According to these features perennials divide into two groups.
TO first group Types of active growing of young shoots over most of the growing season. These include:
- all perennials with winter overhead escapes,
- plants forming pillows and turns;
- rhizopy, corneupry, columnar plants with grassy shoots, blooming late in autumn or flowing early in spring, but differ in prolonged vegetation, the ability to form summer sockets of leaves and shoots.
This group of plants during stalling easily forms the apparent roots, it is possible to harvest the cuttings for a long time - from the end of April to mid-August.
Second group Combines views with active future formation at the beginning of the growing season, sometimes continuing before flowering.

Soothes for cerebrals are made with healthy, well developed, pretty young (3-4-year-old) plants.
At species first group Long shoots can be cut on a cutting of 3 cm in size and more (2-4 interstices). In this case, the lower cut is made at a distance of 3 mm from the leaf node, the top is higher than the sheet node by 6-10 mm.
At species second group Not all of the escape is cut on the cuttings, but only the top of a young escape with concentrated interstices and weakly developed leaves when the escape has not yet become a hollow. Such cuttings give a higher percentage of rooting compared to more weighing cuttings from the bottom of the escape. An exception is peonywhich take the bottom of the escape with the heel. In moisture-loving plants with large or small, but strongly evaporated moisture leaves, part of the sheet plate is shortened by 1/2 or 1/3.
Reproduction with stable or green cuttings
Many spicy-taste plants (wormwoods, sage, mint, lavender, cottberry, etc.) are breeding by shuffling (wormwoods, sage, mint, lavender, and driving plants. Pruning is carried out in June-July, cutting up the tops of the shoots over the stubby kidney. The end of such a cutting should be slightly weed. All leaves, with the exception of two or three top, remove. The cuttings are planted into the sandy substrate, which should always be moderately humid, and are covered with a glass can or plastic bag. They are rooted for 3-4 weeks.

In some cases, the cuttings are not cut, but climb from the parent plant. In May, nyondyarn is so breed. When his shoots reached a length of 5-7 cm, they are climbed or cut off with a heel, leaving at least half of the shoots on the plant. The cuttings are planted in greenhouses or greenhouses, on the ridges, powered by a layer of pure river sand, to a depth of 1.5-2 cm; It is plenty and covered with glass or film. The cuttings are rooted, as a rule, quickly, for 10-15 days. About a month later, they can be planted in an open ground.
Reproduction of leaf cuttings
Some perennials, in which the apparent or sleeping kidneys are formed not on the stem in the leaf sinus, and on the basis of the extended end of the stuff or on the basis of the leaf plate of the sedental sheet (as, for example, at nyonday), can be multiplied sheet cuttings.For rooting, only fully formed leaves with normally developed cutters are suitable. Depending on the size of leafy stiffs, they are planted at a depth of 0.6-1.5 cm, having a slope in one direction. Ridges make in shaded places. For normal root formation, they support the constant humidity of the substrate at the expense of regular irrigation and spraying.
Reproduction root cuttings
Perennials, which in places injuries roots are formed by pressing kidneys, you can breed root cuttings. When separating part of the root from the motherboard, the kidneys develop new shoots with a new root system. Root cuttings are the most reliable method of breeding At primroses. They are digging no later than the first numbers of May. The roots are laundered and somewhat healthy are cut off with a knife directly under a sheet rosette. The separated roots are cut into pieces of 5 cm, and the lower cut is made oblique. The cuttings are planted one in a loose substrate oblique cut down. The straight cut should be at the substrate surface level. In the spring of next year they are planted for a permanent place. For the breeding of the shine, it is preferable to use long root cuttings (30-40 cm). They are digged in autumn, stored in the sand until spring, then planted, burrowing into the soil with a lower end by 10 cm, and the upper, thickened - by 5 cm.
In principle, the technology of reproduction with root cuttings provides for digging of the sumps with the preservation of all roots. Then the selection of the roots with a thickness of 0.3 ° C2 cm, which cut on a length of 5-7 cm with horizontal rows on the pre-prepared shaded bed. From above covered with a layer of sand with a thickness of 0.5 media Earth -2 cm, and then compact and watered. As practice shows, cuttings, harvested in August, are rooted within a month, prepared in September it is better to maintain for spring rooting to avoid posting during autumn landing.
Reproduction of bulbs
Among decorative perennials, vegetable crops There are enough bulbous plants that can be multiplied by bulbs.
