Plants of our reservoirs. Ecology of higher aquatic plants
During the evolution, the turning point was the emergence of photosynthetic organisms. The appearance of chlorophyll can be attributed to the Archean period, and in Paleozoa, starting with Cambrian, there are already the first black algae (Marpolyia, Girwalle, Epiphithton, etc.). Susha in Cambrian, apparently, was deprived of vegetation, although, according to Arda, some cyanic algae, lower mushrooms and liver mosses, related to modern Ricciyami, could already occupy wet coastal biotopes. In the atmosphere at this time, an excess of carbon dioxide and lack of oxygen was observed. In the silver, the world of plants is already richer: a flora of pylofitis appears, characterized by a large variety of forms, is the first detected top green sushi plants. In Devon, the plants continue to conquer land: In addition to psulophytes, the first ferns, calmfits, clinolists, lepidodendrons, Cordateites appear in addition to the plylofitis. Last group - the first representatives of the class coniferous plants. On the shores of the lakes grew horsetails, ferns, sigillaria. In Carbon, Devonian Flora develops the most magnificent. By the end of the coal period, it decreases, and new types of glossopteathered flora and gifted ones come to her place. Strengthening the soil processes leads to a variety of cycle of substances, gives impetus to further evolution. In the Perm system, in later deposits of Paleozoic, further development receives seed ferns (Lesley, Gangmopteris, Tinifeld, etc.) and gamotional plantsSugar and ginkgov began to appear.
In the Mesozoic, the greatest variety of forms is marked since the Jurassic period.
The vegetation of Yura is absolutely not similar to Carbon. Sugdans, Bennettitis, Ginkgo, Bayer, Araucaria prevail in the forests of the Jurassic era, in water bodies - large chests - neochametes. At this time, the gas composition of the atmosphere significantly changed in the direction of increasing the oxygen content, which influenced (as one of the factors) on the further development of the animal world, primarily large vertebrates. The imbalance of the processes of the formation and destruction of the organic matter, which led to the accumulation of carbon in the form of combustible fossils in the upper devone and carbon, is gradually leveling, oxygen increases in the atmosphere. At the end of the mesozoic, in the chalk period, climatic conditions were created, suitable for the occurrence of flowering plants, which had a huge impact on the entire further course of the evolution of the organic world of the planet. In the Upper Layers of Alaska there are such aquatic plants as nymphs or pitches. By this time, there is a massive appearance of flowering plants that have formed characteristic associations and seized a wide variety of biotopes: plains, steppes, semi-deserts, mountains and reservoirs. The Cenozoic vegetation develops very abundantly, but strong cooling in the second half of the era, starting with myocene, significantly changed the amount and composition of plants. In the middle of the tertiary period in Western Europe There are already walkers, Rogoz, Reed, Source (Miocene). In Ukraine, Rogoz, Reed, Retarent, Rogolnik, Salvinia appeared at this time.
The change of ER and periods in the history of the Earth never led to the full death of the former plant world; Part of the past population remained and continued to exist together with new species. A characteristic example of this from aquatic flora can serve as modern horships - the remainder of the rich group presented at the end of the Paleozoic by several families and many clauses, of which only the genus Equisetum is preserved.
Flower aquatic plants, starting their development in the upper chalk, during the evolution process, they acquired all those features that allowed them to survive the harsh glaciation of Cenozoic in the conditions of the aquatic environment. Most families are higher water plants It appears at the end of the mesozoic, starting from the upper chalk, and refers to the era of the heyday of flowering plants with a decrease in the development of voted and already significant decrease in dispute plant. At this time, there is a gradual development and formation of modern flora. In the quarter-time period of the onset of glaciers in Europe, most modern plant species have already been distributed. However, significant weedsennesses of Europe (Günz, Mindelskoye, Rubskoy and Vurm) destroyed vegetation in vast territories, so that some types of plants significantly reduced their natural range or disappeared completely.
General scheme of the evolutionary route of aquatic plants: the sea - freshwater - sushi - freshwater - the sea.
For this reason, modern yewrite aqueous vegetation, living in fresh, brassing and significantly lower marine reservoirs, is customary to be called secondary water. Place of higher aquatic plants in general System The plant world is well illustrated by the scheme of phylogenetic relations of the orders of flowering plants.
The modern flora of higher aquatic plants of the USSR includes 224 species relating to 62 genera and 35 families. According to earlier data, in the aquatic flora of our country, over 260 species, obviously, due to the inclusion of a number of moisture-loving forms that are not directly related to the life of water bodies are noted.
The water medium to a certain extent smoothes the climatic differences that act on the ground flora. By systematic composition, the aquatic flora of all lake areas of the European part of the USSR is quite similar, the community ratio is 66-82%. Many common species occurs in the European part (except for the Arctic) and the Siberian region (59%), as well as in Central Asia and the Siberian and Siberian region (60%).
A mansion is distinguished by a water flora of the Far East, which has a low community coefficient with the views of other areas of the USSR, which is associated with its extreme specificity. A number of species are distributed in certain areas. So, the Middle Eastern, Siberian and South Views are allocated. Under conditions of mountain water bodies with low water temperature, flowering aquatic plants are usually not raised above the borders of the forests, the water flora of the Arctic is also extremely poor, although there are "their" species (buttercup of palmas, arctophila, etc.).
The relative homogeneity of the aqueous medium led to a number of fixtures of the most varying degrees. Many types of aquatic plants have the ability to evolve on land, which is expressed in the phenomenon of dimorphism, when the plants are dry from drying out, and continue to live, changed morphologically into the ground shape. Once in the aquatic environment, these species are able to develop in water. Such is water buttercups, a graonist, a bow, blindfold, the buckwheat of the earth. Ground forms are known even for real immersed guidatoes: water pines, uruses, pita, although they are essentially presthshot to adapt to temporary experience unfavorable conditions Drying reservoirs. Finally, there are types of aquatic plants, fully incurred their lives with a water medium. We note some of the basic devices of higher plants to the water habitat.