Bulb - This is a long-term underground body that serves to preserve the basic nutrients and renewing plants after the rest period. By structure, this is a modified shortened escape consisting of a diagonal stem and scales - modified leaves. At the top of the Donets, an upheat kidney is formed, from which there is an overhead stem, leaves and flowers, on the bottom of the Donets - roots. The bulb may be a different structure:
- tiled (lilies) consisting of individual scales;
- concentric with closed internal juicy scales and with a covering fine outdoor scales (most bully);
The bulb can be many years or annually replaced by a new one.
The bulbous plants are planted at a depth, 3-4 times the superior diameter of the bulbs, and with such a calculation so that there are no empty space under the bulb. It is important to correctly arrange a bulb when landing: kidneys up, and roots or donings down. After landing - it is plenty.

Reproduction of tubers, clubnellukov, root, gods
Clubneelukovitsy
Some perennials (crocosmia, crocus) are equipped with nutrients in clubneelukovitsa, which also serve as material for breeding. Clubneelukovitsa appearance looks like a bulb, but has another building. This is the scorched bottom of the stem. It can be covered with a dense shell or have residues of lower leaves in the form of dry scales. For the vegetative period, the clubnevukovitsa uses nutrients and dies with roots (for some exception). Top above it grows by replacing the clubnelukovitsa, and from the sides - kids. Due to the large number of club workers, the clubnelaukovitsa can be cut into several parts that form a normal clubnelluca, sometimes blooming in the same year.
Tubers
Everyone knows that Georgina, potatoes breed with tubers. Tuber - stocking underground organ. By structure is modified escape, but he does not have a dona, nor the only point of height of the stem; The renewal kidney ("eyes") are scattered throughout the surface of the tuber. Tolls are thick, stuck, of different shapes; As it grows, it may increase or decrease in size. For reproduction, whole tubers are used or cut them into parts with one or more "eyes".
Corneelectric and root
Pip (for example, Topinambur) - Powerful substances are formed in the resulting powerful roots. They depart from the base of the old stem from one point. During the growing season, thin roots grow from them.
For reproduction of plants rootfields (All well-known carrots, beets, radishes, etc.) leaves in the rootfolds-royaltics are cut into so as to leave stiffs with a length of 1-2 cm and the top kidney.
Diggingyou can breed the plants whose shoots lying on Earth give appreciative roots, and new plants develop from the kidneys. Such a rooted escape is cut into parts by the number of new shoots formed and sear as independent plants - weapons. Landing material can serve adult plants (mint, basil, chamber, lavender, etc.), which before the onset of frosts are transplanted into the greenhouses, greenhouses or pots.
Selection and treatment of planting material, landing
- No matter how much the way it is elected for breeding and landing, it is necessary to remember that the seating material should be healthy, free from diseases and pests: various root rot, nematodes, phon. Therefore, during the billet of planting material, the plants will be examined for infection and conduct special processing to avoid the spread of infection or pests.
- The quality of the planting material directly depends on how your plants will look like: a thickness of the pins, the size of flowers, fruits, and the like. If the rhizomes are to divide too small, planting underdeveloped annual seedlings, small bulbs or green cuttings of the first year of rooting, then you will have to reap the fruits of failure: the plants of the first year, and some species and in the second year there will be weakly blossom.
- It is not recommended to transplanted non-small old bushes of perennials. As a result of a long stay in one place, shoots become crowded, the stems are thinned and are made weakly designer, and the flowers and inflorescences are very small. Therefore, old bushes need to be rejuvenated by dividing or thinning, i.e. By cutting part of the stems.
- All perennials breeded by seeds or vegetatively (except in cases where rhizomes are divided into large parts), it is necessary before landing for permanent sites to grow for 1-2 years on well-processed, fertilous ridges.
- Landing perennials is as follows. In the intended place, the pit is digging, the value of which allows you to freely place the root system of the plant. In the pit makes humus. Pre-viewed roots (broken, drowned removed with a sharp knife, slices are sprinkled with coal powder) are evenly distributed in the pit, fall asleep with the soil, they are frumped tightly and pour.
- The depth of planting depends on the size and type of plant. The landmark can be the root neck of the old escape, which should be at the same level, on which it was before landing.
- Plants with a roasting rosette of the leaves are planted so that the center of the socket is not broken into the ground.
Methods of reproduction of some floral annuals, perennials and vegetable crops
Digging
Bulk Creeping, Drug Pepper, Gusina
Bulbs
Bows, garlic, saffron, goose onion yellow, crocosmia
Tubers, cornklubs, root
Topinambur, Potatoes, Stainless, Batat, Batat, Zelenets, Zelenets, Tladynaya, Koznenik, Tladiant, Radest Floating, Flying Edible, Clean
Cherenca
Chrysanthemum, Rosemary, Sage, Major, Halfweight Estragon, Clover Creeping, Lavender Non-Talted, Halfweight, Gorgeous, Rabbard, Veronica, Dubrovnik White-felt, Establishment, Ordinous
Seed from seeds
Garden
: artichoke, basil, cabbage, eggplant, zucchini, patisson, melon, tomato, pepper, leek, onion Schitt, Physalis, Bummy, Celery, Cappers, Amaranth, Mayran, Lagenaria, Momordik, Tladyiant, Anguria, Kotovnik, Beninkaz
Garden : Velhets, Margarist, Issop, Calendula, Nather, Perill, Lufa, Badan
Rowers
Garden:
artichoke, sour, mint, asparagus, oregano ordinary, thyme
Garden : Geranium Largenevarian, Rapunzois-shaped bell, coltsfoot, Pijm, Halfweight Estragon, Flashing Flaper, Cane, Yarrow, Hop, Rhodiola Pink, Aiir Ordinary, Altea Medicinal, Badan, Tolstive, Vassilnicker Small, Veronica, River Gravel, Nather Dudnik, Libraner Creeping, Establishment Big, Canorouper, Heel Drug, Coupling, Laboratory, Gusina, Rogoz, Meadow Core, Susak Umbrella, Hammerion Nickname, Cmin, Roll
Dividing bush
Garden:
onion tubular, shallow onion, bow drooping, shallot bow, bowstock, lovers, marjorane, rhubarb, rosemary, asparagus, thyme, oregano ordinary, sage
Garden : Daisy, bell, Gardening carnation, Peony evaded, wormwood Bitter, Lily, Veronica, Medication Medicine, Plusheliste, Granki, Dubrovnik White-felt, Issop, Pheckle, Swan Garden, Multicrees, Fennelhele, Molded, Orchard, Orly , Primrose, root fragrant.
For breeding wood plants there are not so many ways. And one of them, has long been well-known - reproduction with gangways. Its essence is to force the stalk or branch of the plant to be rooted before it (it) will be separated from the parent plant.
This method has advantage that distinguishes it from another way - reproduction with cuttings: it is not necessary to constantly control the surrounding conditions in order to maintain the viability of the plant until it is diverse. Almost all plants in the garden are well multiplied with the gardens: currants, gooseberries, viburnum, black raspberry, grapes, lemongrass, actinidium, dating, black elder, Clematis, Kizvatis, Loche Silver, Chubuschnik and many others. And with this method, it is possible to preserve old favorite varieties.
As with any method of reproduction, it is important for the molds to correctly select shoots, as well as create the conditions under which the formation of roots will begin. Plants that we want to breed, you need to celebrate from spring.
![]() The escape state is noticed that powerful, good growing shoots are well rooted. It is usually young annual strong shoots that are also easier to bend to the ground.
The escape state is noticed that powerful, good growing shoots are well rooted. It is usually young annual strong shoots that are also easier to bend to the ground.
Light - it was found that the roots begin to grow only after the light stops the light to the cerebral stalk. The earlier it is to cover the stem from the light (to cover the soil or dip), the stronger the plant will have a desire to grow. It is believed that the delay with extracting is one of the main reasons for the failure with the rooting of the messengers even in powerful shoots.
The soil is the land where the root of the escape will be prepared especially. The soil should have a good drainage, so that the tanks do not flick, good moisture-holding ability, to be "air" and fertile. In severe soil, peat, sand. The earth is drunk to a depth of at least the bayonet shovel.
Warm - in the zone of future roots should be warm, so the gods are advisable to send to the side where more penetrates sun ray. However, you need to not forget that heat is useful only if the soil is wet. In a dry summer, rooted drains should be water.
 Property stimulation - the sevent of the formation of roots is to violate the movement of nutrients and phytohormones. For this, it is usually enough to bend a branch at right angles. In difficult crops, it is resorted to additional events, for example, the stalk tightly sink copper wire, or remove the ring of the crust, or make a bias of the cortex, or make-grooves along the stem before the wood - all this is done in places where it is necessary to provoke root growth. The prepared places of formation of future roots on a tank can be pre-treated with stimulants of root root of Kornin type. This will increase the rootability of 2-4 times.
Property stimulation - the sevent of the formation of roots is to violate the movement of nutrients and phytohormones. For this, it is usually enough to bend a branch at right angles. In difficult crops, it is resorted to additional events, for example, the stalk tightly sink copper wire, or remove the ring of the crust, or make a bias of the cortex, or make-grooves along the stem before the wood - all this is done in places where it is necessary to provoke root growth. The prepared places of formation of future roots on a tank can be pre-treated with stimulants of root root of Kornin type. This will increase the rootability of 2-4 times.