A relatively low water temperature (Northern and middle part of the USSR) causes the oppression of the intercession, prevails vegetative reproduction. Strengthened growth compared to land plants, since during a relatively short vegetation period, the NE should. Develop, give Yecesh or winter kidney and stock nutrients in underground organs for the winter period. The underdevelopment or lack of wood in vascular beams associated with the fact that the plant supported by water does not need such extent in the support elements as ground. Mechanical elements in a number of species that ensure the flexibility of stalks and leaves with a strong flow or excitement, are arranged, unlike the sushi plants closer to the center of the stem and the central axis of the sheet. Development of the system of aircraft cavities (Aerrenhima) contributes to improving gas exchange and maintaining a plant in a floating state. Reducing the root system or change its function. So, the root or rifle formations of researches are primarily an equilibrium organ. The well-developed root systems of the nithelies serve both to attach them to the soil and for the supply of nutrients. The large development of the body surface in relation to the mass, which is expressed in the presence of patch, dissected leaves, thin, long stems, or wide, but very thin leaves. The gas exchange of terrestrial plants is provided by the leaves through the dust, communicating with the system of interclause moves, Lakun. These moves take up to 25% of the total volume of plants. The leaves of immersed aquatic plants are deprived of the stittle, but their surface is permeable for gases and all gas exchanges through it. In aquatic plants with floating leaves, the Ustian has, and they are located on the upper side of the sheet. The number of wells compared to terrestrial species is increased. So, in a white pitcher, they are up to 400 per 1 mm2, in Rhoze - up to 1,300 per 1 mm2. The surface of floating leaves is covered with a wax chain, which does not allow it to be saved, in some types of edges of the leaf plate bend up, forming a semblance of a saucer.
Due to a smaller number of light in the water compared to land in underwater plants, partial PLI is observed. The total absence of a sheet parenchyma tissue differentiation on spongy and palisade. Chlorophyll is often found in the cells of the epidermis, which contributes to the best utilization of light energy. Some species among the cells of the epidermis have others, called hydropots, which have greater permeability for water. Namfeiy, in addition, there are special cells - Gautory, located on the bottom of the sheet, capable of intensively absorb nutrients and stock oil.
Heterophilia, discrepancy, is a phenomenon when on one plant is developing both typically underwater lisgrounds and typically air with a number of transitions (sophisticated, graonist, charter). Immersed leaves can be replaced by floating, completely different from the first (views of the Six. Nymphin, floating RDEST). The separation of mucus by special glands prevents leaching from plant nutrients, and is also a protection during the temporary drying of the reservoirs. Perhaps this mucus has a bactericidal protective effect, similar to the phytoncides of land plants. The overwhelming majority of higher aquatic plants are perennials. When overpowing, some of the species falls on the bottom of the reservoir, most winters in the form of rhizomes, tubers or wintering kidneys (tourones). Touriza morphologically represent valid shoots, Power supply to autumn nutrients, first of all starch, and immersed on the bottom of the reservoir. In the spring, the winter kidneys germinate and float to the surface.
These are generally the main devices of higher plants for habitat in the aquatic environment.
Even a short list of these features shows us how large the vitality of species capable of transferring significant adverse changes in the medium, adapting to new conditions. A detailed consideration of the characteristics of the organization of higher aquatic plants can be found in the monographs of the clutter. Despite the sufficiently narrow specialization of immersed aquatic plants, when, on the one hand, we observe the development of specific devices to the aquatic environment, and on the other - a complete or partial loss of a number of organs and systems (mechanical fabric, conductive system, etc.), the evolution of aqueous plants In general, it is impossible to consider regressive.
The presence of a stable mechanism of homeostasis allows higher aquatic plants to capture significant territories and have broad geographical distribution. Such species create populations adapted to the extreme conditions of the range, to significant fluctuations in light, temperature, etc.
In the garden, as in any complex living system, problems may arise. When leaving the flower beds or border, problems can be associated with plants (pests, diseases, damage to frost, lack of moisture, etc.) or with soil (insufficient drainage, poor structure, weed contamination, etc.). If you have a pond, the number of possible troubles increases twice, for they may concern the waterproofing of the pond, water, plants and fish.
The prospect may seem intimidating, because even the flower beds and borders contain in order quite laborious and expensive. If you begin to build the first pond in your life, then the thought itself is about the volume of the work of you subsequently maintaining it in good condition capable strongly shake your determination to bring the case to the end.
Fortunately, despite the fact that troubles can tide you from four sides, it does not mean that you will have to work without rejecting your backs. As we have already emphasized more than once, the care of the pond delivers less hassle than caring for a garden or garden. This is explained as follows:
The number of possible problems with which you will encounter when leaving the pond is limited, while pests and diseases that can hit flowers, vegetables and fruit treesreally a lot. In addition, as a result of their actions, garden and garden plants suffer stronger - each of us had to see the landing with trifle eaten slugs or caterpillars with leaves. Pests, affecting aquatic plants, not so much, but even less diseases. Severe damage to pests and disease diseases proper care Behind the pond can be avoided at all.
Fish, frogs, toads and tritons will be on your side, destroying many insects. Water herself will become your assistant: you do not have to water the plant growing in the pond, they will not threaten numerous pests, and we will not need to grip weeds with a roast.
Thus, care for the pond is not such a time consuming. But under one condition - if from the very beginning you will do everything right and then you will regularly fulfill all the necessary current work, which is described in this book. You will be able to avoid major trouble if you follow the six gold rules.
1 Right build pond Read this. Do not concrete a pond if you do not have sufficient experience and the necessary equipment. Better buy a flexible waterproofing film, which is the guaranteed service life of which is at least 20 years. Find a suitable place for the pond.
2 In advance everything thinking out Read the sealing of the pond. Make sure that your pond conditions are suitable for your chosen plants and fish. Purchase only healthy plants and - which is especially important - fish. One-only newly launched sick fish can infect everyone already living in the pond fish.
Concrete POND
The concrete base of the pond can give to flow if, in the manufacture of the solution, an improper ratio of components was chosen, a thick layer of concrete was laid enough for the bottom, or cracks appeared in the concrete under sediment. The first type of problems occurs when the walls and the bottom of the pond become porous. The reason for this may be the content in the solution of too much sand or sand is not the fraction, as well as the presence of numerous small cracks. In this case, it should be thoroughly clean the walls and the bottom of the pond and to miss them with two layers of sealant, thoroughly observing the instructions for its use. This repair will be enough for several years.