The stalks began to bother from the parent plant in three or four weeks to complete excavation. There are several techniques for performing reproduction.
Conventional letters
 This is the easiest and very effective method The reproduction of many plants in which the parent plant is damaged minimally. It is convenient for this method to take (or give) from the neighbors liked the varieties of plants. We are usually laid at the beginning of spring as soon as it becomes possible to process the soil.
This is the easiest and very effective method The reproduction of many plants in which the parent plant is damaged minimally. It is convenient for this method to take (or give) from the neighbors liked the varieties of plants. We are usually laid at the beginning of spring as soon as it becomes possible to process the soil.
1 Method: The selected branch or escape must be burned to the ground and mark its future position since 20 cm from the top. Then let go of the branch, and on a marked place to dig a groove with a width and depth of 10-15 cm, gradually reducing the depth towards the base of the bush. Then the branch is prepared to the branch (solenit, etc., dust dusty of the root formation), laid on the bottom of the groove, leaving outside the back up the top of about 20 cm long. If the stem resists the bending and seeks to straighten up, it must be pissed to the soil. Now you can float the soil stem. A little tamper and pour. And take measures so that the soil does not dry, especially, in arid periods. For example, cover the surface of a piece of rubberoid or films. The roots were formed on the drain, the rise of the top of the stem will be raised. The grooves are often called horizontal.
 2 Method: Can not dig the groove, but simply put on top on the prepared soil of the gag, the plotting to the soil, to fall asleep the earth. A holmik is formed, which is covered with a film so that the soil does not drive. Usually, the branch bent from the bush takes the arcuate position in this case, so such a chain is called the arc. In the fall, the stalk drag is cut from the parent plant. After 3-4 weeks, they cut the top of the eclipsed escape. If the tank has a good root system, it is digging in autumn or spring and plant on a permanent place. IN otherwise It is struck by another year, not touching.
2 Method: Can not dig the groove, but simply put on top on the prepared soil of the gag, the plotting to the soil, to fall asleep the earth. A holmik is formed, which is covered with a film so that the soil does not drive. Usually, the branch bent from the bush takes the arcuate position in this case, so such a chain is called the arc. In the fall, the stalk drag is cut from the parent plant. After 3-4 weeks, they cut the top of the eclipsed escape. If the tank has a good root system, it is digging in autumn or spring and plant on a permanent place. IN otherwise It is struck by another year, not touching.
3 Method: The grooves pinch to the bottom of the long and narrow groove. When new shoots are growing on them with a length of 5-10 cm, they fall asleep the earth in the form of a holloch. In summer, the soil is being plugged several times. In the fall, the branch is cut off from the uterine bush and cut into parts by the number of shoots formed.
Air chains
 This is also one of the old methods of vegetative reproduction. He was known in China for another 4000 years ago, so it is called Chinese. The method is as follows.
This is also one of the old methods of vegetative reproduction. He was known in China for another 4000 years ago, so it is called Chinese. The method is as follows.
At an altitude of 15-25 cm from the top on the shoot, the ring of the cortex is removed or the longitudinal cuts of the cortex before the wood are taken. It is useful to frozen this part with the Cornstimulator. Then, of the two handful of wet sphagnum make a lump around the processed place, wrapped it with a piece of black polyethylene film, edges grabbing sticky tape. Or put on the prepared part of the stem bag of a light-tight film, which is filled with a humid material - sphagnum, peat, sawdust, etc. Will the substrate does not swing and so that atmospheric moisture does not fall under the film. In warm weather, the roots are formed very quickly. The tanks are cut off from the uterine plant along with the substrate and plant in place - usually do it in autumn.
Spring for melting uses overwhelmed last year's shoots. At the end of the summer you can use semi-respected shoots of the same year. In the latter case, at a distance of 15-30 cm, the leaves are removed from the skewer's top and the above-described manipulations are made. To form the roots you will need the next season. This method is used to reproduce a large number of cultures, including difficult wood crops - apple trees, pears, drain, cherries, and even rhododendrons - at the same time the cornesological varieties are obtained.
Top molds
 This technique is used to reproduce blackberries, black-like raspberries and some other plants. In natural conditions, the growing tip of escape is often bent, falls to the ground, it is bold and gives rise to a new plant. In the garden in this way, the gooseberry and black currant on their own way - in winter, the snow bends them some branches, and I do not always manage to put them in a vertical position in a timely manner.