Another type of problems is associated with the formation of a large crack of 1 cm wide or more. Separate the crack using the chisels and the hammer to in the depths it was wider than on the surface. Remove dust from it, fill in the cement mastic and put the surface with the seal. Once it appeared, cracks in a concrete pond will be formed again. It is usually more reliable to sharpen them with a lime solution and then lay a flexible waterproofing coating. In any case, before the pond plants and fishes again, read.
Hard THE FORM
If you want to build a pond that could serve for many years, do not buy a rigid shape made of polyethylene by the method of vacuum stamping, since polyethylene does not withstand long-term exposure to sunlight. We need to wipe waterproofing materials with a guaranteed service life of at least 20 years. However, and in this case, in the coating of the bottom of the pond, cracks may appear, especially if the alpinarium stones are put on poorly fortified edges of the waterproofing film. Such cracks are not always easy to detect - you can try to define them on the sound, closing the surface of the film. For the repair of synthetic waterproofing films produce special sets of materials and tools.
 Flexible COATING
Flexible COATING
It does not make sense to top up the water in the pond, if there are cracks in its waterproofing. Water in this case will still be green, and the soil around the pond is wound. A crack or hole in waterproofing is not always easy to find. Filling from the pond water, surcharge its walls and bottom. Usually in the place where there is a cut or hole, the film suddenly pushes.
Flexible waterproofing films serve not for a very long time, although if a cheap polyethylene is calculated for only a few years, then a high-quality film from butyl rubber rubber can serve up to 50 years. It does not make sense to repair the cracked polyethylene film, it is better to replace it at a polyvinyl chloride or a film of synthetic rubber.
In case of damage to expensive waterproofing material, you need to purchase a set for its repair. Pump water so that it is lower than the place where there is damage. From a piece of films available in a piece set, cut the patch, twice the size of cuts or cracks in length and width. Declaring the pay and the place of damage to denature and wake the waterproof glue. When the glue snacks slightly, attach a pay to the desired place and scream its surface to remove air bubbles.
Put the load on the pay, as the instruction attached to the repairs is recommended. Do not fill the pond until the time specified in the instruction. Sit down plants and start fish in accordance with the recommendations of the article.
Aquatic plants are less susceptible to pests and diseases than ordinary garden plants. This is very by the way, since chemicals cannot be used in the pond - they can be harmful to fish, useful insects and other animals. The main method of combating pests and diseases of aquatic plants is to simply remove damaged leaves or a whole plant, depending on the degree of damage or severity of the disease. It is necessary to do this in a timely manner, without waiting until the problem comes out of control. Some pests can be washed off from plants with a strong jet of water from the hose into the pond on the feed fish. Another way is to cover the plant with a bag, under the weight of which it drops into the water and the insects sitting on the leaves will die.
Another common problem is the quality of flowering water lisms - is not associated with pests and diseases, but is due to the conditions of culture. Poor or not at all flows too young or incorrectly planted pita. The adult plant blooms poorly, if it is planted in a shallow water or, on the contrary, it was too early to immediately lowered to a greater depth. The quality of flowering may decrease if the plant lacks sunlight, it bothers the flow of water or on the leaves splashes from the fountain. If earlier the water lily is well bloom, and then the quality of flowering suddenly deteriorated, the plant should be filtered (special fertilizers in granules or in the bags in the soil in the basket). Maybe it's time to divide or transplant your pit. The article is told how to do it.
 Motyl
Motyl
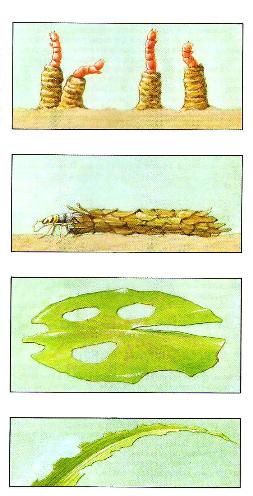
These larvae of non-applicant mosquito-dergun are almost in every pond, at the bottom of which there is Il. Red coloring of the moth is due to the presence of hemoglobin in its blood, which allows you to absorb oxygen from the water. At the bottom of the pond larvae build tubular houses from the soil, sand and organic residues. The length of the larvae is about 2.5 cm. The larvae sometimes leave their house and eat the roots of water lishes and other aquatic plants. If the pond is well monitored, then you don't need to fight with a moth: it will be eagerly eaten fish and thus regulate its number.
Cutter
These dangerous for aquatic plants of the larvae reminiscent insect butterflies are built at the bottom of the pond portable tubular shelter houses from solid particles - sand, cropping roots, leaves, etc. These vegetative larvae can damage any plant in the pond, as they move along with their Domich. In a healthy pond with the swirl, there is no need to fight, because they willingly eat fish.
Bolotnaya Fireman
At the end of the summer, the butterfly of the marsh, or a jug, fires laying the eggs on the water springs floating on the surface of the water, the ridges and other aquatic plants. From eggs developing the next year 2.5 cm in the length of the caterpillars of cream color with a brown head and a strip on the back. Caterpillars stretch out of the leaves oval pieces and build themselves from two such pieces, connecting them by a web, a house. This is not a very dangerous pest, but floating on the surface of the water the houses from the leaves should be seized and destroyed, because the caterpillars living in them actively eaten the leaves.
Irisova SAWFLY
The gray-blue larva of the iris sawder reaches 2 cm long and lives only on garden and wild irises. In the summer, the larvae feed on the leaf cloth, leaving characteristic jar in their edges. Insect sometimes postponing the second masonry of eggs in the fall. The larvae should be destroyed, and damaged leaves are deleted.
Mining LEAVES Small Mukhi
Rarely encountered, but very dangerous pests. Shut off eggs on the leaves of many aquatic plants, including water lily. Small thin, almost transparent and there are also low-challenging larvae, which can fully eveny soft leaf fabrics. Damaged leaves are necessary to delete if possible.
Snails
In the ponds there are different snails. Often they come there together with new plants, attaching to the bottom of the sheet. Snails eat small algae and various organic residues, but their benefits usually overestimate. On the other hand, it also exaggerates the harm that snails are applied to aquatic plants, allegedly feeding them with their leaves. Basically, they eat rotting leaves and almost never attack healthy plants. So with snails there is no need to fight, unless, of course, they are not too much and they do not pose a threat to young plants. If there was too much snails in the pond, put a cabbage knife into the water, and get it out of the pond in the morning and destroy it along with her shreddes. Never use fire granules in the pond.