This technique is used to reproduce blackberries, black-like raspberries and some other plants. In natural conditions, the growing tip of escape is often bent, falls to the ground, it is bold and gives rise to a new plant. In the garden in this way, the gooseberry and black currant on their own way - in winter, the snow bends them some branches, and I do not always manage to put them in a vertical position in a timely manner.
Usually, in this method, it can be used with a bush only part of the branches, without interfering with the rest of the branches normally grow and fruit. Having burned the intended stem, there is a place on Earth, which touched the painting of escape. Then the soil in this place jumps up and fertilizes, the groove is made to which the stem tops are stacked and pinned. The groove falls asleep with the "head", is compacted, watering and hides from drying. And on three weeks on the surface of the groove, the top of the growing escape will appear. In the fall, the upper part of the rope with roots is cut from the uterine plant and transplanted at a permanent place.
Vertical challenges
 This method is used for plants with fragile, poorly rush branches, as well as when a lot of planting material of this variety is required, for example, to obtain special confuses for apple trees or for mass reproduction of currant, etc. Usually for this method, uterine bushes are prepared, which At the end of the growing season, the entire ground part of the stems are cut off, leaving a foam height of 2-10 cm. The next spring is, when the shoots have been reached 15 cm long, it is done (for example, a bucket-other fertile soil) so that all the sprouts are under Earth with Head. As further growth continues to gradually dip the stems, until they grow up to a height of 25 cm. The resulting land hill is maintained in a wet state.
This method is used for plants with fragile, poorly rush branches, as well as when a lot of planting material of this variety is required, for example, to obtain special confuses for apple trees or for mass reproduction of currant, etc. Usually for this method, uterine bushes are prepared, which At the end of the growing season, the entire ground part of the stems are cut off, leaving a foam height of 2-10 cm. The next spring is, when the shoots have been reached 15 cm long, it is done (for example, a bucket-other fertile soil) so that all the sprouts are under Earth with Head. As further growth continues to gradually dip the stems, until they grow up to a height of 25 cm. The resulting land hill is maintained in a wet state.
In the fall, when the leaves completely fall, the land from the melts is gently shaken. At the base of each escape, the roots are formed by this time. The borne tanks are cut off by a secateur from the parent plant so that no hemp remains, and immediately planted in place.
In the spring, the whole cycle will repeat. You just need to not forget to feed the parent plant with a full fertilizer.
Bal Senich
|| Sowing seeds in the open soil || Seedling || Lawn care || Lawn from seeds || Power || First steps in pruning || Pipher and step-down || Shining || Reproduction with tanks || Root chain || Berry cultures || Miniature fruit trees || Shrubs || Rusy perennials || Bulbs, rhizomes, clubnelukovitsa, tubers || Curly and crawling
And for experts and for beginners, this method will almost certainly provide a set of plants - for the garden and indoor.
It is easier to multiply strawberries by a mustache, until they are separated from the parent plant. As soon as the roots are formed, the mustache can be separated. The bushes of strawberries in a special barrel give a mustache at different heights, so that some pots require a brick stand.
The reproduction of grains is that escape or stem rooted while he is still part of the parent plant. It has an advantage over grinding: less risk that Escape will die before the formation of roots. Preparation for the process is simple, as the subsequent care, so that this reliable way can even apply newcomers. Weeping is a natural method of vegetative reproduction, the invention of nature itself. Blackberry, for example, shoots, drop off to the ground, and their tops are rooted. The branches of some trees, for example, beaks, often give roots at the point of contact with the soil, and Rhododendron will start roots and forms a new escape where his stem becomes contact with the ground.
Why do we need a gag?For reproduction, there are many reasons. First of all, many bushes and trees are very difficult to multiply with cuttings and other ways, and rooting the glasses can be easily. Examples of Rhododendrons, Magnolia, Gamamemis, Camellia, Pieris, Loch and Holly. Strawberries and a number of other plants have a new plant almost impossible to obtain in another way. For this occupation, you need a minimum of equipment and experience, not necessarily artificial heat (except for indoor plants). Not only those plants that are poorly multiplied with cuttings, but almost any shrubs and creeping plants whose stalks can be buried to the ground. The ideal time for this is the growth season, usually from the middle of spring until the end of the summer. Select the young, of this or last season, since old and weird will be rooted very long and reluctantly. From one bush, you can immediately take several shoots.
How it's done.First, you need to prepare the soil around, rustling or breaking it to the depth of 30 cm. Low a bit of large garden sand and a wet sphagnum peat or fibers from a shell coconut. Grind all lumps. Eugene processing: at a distance of 30 cm from the end tear the leaves, leaving a naked stem. Make an oblique incision "tongue" with a length of 5 cm, in about the middle of the stem. Scroll at the site level (at the site attachment). Begin the "tongue", fasten it with a chips or peasant and sprinkle with a hormonal powder stimulating the root formation. The processed part of the stem is now immersed in a 15 cm depth of 15 cm in the prepared soil. Fasten with a piece of wire covered in the shape of a hairpin, and make sure that the incision is still open. The top of the escape is behind the sand, so that it grows up, you need to tie up vertically to a short bamboo backup. Pressed part of the escape Pop the layer of Earth 15 cm and slightly compact. The soil around the propal stem must be kept wet until a good root system is formed.
Graduality.Roots are formed in the place where an incision was made. The stem is not cut until the root system is formed. This process can last up to a year in one shrubs (for example, forsilation) and from one and a half to two years in others. If, lifting the gag, you will find that there are no roots, return it to the previous position and compact the Earth. Carefully raise the tanks in the fall or early spring with small garden forks. If good roots were formed, cut the parent branch slightly above the roots. The rooted glasses should be immediately transplanted to another place in the garden. Either put them on the final place, or, if the place allows, in a smooth bed, where the plant can grow up.
Another way.The assignment of the tops is even easier and is used for blackberry, coumenic, Logano berries (raspberry hybrid with blackberry) and similar hybrid berries with long stems. It is carried out in the middle of the summer, using the stalks (whites) of this season. The soil is prepared in the same way as for ordinary chains. Just insert the end (top) of the scourge of about 8 cm into the soil. If necessary, fasten the wire bracket. You can also roighten the tops of a row of 9 cm deep, with a mixture of peat and sand. Pot plunge to the edge to the ground under the stem. In the late autumn of the same year, cut the tops of the stem (if they were rooted) and transfer somewhere in the garden. The best place is a special emergency bed, where young plants can be grieving.
Air pressure.Stems and branches of some shrubs and trees can not be burned to the ground. They can be multiplied by forming drags in the air. Prepare a young escape, like a simple gag, but keep an open incision, snapped into it a loud moss-sfagnum lump (it can be purchased in a flower shop). Take a larger piece of MCH and wrap to them the prepared part of the stem, securing the polyethylene film. When the roots appear (in one or two years), try not to miss it. Process the roots as already described. Remove the film, and leave the moss to not damage the delicate roots.
Air chains
Air chains are the most convenient way of breeding ficuses. The cuttings are not always taken on, in particular, because they need to be closed at a fairly high temperature, and it is quite difficult to provide.
Carnations for flower.No matter how unexpectedly, it sounds, reproduction with carnations (in the open soil) - a more reliable and easy way to reproduction than shilling. This plant is quickly degenerated, so it makes sense to "remove" in two or three years. Best time To do this, the end of summer when flowering stopped. Use the shoots of the current year until they started, each plant you can stick a few shoots. Initially, a manual garden fork slide a little bit around around. Then pour on the treated soil with a layer of artificial substrate for pots (for example, a substrate "John Innes") with a thickness of 5 cm. By choosing the escape without flowers, gently cut the leaves from its base. Then make an abscess 3.5 cm long. Do an incision through the sheet knot. Hormonal powder treatment is not needed.
Join the processed shoots into the ground, fixing on the place of the cooled wire. The incision on the stem must be ajected. Covering this part of the stem layer of an artificial substrate for pots (for example, "John Innes") 5 cm thick. Water the groove; Roots should appear after two months. Cut them from parent plants and leave on the ground for a few days so that they recover from the "shock". Then, forks, remove them and transfer them to the final place in the garden. These new plants will begin to bloom in the middle of the next summer.
Garden strawberry.The garden strawberry breeds creeping stems - mustes, at the ends of which new rabid is formed. Bushes strawberries, like carnations, quickly degenerate, and they should be replaced by young every three years so that the yield does not fall. If the mustache is not needed for reproduction, remove them. Usami reproduction can be carried out at the beginning and middle of summer. Always use for this the first raptice on the shoot, removing the rest. From each bush, you can stay five to six subsidiary plants. Cry the end of the Us to the Earth and secure the wire with a wire align right behind the daughter's chest. It is possible to root directly into the soil or in a shopped pot with a special substrate ("John Innes"). The substrate must be constantly wet. When the plant is well rooted, at the end of the summer or early in autumn, cut them away from the mustache and transfer to the diverse bed. The next summer you can wait for flowering and fruiting.