Jugging APHID
This pest is similar to black TRU, affecting beans and other vegetable plants. In the dry hot summer, the TLA can strongly damage the plant. In the fall, these insects are moved from the pond on shrubs and trees from the slice subfamily, where the eggs are laying. Consequently, the appearance of aphid is more likely if plum or thorn grow next to the pond, and putting a mold cherry near the pond, you simply ask for trouble. Tar can be flush from the leaves with water and leave in the pond on the fish fish.
Jug Leaf
One of the most dangerous pests for water lily. Fortunately, he prefers to live in large water bodies, and not in garden ponds. At the beginning of the summer, a small brown beetle lays on the top surface of the egg sheet, of which black with a yellow abdomen of the larvae emitting holes on the leaves. The leaves are sometimes folded and poured. The most effective means of combating pests - remove all the damaged leaves and wash the foliage from the hose. This procedure may have to repeat several times, since for the summer the beetle can postpone several madges. The beetle winter in dry stems of coastal plants, so they need to cut them in the fall.
Root ROT Runners
Usually diseases are not very annoyed by aquatic plants, but this disease can deliver a lot of trouble. Root rotting water lishes is similar to the fungal phytoophylary of potato disease and can be just as dangerous. The leaves are yellow and fall off, the rhizome is black and becomes an unpleasant smell. The disease is incurable, so the sick pitcher is better to destroy immediately so that other plants are not infected. If the disease has already spread, you need to roll out water out of the pond, as it should be cleaned and plant new pitches. In order not to make a disease in the pond, always carefully look at the root jugs before boarding and do not land the plants with dark or soft spots on the roots.
Spotted Leaves Runners
This disease is sometimes developing on the leaves of water lishes in warm raw weather. On the top and bottom surface of the sheet closer to the edges appear stains in the form of concentric circles, which are then blurred and acquired incorrect shape. The leaves are black, the stains are rotated, holes are formed in their place. The only thing that can be done with the disease is to remove contaminated leaves so that the plant growing nearby is infected.
Fish can live and multiply in tap water. We only need to keep in mind that usually tap water is chlorinated, and chlorine with water compounds forms hydrochloric, chlorothy, chloride and chloropy acid. The latter decomposes quite quickly. Therefore, before running fish into a pond with fresh water, you should give it for several days to settle. It is even better to cope in advance at the local water supply station, which disinfectant is added there to water, because some substances decompose longer than chlorine compounds.
In dry weather in summer, water in the pond should be treated with a thin flowing of the hose. If you add a lot of fresh water into a small pond, it will lead to a sharp change in temperature and to increase the content of chlorine in water. In addition to chlorine, its acid-alkaline balance has a large influence on the quality of water. Fish is capable of carrying fairly large oscillations in the acid-alkaline water balance, but in some cases water may be too acidic or too alkaline.
Finally, both gold and rainwater are contaminated with time, and it has to somehow fight. You can avoid falling into the pond of harmful substances from the soil, in your area there may be clean air, but nevertheless chemical composition Water will inevitably change as a result of decomposition of the waste of fish and other organic residues. If you have a little pond and there are many fish and plants in it, you will have to do it from time to time clean. The following is described how to do it.
 Green WATER
Green WATER
Water becomes green due to a large number of small algae, which live both in the thickness of water and its surface. These small algae are harmless to fish, but water becomes muddy.
In any new pond, the water week two after filling the pond becomes greenish, and if it does not fight with it, then the situation will deteriorate. If the pond surface is heated by the Sun and the water contains a sufficient number of some mineral substances and carbon dioxide, then algae will multiply very quickly. So that water does not bloom, it is required to create conditions unfavorable to grow green algae, article - care for a pond. This can be achieved if the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe pond is quite large (at least 3.5 m2) and there are plants that shadow the surface of the water and absorbing mineral salts dissolved in it and carbon dioxide. To prevent water bloom, it is also necessary to remove from the leaves of the plants in time, to ensure that the fife unselected fish remains in water, etc.
Unfortunately, it's not so easy to fight blossoming water, even if you fulfill all the recommendations for maintaining equilibrium in the pond leading to the article. The main reason for failures is the fish-raised from the bottom of the dirt or strong stirring of water too powerful pump.
Sometimes creating the necessary balance is simply impossible in the pond due to the fact that the water surface area is too small (less than 3.5 m2), the depth in the deepest part does not reach 45 cm, from the surface of the soil or the crucible site near the pond, it falls into it containing mineral Substances or organic remnants of water, or there are few or no higher plants in it (for example, in a pond with koi carp or with a fountain). In this case, you need to resort to any method of combating algae. There are several of them, and among them there are both cheap and expensive. For example, the bottom of the pond can be put a bag with barley straw or peat, but this is usually not a lot of benefit. Can be launched into duffy pond, although the fish will eat daphneus faster than they will eat algae. Obvious solution - chemical means of combating algae. There are quite a lot of such algicides, and most of them selectively act on small algae and are less harmful to other plants and fish. Carefully follow the instructions for the use of algicides. It should be started to apply them before the algae becomes too much. Election algicides give only a temporary effect, they must be applied every 1-4 months. Another type of algicide is substances that bind the clogging pond algae and the organic, as a result of which they settled at the bottom. The third way to combat algae usually brings the greatest effect. This is an harmless dye that does not let into the water necessary for the development of algae sunlight. But all these funds are a temporary solution. You can solve the problem of cleaning the water with a cardinal oracle, only by installing the filter.
 Weed PLANTS
Weed PLANTS
There are several types of weeds that spoil the appearance of the pond, impede the growth of the necessary aquatic plants and interfere with looking at fish. First of all, these are nichly green algae, or threads. Their long and silky threads are attached to the bottom and walls of the pond or form the balls floating in the water. Nichtokes and microscopic algae usually do not happen in a pond, in which the balance is achieved with the help of higher plants. The filter installation will save the pond from small algae, but, on the contrary, will contribute to the growth of filamentous algae. These weeds are better removed from the pond with saccics, robbles or courtya forks. Rotating a rake or a pitchfork, turn on them as much as possible algae and remove from the pond by laying into a compost bunch. Chemicals The fight against threads is recommended to be used only after mechanical cleaning. To clog the pond can also grow sometimes over all measures floating on the surface of water plants, such as rod. Such plants need to be removed in a timely manner from the water with a stitch and not give them to grow. Danger can also be presented to the terrace in the pond and rapidly growing coastal plants, which need to be cut down, if they begin to drown more gentle plants.
 Polluted WATER
Polluted WATER
Polluted water may not have an unpleasant odor and not change colors, but nevertheless to be a life-threatening plants and / or fish. There are several types of pollution. As a result of rotting the leaf of water lishes and other underwater plants on the surface of the water, an oily film may form, which prevents the penetration into oxygen into water. You should remove this film - stretch the newspaper on the surface of the water. If dry leaves are rotting in the pond or dead fish, water acquires black. With severe pollution, you will have to roll out water from the pond, clean it and only then fill out again. Equally decisive measures should be applied if the pond has paint, herbicide or any other harmful chemical substance. Finally, in small ponds with a large number of fish and plants, the waste of fish, the remains of feed, organic waste, etc., accumulate for several years, accumulates, is accumulated in the decomposition of which toxic substances. This problem is solved by partial replacement of water in the pond in spring and autumn. Pump the pump to a quarter of the volume of water, and then a thin rod in the pond of tap water to a regular level.
Muddy WATER
Brown turbid water is harmless to fish and plants, but spoils the appearance of the pond. Water turbines mostly for two reasons: Fish-emerging in Ile raise a torment from the bottom of the pond and from the surface of the soil in baskets with plants, or too powerful pump creates a strong flow that also raises from the bottom of the pond. Of course, the prevention is better than the treatment, therefore baskets with plants should cover the burlap, buy baskets with solid walls, fall asleep the surface of the soil in them with gravel and install the pump in such a way that the water movement is too strong. You can get rid of this problem for a while, applying special chemicals - flocculants, as a result of which the dirt will fall in flakes at the bottom of the pond. This dirt layer on the bottom must be removed by a special vacuum cleaner or other means. Unfortunately, the water will again become muddy, if you do not eliminate the main cause of vigorion.
Sour AND Alkaline WATER
To determine the pH of the water, there are easy-to-use sets. At pH values \u200b\u200bfrom 6.5 to 8.5, water is suitable, and with some low or higher values, it is also dangerous to live both plants and fish. The pH 9.0 value and above means that the water is too alkaline. This is usually water in ponds with waterproofing from concrete or artificial stone. All concrete surfaces so should be painted, try to remove from the pond as much as possible algae and dust into the water of the buffering reagents that can be bought in the same place where the aquatic plants sell. Aclest medium (The pH value is less than or equal to 6.0, which is not very often), due to the drop in the pond of water from the surrounding peatlands. In this case, it is necessary to partially change the water, put in the pond limestone or add wakery reagents.
CLEANING Pond
The pond must be cleaned, if he began to flow, a thick layer of Slah was formed at the bottom or polluted water. In the dwelling day late in spring or in the summer, get all the coastal, and then deep-sea plants. If possible, transfer them to a temporary pond; If there is no such possibility, wet the plants with water from the hose, without giving them to push. Temporary pond Constructure in the shade of plastic or bu-tilcukee film, make separate compartments for fish and plants and fill with water. Plants with water floating on the surface of water and plants - oxygenator plants in plastic containers with water. Start pumping water. When the water remains a bit, you get fish with a chick and put them in a temporary tank. Check the condition of the fish and cover their temporary dwelling with a fine grid.
Rush all the water from the pond and remove from the bottom Il. Square dirt from the walls, trying not to damage the surface. Refill the pond with tap water and add some old pond water if it is not contaminated. Separate plants, if necessary, wash the basket and return the plants into the pond. And finally, carefully release back fish.
So, if you comply with the basic rules for fishing, it is not necessary to worry about their health. Start with the fact that when buying fish, check whether they are healthy. Contact a reliable seller, carefully inspect the fish, asking the Council if necessary. If the state of the fish causes doubts, push them into quarantine before running into the pond. Make sure that the conditions are suitable for them - to create them is easy, just follow the recommendations on this site.
Pay attention to the unusual behavior of the fish. You should be alert if some of the fish is minor, while others are active.
If you have any doubts about the well-being of the fish, it may be worth squinting it into a separate water container and inspect the "Fish Inspection" section. Perhaps you will need to be treated - many different drugs have appeared, but you need to make sure that the medicine is intended for the treatment of this disease and is suitable for this breed of fish. Carefully follow the instructions. There are local applications (they are applied directly to the affected portion of the body of the fish), some need to be breeding in water and for some time to withstand fish in this solution in aquarium or in another capacity, others are added directly to the pond water. Unfortunately, not all diseases can be cured, and sometimes the patient or wounded fish can be killed. Do this unpleasant operation as possible as possible for fish in the way - as described on below.
BIRDS AND Cats
Cats are often sitting on the shore of the pond and watch the fish. It is not surprising that they are often accused of disappearing goldfish and redfire, although usually cats are not to blame. They do not like water and do not pose a danger to healthy fish. If they catch sometimes fish, then only patients or lazy.
Birds for fish are much more dangerous. Seagulls can grab one or two fish out of the pond, cute kingfishers sometimes dive for small fish. But the main robber - herons, who hunt, standing on shallow water and waiting for her prey, at dawn. You can protect the fish by pulling the network over the pond, or by driven into the bottom around the perimeter of the pond, several 15-tisantimeter pegs and riding their upper ends with a rope or strong thread. Heron will not be able to step over this construction.
Fish's death
 DROPSY
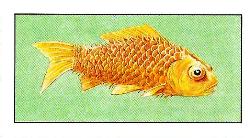
DROPSY
Rare, but very serious illness. The fish becomes a spray, the body will swell her, scales behind the skin and all the fish becomes like a pine cone, which is a characteristic sign of this disease. There are several forms of water, one of them causes bacteria. In the catalogs, they sometimes mention drugs for the treatment of water, in some cases the disease passes by itself, but intelligently sick fish to kill.
PROBLEMS Surrounding Environments .
Chlorine is also harmful to fish. If you run fish into fresh tap water, then they will become slow, and they travel them to them.