Houseplants.Reproduction with tanks are used not only for garden, but also for a number of indoor plants. For tree shapes, such as rubcomters, ficuses (Ficus Species), Croton (Codiaeum Variegatum), Philodendrons and Diffenbachia (Dieffenbachia Species), use the method of air regulations. This method is often used when these plants grow too high, and they have to be replaced with smaller samples. This can be done in indoor conditions in spring and summer.
Prepare a stalk with a length of 30 cm from the top, as described above ("how it is done"). The cut forming the tongue is made from the bottom up. Treat the hormonal powder, wrap the cut of moss and from above - polyethylene film. In the heat of the root will appear in a few weeks. Remove the polyethylene (but not moss!) And place the grooves in the pot of suitable size filled with artificial substrate or soil. If you can, for a few weeks, hold young plants in a well heated room. If you want, you can cut the parent plant about half or two thirds. Forming side shoots, it will become more lure and more attractive.
| Serpentine clamps creeping plants. Using this method, from one escape in the creeping plants you can get not alone, but several chains. It is suitable for Clematis, Wisteria, Humanities (Lonicera), Jasmine (Jasminum) and grapes. This is a variant of simple reproduction by leaning. Instead of rooting the escape only in one place, a long young escape is cheered in length in several places. Cleving plants can be rooted faster than shrubs - sometimes in just a year. We advise you to mark your chains with chopsticks so that you can find them. Expand the date to know when checking the roots. | |
 1. Take the young, flexible Escape of the Czczuchny Plant - here it is a honeysuckle - and put on the ground where you want to touch it. |
 2. Make oblique cuts with a sharp knife with a length of 1.5-2 cm. Make cuts close to leaf nodes. You can make several cuts. |
Not always and not all plants can be well and quickly propagated by seeds. Therefore, for a long time in horticulture and flower growing, the so-called vegetative methods of reproduction - with gag, cuttings, root siblings or mustes are used.
The reproduction of grains is considered to be one of the most ancient ways, because at one time he, apparently, was noticeable and borrowed from nature itself. And today, those who grow in their sites, for example, the gooseberry, know: I will not sleep a little, and a small neat bush turns into solid spiny debris. It happens because the lower branches of this shrub, barely touching the earth, immediately rooted and give rise to new shoots.
The rooted branch, which can already exist independently, but not yet lost ties with the main (maternal) plant and is called a molding. The main advantage of the reproduction of plants by gangways is that the new copy retains all properties and signs of the main plant, including varieties. It is well amenable to reproduction with tanks not only shrub, semi-staple, but also many tree breeds curly and ampel plants. Such is the formation, hydrangea currency, roses, carpenter., Beautiful, Ceanotus, Dale and many other plants.
The easiest way to produce one or more reproduction gifts is to go by analogy with how this happens in natural conditions. That is, press or pin down the root part of the escape to the surface of the soil and sprinkle with damp ground. And then watch regularly to respected the necessary conditions For the growth and development of the chain - water, loose, make the necessary fertilizers. For woody breeds to achieve a greater effect, they dig a special groove, which is placed in the bore escape, leaving its upper part on the surface. Both of these ways are called horizontal chain And they are used more often for crops growing in the garden, where enough space to turn around. Young 1-2 year old shoots are usually rooted better than old.
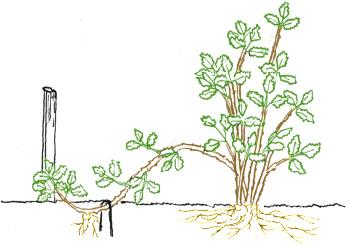
For potted plants, the method of the arcoid tank is more suitable, when the same escape is bent the arc and bother in a special container with a substrate or in a separate pot prepared for growing a new plant.
For reproduction of tall indoor colors, for example, drazes, you can use the so-called air chain method. At the same time, the new plant is grown directly on the trunk of the old. Since it is easy to sprinkle the land necessary for rooting the part of the barrel will not work, go to different tricks. Gently fix B. right place Polyethylene sleeve with a substrate, in which the root system of the future weapon will develop. Some use the old pot for these purposes, cut in half, and then connected by scotch, and the cylindrical part is suitable plastic bottle. The main thing to ensure that the earthen com did not shifted, did not save and was not overcooked. It is well suitable as a substrate various peat mixtures.
As soon as the root weight of the air chain will be comparable to the volume with the volume of the earthlom itself, the upper part of the plant is cut down just below the last root and determine the permanent place of "residence". From the parent plant or get rid of, or expect new young shoots on it. The method of reproduction can also be used for fakes, diffenbahia, phyloodendron, monsters, some species of palm trees and other indoor colors with large leaves. Tightening such plants multiply, as a rule, it is bad, because a large above-ground green mass evaporates too much moisture.