The lack of oxygen may present a serious threat to the health of the fish, especially at night, in hot summer weather or during a thunderstorm. Then the fish float to the surface and greedily swallow air. This happens not only due to lack of oxygen, but also due to excess carbon dioxide in water. To correct the situation, you need to include a fountain or waterfall, spray water from the hose above the pond or mix the water in the pond stick. Other environmental conditions are sharp fluctuations in temperature and ice formation. Never transplane fish from cold water In warm and vice versa, and never leave the pond for a long time under the ice. However, the most serious problem associated with environmental - It is water pollution. If you throw fish or your pond is overcoiled, toxins can accumulate in water and it will take partial replacement. But if the pond fell herbicide or containing leaves toxins, water should be replaced completely as described in the article.
 ROT Plavniks
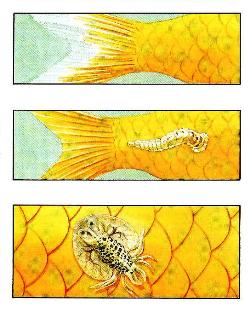
ROT Plavniks
Bacteria, causing this disease, destroy soft tissues between the bones of the tailflower and can destroy the fish, if you allow them to penetrate the body. In the early stage, the disease can be cured by cutting off a damaged part of the tailfold and placing the fish into the solution of the disinfecting drug. A recovered fish rays of the fin will grow again.
Fish LEECH
Karpova LOUSE (Carpore )
FROG
The frog is mentioned here soon for the sake of interest, because it is hardly a frog can cause any serious harm to fish in the pond. However, in the marriage season, the males frogs try to cover any moving object to the front paws, and quite often the fish suffer and even die when the frogs are absorbed by the passion clap their heads.
INSPECTION Fish
In the event of many of the troubles described above, it is necessary to catch fish out of the pond to inspect it carefully and cure. For this sell special colts. Put a little feed into one of the corners of the pond and gently lower the cuckoo into the water. Slowly lead a cuckoo to the corner with food until you approach the fish, then quickly raise the net. Place the fish in the vessel with pond water, the temperature of which should not differ from the water temperature in the pond itself. Touch the fish only with wet hands, because any dry surface destroys the protective film from the mucus on its body.
![]() Saprolegny Fungi
Saprolegny Fungi
The most common disease of the pond fish. The disputes of the fungi Achlya and Saprolegnia are in any pond, but they are harmless until the protective mucous layer on the surface of the body of the fish is not disturbed and its immune system is in order. Immunity declines when damaged skin cover or fish is experiencing stress due to the rapid change of temperature or during spawning. The disease is usually recognized by the Mitcelion fungus on the skin of the fish. At an early stage of the disease, fish is easy to cure, placing it in a water vessel, in which special fungicidal drugs are pre-dissolved.
BRANCHIAL Slacher
The disease causes microscopic flatwormwhich is attached to the gills of fish. The affected fish becomes restless, often twisters fins and slams with gill lids. Usually they do not pay attention to this pest, although it can cause the death of fish, and some experts believe that it is widespread than it is considered. There are preparations for the fight against the loser who need to be treated not only fish, but also a pond in general.
ORAL FUNGUS
The name is deceptive, because the disease is not a mushroom, but bacteria. On the jaws of the fish appear white growths and soft tissues are destroyed. The cause of the disease is usually pollution of water, which leads to destruction immune system fish. Try to partially replace water in the pond. At the beginning of the disease, it is enough to simply treat the fish in a separate vessel with a bactericidal solution.
 Pond Insects
.
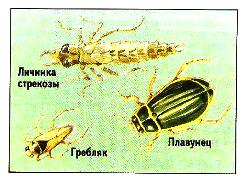
Pond Insects
.
The predatory insects living in the water are a hidden danger for the pond - they harm carac, fel and small fish and can damage large fish. For example, larvae attractive on the type of dragonflies. For several years, this larva, growing up to 5 cm in length, crawling along the bottom or sitting under water on the stalks of plants, from time to time it is enough to prey with tick-shaped teeth of his lower lip. An even more dangerous to the beetle of the plaguan, in which both adult individuals reaching 4 cm in length and the larvae attack the fish and other inhabitants of the pond. Other predatory insects include: Golding and Gladsh, with characteristic weary legs, water scorpion, which sucks all juices from his victim, and which can be identified by the breathing tube located in the back of the body, and swimming fighters and living in the water their larvae. You can fight these insects in the only way - catching them from time to the sacca pond.
ULCER
The disease causes penetrating through damaged skin sections inside the body of a bacteria from the genus Aeromonas. In the affected area of \u200b\u200bthe skin, bloating is formed, and then a large open ulcer. There are proprietary drugs for the treatment of this disease, but with a strong lesion there is nothing else, except to kill the sick fish. For the treatment of expensive fish, the local veterinarian can assign antibiotics.
 Infusoria. Ichthyophthyrius
(Ichtyophthirius)
Infusoria. Ichthyophthyrius
(Ichtyophthirius)
The sick fish begins to move quickly and unusually. Upon closer examination, you can see numerous white specks on its body, similar to the semolia cereal (do not confuse them with white spots on the fins of the males of some fish during the marriage period). The disease should be treated in the early stages. For this there are several drugs, but if the fish are seriously amazed, it will have to be put to sleep. To get rid of the infusoria, you do not need to resort to chemical processing of the pond. Just place the fish of the week for two in a separate vessel by adding tryptoflavin into the water, or increasing the temperature of the water in the vessel to the Z0-Z1C for 5-8 days (the water should be periodically enriched with oxygen, passing through it air).
Sections of the site



The role of plants of purifiers in reservoirs - page number 1/1
The role of plants of purifiers in reservoirs.
The main sources of pollution of water bodies are household, industrial and agricultural drains. Household and agricultural estates contain a large number of all sorts of organic
substances, detergents, pesticides, mineral fertilizers and their decay products, while industrial is a huge set of various chemical compounds, most of which are toxic. The pollution of many reservoirs of the Russian Federation exceeds the maximum permissible concentrations (MPC) on average for petroleum products by 47-63%, phenols at 45-68%, an easy-oxygenated organic matter (BPK5) by 20-23%, ammonium nitrogen by 24%, etc. (Morozov, 2001).
Purpose contamination is divided into allochton-made from the outside, and autochthonic - its own contamination. Autochthonic pollution occurs as a result of the vital activity of aquatic organisms, including coastal water
vegetation. After moving on Wednesday, their metabolites, biogenic substances and decay products are coming. Allochtonal contamination is all that they bring wastewater in water bodies, surface drains, rain and air masses.
The special form of pollution is the eutrophication of water bodies, that is, the enrichment by their biogenic substances, which leads to the intensive development of algae and coastal plants. This is most often due to the receipt of domestic and agricultural reservoirs. The ability of aquatic vegetation to the accumulation and use of these substances (primarily phosphorus and nitrogen) makes them active participants in the process of self-purification of natural waters.
Purpose contamination leads to a change in the structure of communities, their species and quantitative composition. Intensive contamination with agricultural and domestic runoff leads to overclocking of water bodies, and industrial - to violation and complete degradation of biocenoses. The reservoirs have a unique property - self-cleaning ability. Under self-cleaning means a complex of influence of chemical, physical and biological factors on a reservoir ecosystem, as a result of the activity of which the quality of water comes to the original (or close to it) state. Of course, this is observed with a small degree of reservoir contamination.
The biological self-purification of water bodies is carried out due to the vital activity of plants, animals, mushrooms, bacteria and closely related to physicochemical processes. Self-cleaning of water bodies is carried out in anaerobic and aerobic conditions. Anaerobally processes of the destruction of organic substances with the predominant participation of bacteria, mushrooms and the simplest. In this case, in the process of decomposition of organic material in the medium, intermediate products (ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, low molecular weight fatty acids, etc.) are accumulated, which in the presence of oxygen are oxidized further.
In aerobic conditions, the destruction of the organic substrate is carried out in the presence of oxygen to simple compounds, which are further involved in
biotic cycle. In this process, almost all population of reservoirs take part. Water-and-water plants play a major role in the processes of self-purification of polluted waters.
Coastal water vegetation, highlighting oxygen in photosynthesis, has a beneficial effect on oxygen mode. coastal zone reservoir. Bacteria and algae (periphyton) dwelling on the surface of plants perform an active role in water purification. In the thickets of coastal water plants, phytophilic fauna develops, which also takes part in self-cleaning of water and bottom sediments; Benthos organisms utilize the organic substance of the catch and bodies living there. Under the influence of all these processes, the content of dissolved oxygen increases in water, its transparency and the content of nutrients increase, the mineralization of water and the number of intermediate spree products of the organic matter (Kuznetsov, 1970) decreases.
In recent years, macrophytes have become successfully used in the practice of water purification from biogenic elements, phenols, aromatic hydrocarbons, microelements, oil and oil products, heavy metals, various mineral salts from sewage and natural waters, in disinfecting livestock breeding from various forms of pathogenic microorganisms.
The role of coastal water plants in self-cleaning of water bodies in a general form can be reduced to the following:
A mechanical cleansing function when weighted and undermining organic substances are delayed in the thickets of plants;
Mineralization and oxidative function;
Detoxification of organic pollutants
Perennial an herbal plant with a length of 10 to 150, sometimes up to 300 cm. It dwells entirely in the water temperature (hydrophitis), only inflorescence rises above the water surface.
Forms winter kidneys (touria), it is one of her characteristic features. TURIONES UVUCHU MUTUTHY LOOK LOW LONG YOLITY-GREEN ROLLED KIDNESS WITH RIGHT LIFT LETTERS, tight pressed to the stalk. Spring small, thick, dark green tourius is enlivened and separated from the stem. As soon as the plant is rooted and proceeds to growth, large green summer leaves are formed on its tip. Touring leaves at the base of the plant can sometimes notice even in July. In the fall, touring with some parental vegetation material is again separated, rooted and thus capture new territories. Such fragments can be found along coastline Late in the fall.
The stem is usually green.
A distinctive feature of the tough Mutovaya is the test of two types of leaves. The first type includes underwater leaves. They are filamentous, complex, consist of 5-14 leaves. Mutovka are located on the stem at a distance of about 1 cm from each other, contain 4-5 leaves. Other type - surface leaves. Such leaves are assembled into a reprehensive beam, pouring. Their length is usually 2 or more than the length of flowers and fruits.
Seaweed
Role in biogeocenosis
Algae - the main manufacturers of organic substances in the aquatic environment. About 80% of all organic substances annually created on Earth are accounted for by algae and other aquatic plants. Algae directly or indirectly serve as a source of food for all aquatic animals. Mine rocks are known (diatomites, combustible shale, part of limestone), resulting from the life of algae in past geological era. By the way, it is precisely in diatoms of algae that the age of these rocks is determined.
Water treatment
Many algae are an important component of the process of biological wastewater treatment.The rapid development of the pitching and plankton algae (water flowering) can create problems in the work of the water supply systems of water supply facilities.
In the sea aquarium, algae is used in biological filtering systems. Algae tanks are used ("algaelets") and scrubbers. Either specially planted macrosways (usually from the generics of the hatomorph and caulepara) are grown, or natural algae is used. Intensive lighting provides rapid growth of algae and active absorption of pollutants. Periodically, the mass of the resulting algae is removed from the filter.
Wastewater can also be cleaned thanks to higher plants, aswater hyacinth, writing, Arundo . In many tropical countries a merciless struggle is underwayaqueous hyacinthas with a dangerous weed. In just a few weeks, this plant can grow throughout the reservoir, bring damage to fisheries, and fail the power plant. But the US scientist managed to establish that aqueous hyacinth is able to remove harmful impurities from water intended for industrial and economic needs. Similar "botanical" settles are introduced into practice. The beveled green mass of water hyacinth can serve as a good fertilizer or applied in production.biogas.
Water plants are included with botany to special ecological group hygrophytes.
Some plants of this group live only in water (hydrophitis), others on land, but in places with high or excess soil humidity. All hygrophytes have common features in the structure and lifestyle. The vital processes in the organisms of aquatic plants are addressed under the influence of the same factors as on land.
In 1 liter of water, it is contained in a dissolved state of 20 - 25 cm3 of air, the fraction of oxygen accounts for no more than 6 - 8 cm3. When the content of 0.5 - 0.3 cm3 of oxygen on 1 liter of water, life is stopped: not only ichthyofauna and higher vegetation, but also microflora die.
Oxygen is absorbed by water from the air at the boundaries of the integrity of media, especially intense with stirring, excitement, tidal flows, and also released by plants in the process of photosynthesis.