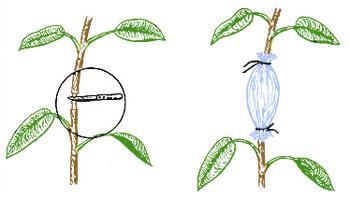
There are a number of techniques that allow you to speed up the process of forming additional apparent roots on stems and shoots for most plants. All of them are aimed at the fact that the plant has accumulated in the right place the necessary supply of nutrients and used them precisely on the root formation. On the weathered shoots, for example, before sprinkling or place them in the grooves, there are several shallow transverse cuts or one solid ring remove the bark of a width of 6-8 mm., Or tighten the stem with a metal wire ring. Another option is to make an abscessive incision for 2/3 of the thickness of the barrel. In the incision to insert matches or other struts so that it does not drag into a natural way.
In thin green escapes of the same effect, you can achieve the same effect, if you simply stretch them at an angle of 90 degrees. For stimulating the root formation and special chemicals - heteroaceksin, corneumine, etc. They are treated with both the cuts themselves and nearby spaces.
The best time for reproduction of plants with plants in the garden is spring and the beginning of the summer, when there is a strengthened education of new shoots. They are separated and decomposed with a maternal plant usually at the end of the season. But it happens that they leave for the next year, they gave a little greeted and strengthen.
- One of the oldest, simple and affordable methods of vegetative reproduction of plants, allowing without special hassle and additional structures to roighten the weed and growing shoots of both old and young bushes and Lian. It is very convenient for gardeners that appear on its site only on weekends.
To multiply the fanand very simple. To do this, it is enough to choose a parent plant and on one or more shoots to create favorable conditions for the formation of roots, and after rooting the new bush separate.
Typically, the hydrangea, the canbushnik, lilac, honeysuckle, actinidia, barbaris, pallets, roses, rosendrons, clematis and many other decorative and berry cultures are so cleaned. And even the trees.
To form roots on the selected shoot, it is necessary to create such conditions so that on the part where they will be formed, the light has not come. You can speed up the process of their formation by having suspended the movement of nutrient and growth substances by stalk. In most cases, it is enough to bend the escape, consolidating it in the ground.
To bookmark the messengersTypically take annual branches that have a high root formative ability.
The soil around the maternal plants and the one whose rooted stems are sprinkled should be loose, fertile and wet.
The root system will develop stronger, if in three or four weeks before disembodies separating the grooves from the uterine plant and to cut down the young shoots from them.
Depending on the technology of rooting distinguish arcuate, vertical and horizontal chain.
In reproduction of leaps From each rejected escape, one rooted plant is obtained. In the spring around the uterine bush, one or more pits of a depth of 10-15 cm are digging. In them and the one-two-year-old branches are flexing, pinching them into the ground in the bend. The holes fall asleep with the soil, leaving a third of the branch or escape on the surface of 10-30 cm.
Sit down to a permanent place of the rooted chain of the next year. Virtually all decorations and berry bushes and lianas can be multiplying.
Vertical discharges are obtained by high impairment Escapes growing on the maternal bush. This method of reproduction is used to obtain hazelnuts, viburnum, lilac, currant, gooseberry, clone apple trees.
First lay the uterine plot by rooting-day shoots, cropped at an altitude of 15-20 cm. In the first year of the plant, the plants grow freely and develop the root system. In the spring of the second year, the above-ground part is cut into a penet. The shoots grow from it are plunged by the soil when they reach a height of 15-20 cm. During the vegetation, the dips is repeated 2-3 times. In the fall, the bushes are intersecting and separated by the ukore-noisy shoots.
Reproduction horizontal chains- The most common way. It gives the opportunity to quickly get a large number of seedlings from the uterine growing. In the spring before the start of flowering around the Musician, in different directions, the grooves are digging a depth of 5 cm and remove the desired number of well-developed shoots. All the leaves are removed from them, leaving only the top and laid into the groove, piring to the ground.
The chains remain open while they will not grow vertical shoots with a length of 10-15 cm. Only then the grooves fall asleep with loose fertile land, leaving on the surface only their tops. As shoots grow, they are constantly dipped. In the autumn or future spring, the rooted tank is separated by the secateur from the parent plant with a part of the horizontal stem. In this way, lilac, rosa, mountain-tensulation, potassium, scamps, Clematis, Dale, Weigel, Papechatka, and many others are successfully breeding.
On a note:
Exotic appearance Together with unpretentiousness makes narine care very simple, and this plant is often choosing to decorate houses, offices and spacious halls of various institutions.