The carbon dioxide dissolved in water is formed in the process of respiration of aquatic animals, as a result of rotting organic residues, and is also absorbed from the air.
Cold and fresh reservoirs are richer gases than warm and salty. Gases are needed by water plants not only for breathing and photosynthesis; They increase the pop-ups, support plant organs in a vertical position.
The radiant energy coming from the Sun is strongly reflected from the water surface. A lot of heat is spent on evaporation: the land is the air, the more evaporation. In the spring water warms up much later sushi, delaying the development of aquatic plants.
Even in the same reservoir, each type of plants are inherent in its temperature deviations. For example, wild water rice (Zizania Aquatica) germinates at 6 - 7 ° C, and the water walnut (Trap Natans) at 12 - 14 ° C, although they grow in close proximity to each other.
Water plants are comparable relatively late, and vegetative reproduction prevails with them over seed. In addition, most aquatic plants are perennials, which, apparently, is also explained by the lack of heat during the growing season.
The illumination of water is very quickly decreasing with depth: the lower the sun over the horizon, the smaller the light goes into the thickness of the water. The depth of 3 m is the limit for growing higher aquatic vegetation. Algae B. fresh waters Deeper than 30 m were not observed.
In the CIS, the greatest transparency possesses water. Baikal, and the smallest - water of Amudarya and other Central Asian water bodies carrying a huge number of trembled substances.
With a depth, the spectral composition of the light changes: orange-red rays are absorbed by surface layers, blue and green rays penetrate deeper. The leaves immersed in water are inherently photosynthesis: with weakened lighting and flow of CO2 from the water. Under these conditions, it is more profitable to have the leaves very thin and strongly dissected on narrow slices.
Chlorophyllon cells get in them the greatest number Lights (in thick leaves, the internal cells would have lack of light). In thin and thick leaves inside the cells penetrate various amounts of water with CO2 and CA (NSO3). The dissection of leaves on thin filamental shares is characteristic of the laid leaves of the rogol, periodic, bubbles, etc.
Wide, but very thin underwater leaves have pita and cubes. The finest leaves at the Eldine (only two layers of cells) and water moss (one layer).
Water is many times more denser of air and herself supports the plants living in it. This leads to underdevelopment or disappearance of their support fabrics, so the stems and leaves of many aqueous plants are soft, flexible and easily moved by the flow.
The flow of water, the presence of turbulent movements, excitement and convection currents contribute to the supply of plants with nutrients, warmth and air.
Slow temperature deviations in water can be created due to showers (especially in the conditions of tropics and subtropics). The reservoirs are very different in thermal regime, in deep-moisten, stagnation and water flow, by wind exposure and many other indicators.
Even inside the same reservoir, the environmental characteristics of aquatic plants are very unequal. With an increase in water temperature, the solubility in it gases is significantly reduced, therefore, the oxygen content and carbon dioxide decreases, which can adversely affect the development of plants.
Plants possess many devices that protect them from the lack of oxygen and contributing to the improvement of gas exchange. The water-coming organs of aqueous plants can absorb water with dissolved oxygen in it with its entire surface due to the special structure of the shells of the cells of coating tissues.
The improvement of gas exchange is also promoted by the strong dismemberment of submarine leaves, which increases the surface of contacting them with water and causes development in all organs of large interclausers and air cavities.
Very large value for plants has a chemical composition of water. In reservoirs, which contains many chlorides, sulfates, sodium carbon dioxide, freshwater plants do not live.
Most aquatic plants do not make contamination of water bodies. Even various snaps, often used for decorative design of aquariums, bring harm to plants.
Due to the ability of aquatic plants to absorb water with the substances dissolved in it with the entire surface of some of them, the root system is developing poorly, as well as water tanks.
In some cases, it disappears at all or serves only to attach the plant to the soil, but practically does not give it nutrients.
For example, the roasted (lemnasee) root performs the role of the equilibrium organ. This is confirmed by the lack of root hairs on it. Developing rhizomes serve as storage facilities and vegetative reproduction authorities.
The development on the same plant of the leaves floating on the surface of the water and towering over it is the usual phenomenon in aquatic plants.
Floating leaves on the outside, communicating with air, carry the dust. The greater the dust, the stronger the interconnect cavities are developed.
The interconnect cavities provide washing with water containing gases and salts, internal cells, increase the buoyancy. In addition, the organs communicating with the air environment, these cavities through the dusts perform the role of a ventilating system for underwater shoots and roots.
The most strongly expressed adaptability to the aqueous medium in plants, fully immersed in water. Plants, at least partially contact with the air medium, detect the features characteristic of land plants.
For example, Sagittaria Sagittifolia (Sagittaria Sagittifolia) in deep waters develops the leaves of three types: underwater, floating and air.
If the graonist grows in a swamp, only the air strike-eye leaves develop on it, the vascular channels and the sheet increases in the stem and the common structure is acquiring as a land plant.
For all aquatic plants, as well as for land, are characterized by two main periods: a period of growth and a period of rest.
Growth period.
In countries with a cold, moderate and subtropical climate, the growth period of plants falls mainly on the spring and summer months, and in countries with the tropical climate it comes after tropical rain.
During the growth period, the plants develop intensively, give new shoots, leaves, flowers and fruits accumulate nutrients. At this time, they need a lot of light, heat and nutrients.
The period of rest.
It may be preliminary or complete. With a preliminary subshield part of the plant persists, the process of photosynthesis is underway, breathing flows normally.
With full, the plant loses the subshield part, the photosynthesis does not occur, and the breath flows weakly. In countries with a cold, moderate and subtropical climate, the period of rest in plants occurs in the autumn and winter months, and in countries with a tropical climate in the dry period of the year or after flowering and fruiting.
In winter, deep reservoirs are not freezed, and the temperature of the water in depth remains more or less constant, so the river plants and lakes are divered into the water and fall on the bottom of the reservoir. Some of them simply immerse themselves so that in the spring again to surface (outer), the other winter in the form of rhizomes, sharpen along the bottom, or immerse themselves in the ground (pita, rideats, etc.), third-to-autumn formed special winter shoots or kidneys. which by the time of frozen the reservoir is immersed on the bottom, and in the spring again pop up and give rise to new plants.
The ability of plants to move into a state of rest was developed in the process of evolution.


